Presentation on Competencies
advertisement

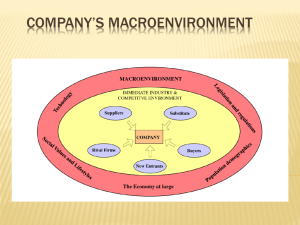
Strategic Management Industry and Competitive Analysis Session 3 Prof. Chitra Parthasarathy Session 3 1 Starting point Decisions on what strategy to pursue should flow directly from solid analysis of a company’s external environment and internal situation. Session 3 2 The two most important situational considerations 1. Industry and competitive conditions 2. A Company’s own competitive capabilities, resources, internal strengths and weaknesses and market position. Session 3 3 The environment All organizations operate in a macro environment consisting broadly of the economy at large, population demographics, social values and lifestyles, governmental legislation, technological factors and the company’s immediate industry and competitive environment. Session 3 4 Immediate external environment The biggest influence / impact on a company’s strategy is the company’s immediate industry and competitive environment. Session 3 5 A Requirement Accurate diagnosis of the company’s situation is a necessary managerial preparation for deciding on a sound Long Term direction, setting appropriate objectives, and designing a winning strategy. Session 3 6 THINKING STRATEGICALLY ABOUT INDUSTRY AND COMPETITIVE CONDITIONS The Key questions: 1. What are the industry’s dominant economic features? 2. What is the competition like and how strong are each of the competitive forces? 3. What is causing the industry’s competitive structure and business environment to change? 4. Which companies are in the strongest/weakest positions? 5. What strategic moves are rivals likely to make next? 6. What are the key factors for competitive success? 7. Is the industry attractive and what are the prospects for above-average profitability? WHAT STRATEGIC OPTIONS DOES THE COMPANY REALISTICALLY HAVE? •Is it locked in to improving the present strategy or is there room to make major strategy changes? WHAT IS THE BEST STRATEGY? The key criteria •Does it have good fit with the company’s situation? •Will it help build a competitive advantage •Will it help improve th company performance THINKING STRATEGICALLY ABOUT A COMPANY’S OWN SITUATION The key questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. How well is the company’s present strategy working? What are the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats? Are the company’s prices and costs competitive? How strong is the company’s competitive position? What strategic issues does the company face? Session 3 7 Analyzing the industry and competition Industries differ widely in their economic characteristics, competitive situations and future profit prospects. Session 3 8 Analyzing the industry and competition The economic character of industries varies according to such factors as overall size and market growth rate, the pace of technological change, the geographical boundaries of the market (local to world wide) the number and size of buyers and sellers, whether sellers products are virtually identical or highly differentiated, the extent to which costs are affected by economies of scale and the types of9 Session 3 distribution channels. Methods of Analysis A tool kit of concepts and techniques to get a clear fix on key industry traits, the intensity of competition, the drivers of industry change, the market position and strategies of rival companies, the keys to competitive success, and the industry’s profit outlook. Session 3 10 Insightful answers to 7 questions 1. What are the industry’s dominant economic features? 2. What is the competition like and how strong are each of the competitive forces? 3. What is causing the industry’s competitive structure and business environment to change? 4. Which companies are the strongest / weakest positions? 5. What strategic moves are rivals likely to make note? 6. What are the key factors for competitive success? 7. Is the industry attractive and what are the Session 3 prospects for above-average profitability? 11 Q1: What are the Industry’s dominant economic features? An Industry’s economic features help frame the window of strategic approaches a company can pursue. Industries differ significantly in their basic character and structure. Industries and companies analysis begins with an overview of the industry’s dominant eco featured. Session 3 12 The factors to consider • Market size • Scope of competitive rivalry (local, regional, national and global) • Market growth rate and position in the business life (early development, rapid growth & take-off, early maturity, maturity, saturation, stagnation and decline) • The number of rivals and their relative sizes • Whether and to what extent industry rivals have integrated (backward and/or forward) Session 3 13 The factors to consider • The types of distribution channels used to access consumers. • The pace of technological change in both production process innovation and new product introductions. • Whether the products and services of rival firms are highly, weakly or essentially differentiated • Whether companies can realize economies of scale in purchasing, manufacturing, transportation, marketing or advertising. Session 3 14 Contd…. • Whether key individual participants are clustered in a particular location • Whether high rates of capacity utilization are crucial to achieving low-cost production efficiency • Capital requirement and the ease of entry and exit. • Whether individual profitability is above/below par. Session 3 15 Q2:What is competition like and how strong are each of the competitive forces? Industrial and complete analysis involves delving into the industry’s competitive process to discover what the main sources of competitive pressure are how strong each force is. This analytical step is necessary because managers cannot devise a successful strategy without in-depth understanding of the industry’s competitive character Session 3 16 A well-proven Model Professor Michael Porter declares that - the state of the competition in an industry is a composite of Five forces Session 3 17 Firms in other industries offering substitute products Competitive pressures coming from the markets attempts of outsiders to win buyers over to their products Suppliers of Raw materials, Parts, Components or other Resource inputs Competitive pressures stemming from supplierseller collaboration and bargaining Rivalry Among Competing sellers Competitive Pressures created By jockeying For better Market position And competitive advantage Competitive pressures stemming from supplierseller collaboration and bargaining Buyers Competitive pressures coming from the markets attempts of outsiders to win buyers over to their products 3 PotentialSession New Entrants 18 Rivalry among competing sellers . In some industry, rivalry is based on attractive combination of performance features, being first to market with attract features out competing with higher quality, offering longer warrantees, superior after sales service, creating a stronger brand image. Session 3 19 A principle of competitive Markets Competitive jockeying among rival firms is a dynamic ever-changing process as new offensive and defensive moves are initiated and emphasis swings from one blend of competitive weapons and tactics to another Session 3 20 The fierce nature of competition Competitive markets are economic battlefields. It is dynamic and rivals try to out-compete one another and build customer loyalty. Session 3 21 Some common factors that influence the tempo of rivalry • Rivalry intensifies as the number of competitors increases and as competitors become more equal in size and capability. • Rivalry is usually stronger when demand for the product is growing slowly. • Rivalry is intense when customers find it easily to switch brands. • Rivalry is more when it costs more to get out of business than to stay in and compete. Session 3 22 The potential entry of new competition The competitive threat of depends on two factors. 1. Barriers to entry 2. The expected reaction of incumbent firms to new entry barriers. Session 3 23 Types of entry barriers • Economies of scale • Cost & resource disadvantages irrespective of size • Learning & experience curve effects. • Inability to match the technical & specific know-how of existing players. Session 3 24 More barriers • Brand preferences and customer loyalty • Capital requirements • Access to distribution channels • Regulatory policies • Tariffs and internal trade restrictions Whether an industry’s entry barriers ought to be considered high or low depends on the resources and competencies possessed by the pool of potential entrants Session 3 25 Competitive pressures from substitute products Firms in one industry are quite often in close competition with firms in another industry because their respective products are good substitutes. . Session 3 26 Principles of competitive markets The competitive threat based by substitute products is strong when substitutes are readily available and attractively priced, buyers believe substitutes have comparable or better features, and buyers’ switching costs are low.. Session 3 27 Principles of competitive markets The suppliers to a group of rival firms are strong competitive force whenever they have sufficient bargaining buyer to put certain rivals at a competitive disadvantage based on the prices they can command, the quality and performance of the items they supply or the role of their deliveries Session 3 28 Competitive pressure from Supplier bargaining power • Suppliers have no bargaining power or leverage over rivals whenever items they provide are freely available from numerous suppliers • Similarly when good substitutes for the item are available and buyers find it neither costly nor difficult to switch • Also when it is a major customer Session 3 29 Competitive pressure from Supplier bargaining power Major suppliers have strong bargaining power • if an item that accounts for a sizable portion of the costs of an industry’s product • Is crucial to the industry’s production process • Or significantly aff3ects the quality of the industry’s product • they have considerable influence on the competitive process E.g. true when a few suppliers control most of the available supplies and have pricing leverage Suppliers with good reputations and growing 30 Session 3 demand for their output Principle of competitive Markets Buyers are strong competitive force when they are able to exercise bargaining leverage over price, quality, service, or other terms of sale. High switching costs create buyer lock-in and weaken a buyer’s bargaining power. Session 3 31 Competitive pressure from Buyer Bargaining and Seller-Buyer collaboration When buyers cost of switching is low If buyers well informed about sellers product, price & costs If buyers pose credible threat of backward integration Have discretion in whether and when they buy. Session 3 32 Strategic implications of the 5 competitive forces A company’s competitive strategy is increasingly effective the more it provides good defenses against the five competitive forces, shifts competitive pressures in ways that favor the company, and helps create sustainable competitive advantage. Session 3 33 Q3: What is causing industry’s competitive structure and business environment to change? Industry conditions change because important forces are driving industry participants (competitors, customers, or suppliers) to alter their actions; the driving forces in an industry are the major underlying causes of changing industry and competitive conditions. Session 3 34 The most common driving forces a. The internet and e-commerce b. Increasing globalization of the industry c. Changes in the LT industry growth rate d. Changes in who buys the product and how they use it e. Product innovation Session 3 35 The most common driving forces f. g. h. i. Technological change Market innovation Entry/exit of major firms Diffusion of technical know-how across companies and countries j. Changes in cost and efficiency Session 3 36 More of them k. Regulatory influence and government policy changes l. Changes societal concerns, attitudes and lifestyles m. Reduction in uncertainty and business risk. Session 3 37 Environment scanning Environment scanning techniques involves studying and interpreting the sweep of social, political, economic, ecological and technological events in an effort to spot budding trends and conditions that could become driving forces. Session 3 38 Why environmental scanning? The purpose of environmental scanning is to raise the awareness of managers about potential developments that could have an important impact on industry conditions and pose new opposition and threats. Session 3 39 Q4:Which companies are in the strongest/weakest positions? A technique for revealing the competitive positions of industry participants is Strategic Group Mapping A strategic group consists of those rival firms with similar competitive approaches and positions in the market. Session 3 40 Use of Strategic Group Maps Dividing industry members into strategic groups allows industry analysts to better understand the pattern of competition in complex industries and to pinpoint a firm’s closest competitors Session 3 41 Constructing a strategic group map Identify the competitive characteristics that differentiate firms in the industry – price/quality range, geographic coverage, degree of vertical integration, product-line width, distribution channels, degree of service offered. Session 3 42 Constructing a strategic group map • Plot the firm on a two variable map using pairs of these differentiating characteristics. • Assign firms that fall into the same strategic space to the same strategic group. • Draw proportional circles around each strategic group to show the group’s share of global industry sales revenue. Session 3 43 Q5:What strategic moves are rivals likely to make next? A company cannot expect to out maneuver its rivals without monitoring their actions, understanding their strategies and anticipating what moves they are likely to make next. Competitive intelligence about competitors strategies, monitoring their actions, sizing up their strengths and weaknesses and using what they have learned to anticipate what moves rivals are likely to make next Session 3 44 Competitive Intelligence Successful strategists take great pains in gathering competitive intelligence about competitors’ strategies, monitoring their actions, sizing up their strengths and weaknesses, and using what they have learned to anticipate what moves rivals are likely to make next. Session 3 45 Monitoring group’s strategies The best source of information comes from examining what it is doing in the market place and from what its management is saying about the company’s plans. Managers who fail to study competitors closely risk being overtaken by surprise actions Session 3 46 Q6: What are the key factors for company’s success? • Key factors concern the product attributes, competencies, competitive capabilities and market achievements with the greatest direct hearing on company’s profitability. • An industry’s key success factors are those things that most affect industry members’ ability to prosper in the market place – the particular strategy elements, product attributes, resources, competencies, competitive capabilities and business outcomes that spell the difference between profit and loss and, ultimately, between competitive success or failure. 47 Session 3 Identifying the Key Success Factors Three questions help identify an industry’s KSF • On what basis do customers choose between the competing hands of sellers? • What product attributes are crucial? • What resources and competitive capabilities does a seller need to have to competitively successful? • What does it take for sellers to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage? Session 3 48 Strategic Management Principle A sound strategy incorporates efforts to be competent on all industry key success factors and to excel on at least one factor Session 3 49 Q7: Is the industry attractive and what are its prospects for greater average profitability? The final step of industry and competency analysis is to use the answers to the previous six questions to draw conclusions about the relative attractiveness/ unattractiveness of the industry, both Short term and Long term. Session 3 50 Factors on which to base conclusions • The industry’s growth • Whether company currently permits adequate profitability and whether company forces will get stronger or weaker. • Whether industry profitability will be favorably / unfavorably affected by the prevailing driving forces. Session 3 51 More factors • The company’s competitive position in the industry and whether its position is likely to grow stronger / weaker. • The company’s potential to capitalize on the vulnerabilities of weaker rivals. • Whether the company is able to deferred against or counteract the factors that make the industry 52 Session 3 unattractive. Contd… • The degree of risk and uncertainty in the industry’s future • The severity of problems confronting the industry as a whole. • Whether continued participation in this industry adds importance to the firm’s ability to be successful in other industries in which it may have business interests. Session 3 53