Evaluating a company's external environment
advertisement
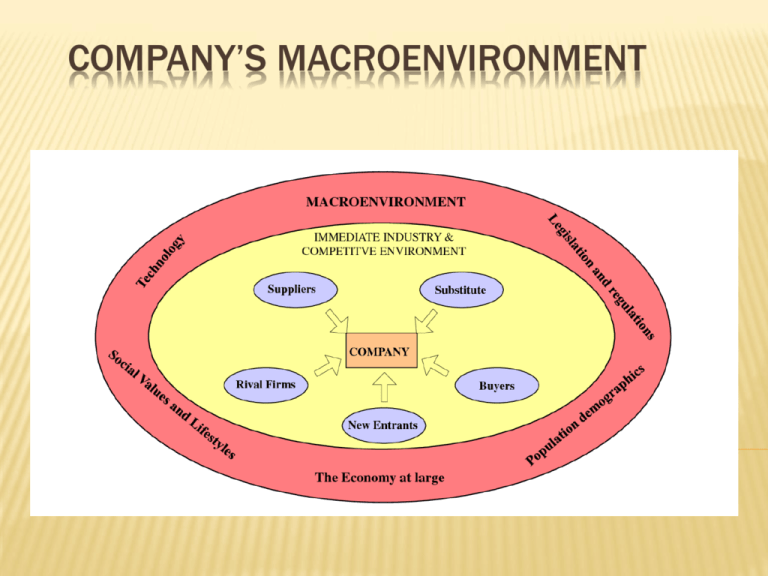
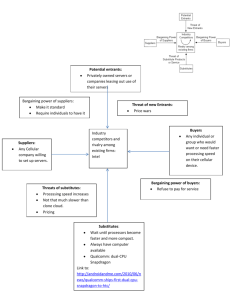
COMPANY’S MACROENVIRONMENT Q1. WHAT ARE THE INDUSTRY’S DOMINANT ECONOMIC FEATURES? Market size growth rate the number & sizes of buyers and sellers the geographic boundaries of the market The degree of product differentiation the speed of product innovation the extent of vertical integration. The extent of scale economies& experience/learning curve effects. LEARNING/EXPERIENCE CURVE EFFECTS Most goods or services show the experience curve effect. Each time cumulative volume doubles, value added costs (including administration, marketing, distribution, and manufacturing) fall by a constant percentage. The company can gain a cost advantage with largest cumulative production volume. RECOGNIZING THESE FEATURES HELPS.. managers to prepare for the analysis managers to understand the kinds of strategic moves that industry members are likely to employ. QUESTION 2: WHAT KINDS OF COMPETITIVE FORCES ARE INDUSTRY MEMBERS FACING, AND HOW STRONG ARE THEY? THE FIVE-FORCES MODEL OF COMPETITION Michael E. Porter Tool for diagnosing the principal competitive pressure Build the model of competition in 3 steps · Step1: For each of the five forces, identify the different parties involve · Step2: Evaluate how strong the pressures stemming form each forces are · Step3: Determine whether the strength of the five forces is helpful to earning profits THE FIVE-FORCES MODEL OF COMPETITION COMPETITIVE PRESSURES CREATED BY THE RIVALRY AMONG COMPETING SELLERS Competitive pressures coming from other firms in the industry · when one firm deploys a strategy that produces good results, its rivals respond with offensive and defensive countermoves of their own. · competitive battle among rivals can assume many forms that extend well beyond lively price competition. The intensity of rivalry varies from industry to industry and depends of many identifiable factors FACTORS AFFECTING THE STRENGTH OF RIVALRY Rivalry is stronger when: Buyer demand is growing or falling off slowly Sellers find themselves with excess capacity Buyer costs to switch brands are low Products are commodities Firms have high fixed and storage costs Competitors are numerous/similar(size, strength) Rivals have diverse objectives/strategies/origin Rivals have high exit barriers FACTORS AFFECTING THE STRENGTH OF RIVALRY Rivalry is weaker when: Buyer demand is growing rapidly Buyer costs to switch brands are high Products are strongly differentiated Customer loyalty is high Fixed and storage costs are low Sales are concentrated among a few sellers Rivals are homogeneous Exit barriers are low Crafting & Executing Strategy – Chapter 3 EVALUATING A COMPANY’S EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT COMPETITIVE THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS 1. 2. The ease of a firm entering a new market is dependent on 2 main factors: Barriers to entry Expected reaction of existing firms The size of the barriers and expected reaction is a huge determinant of any potential new firms ability to survive in the market BARRIERS TO ENTRY Economies of Scale Experience Customer loyalty Intellectual barriers Networks Other cost advantages Threat of entry can easily fluctuate as factors change FACTORS AFFECTING THREAT OF ENTRY Growth/Profit potential – If this is high, firms will be less deterred to enter the market Usually attracts larger, established firms with sufficient resources in related markets to enter Potential entrants & capabilities – Large existing companies with a strong brand image may be able to enter some markets easily The bigger the pool of potential entrants with the capabilities to enter the market, the stronger the threat of entry COMPETITIVE PRESSURE OF SUBSTITUTES Substitute products can adversely affect demand providing: Good substitutes are available They are attractively priced Comparable/better features Consumers have low costs in switching to substitute Whether a substitute product is a threat can be determined by; sales growth comparison, addition of capacity and profit increases COMPETITIVE PRESSURES STEMMING FROM SUPPLIER BARGAINING POWER. Bargaining power : the relative ability of parties in a situation to exert influence over each other. Suppliers with Bargaining Power : can erode industry profitability. FACTORS DETERMINING THE STRENGTH OF SUPPLIERS’ BARGAINING POWER. Suppliers’ bargaining power is stronger when Supplier products are in short supply. Supplier products are differentiated. Supplier products are critical to industry. High costs in purchasing alternatives. No good substitutes. Suppliers are not dependant on industry. Suppliers industry is concentrated. Suppliers’ bargaining power is weaker when A large entity of suppliers. The item is available from many suppliers. Low costs for finding alternatives. Good substitutes. Industry members account for a big fraction of suppliers’ sales. No suppliers with large market shares. Possibility for industry members to integrate into the supply business. (self-manufacturer) COMPETITIVE PRESSURES STEMMING FROM BUYER BARGAINING POWER AND PRICE SENSITIVITY Price-sensitivity = price elasticity : It is a measure of responsiveness of the quantity of a good or service demanded to changes in its price. Buyers with strong bargaining power : can limit industry profitability. Buyer price sensitivity : limits the profit potential of industry members. FACTORS DETERMINING THE STRENGTH OF BUYERS’ BARGAINING POWER. Buyer bargaining power is stronger when Low costs in switching to other product. Products are undifferentiated. Large number of buyers. Few relation with industry. Buyers demand is weak. Buyers are well-informed. Buyers with ability to integrate into the business of sellers. Buyers with ability to postpone purchase Buyers are price-sensitive. Buyer bargaining power is weaker when High costs in switching to competing products. Sellers’ products are differentiated. Buyers are small and numerous relative to sellers. Sufficient supply for satisfying buyers demand. Limited information about sellers. Buyers are not price-sensitivity. IS THE COLLECTIVE STRENGTH OF THE FIVE COMPETITIVE FORCES CONDUCIVE TO GOOD PROFITABILITY? The effects that each of the five competitive forces set the stage for evaluating whether the strength of the five competitive forces is conducive to good profitability. Competitively Unattractive Industry When all five forces are producing strong competitive pressures, the competitively unattractive industry occurs. Rivalry among sellers is vigorous. Low entry barriers. Competition from substitutes in intense. Suppliers and buyers can exercise considerable leverage. Attractive Industry When the overall impact of the five competitive forces is moderate to weak, the attractive industry occurs. The members of the industry can expect to earn good profits and a nice return on investment. QUESTIONS 3: WHAT FACTORS ARE DRIVING INDUSTRY CHANGE, AND WHAT IMPACTS WILL THEY HAVE? ANALYZING INDUSTRY DYNAMICS 1 step: Indentifying the drivers of change. 2 step: Assessing whether the drivers of change are, individually or collectively, acting to make the industry more or less attractive. 3 step: Determining what strategy changes are needed to prepare for the impacts of the anticipated change. IDENTIFYING AN INDUSTRY’S DRIVERS OF CHANGE Changes in an industry’s long-term growth rate Increasing globalization Change in who buys the product and how they use it Technological change Emerging new internet capabilities and applications Product and marketing innovation IDENTIFYING AN INDUSTRY’S DRIVERS OF CHANGE Entry or exit of major firms Diffusion of technical know-how across companies and countries Improvements in efficiency in adjacent markets Reductions in uncertainty and business risk Regulatory influences and government policy changes Changing societal concerns, attitudes, and lifestyles ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF THE FACTORS DRIVING INDUSTRY CHANGE 1. 2. 3. Overall, are the factors driving change causing demand for the industry’s product to increase or decrease? Is the collective impact of the drivers of change making competition more or less intense? Will the combined impacts of the change drivers lead to higher to lower industry profitability? Key Question: whether a new strong force is emerging or whether forces that are strong presently are beginning to weaken DEVELOPING A STRATEGY THAT TAKES THE CHANGES IN INDUSTRY CONDITIONS INTO ACCOUNT What strategy adjustments will be needed to deal with the impacts of the changes in industry conditions. WHAT STRATEGIC MOVES ARE RIVALS LIKELY TO MAKE NEXT? Competitive intelligence - latest action & announcement - financial performance - strength & weakness - thinking & leadership style WHAT STRATEGIC MOVES ARE RIVALS LIKELY TO MAKE NEXT? Prepare defensive countermoves Craft it’s own strategic moves Exploit any openings WHAT ARE THE KEY FACTORS FOR COMPETITIVE SUCCESS? Particular strategy elements Product attributes Operational approaches Resources Competitive capabilities WHAT ARE THE KEY FACTORS FOR COMPETITIVE SUCCESS? Should consider three question A. On what basis do buyers of the industry’s product choose between the competing brands of sellers? B. What resources and competitive capabilities must a company have to be competitively successful? C. What shortcomings are almost certain to put a company at a significant competitive disadvantage? Q7. DOES THE OUTLOOK FOR THE INDUSTRY OFFER THE COMPANY A GOOD OPPORTUNITY TO EARN ATTRACTIVE PROFITS? if an industry’s overall profit prospects are above average →industry environment is attractive If an industry profit prospects are below average →industry environment is not attractive BUT! This attractiveness or unattractiveness is not same for all industry participants and all potential entrants. If company decided that industry is attractive, it should invest aggressively to capture the opportunities and to improve its long-term competitive position in the business. If company decided that industry is unattractive, it should protect its present position, invest cautiously, and try to find opportunities in other industries.