Flower is the reproductive unit in the angiosperms. It is meant for
advertisement

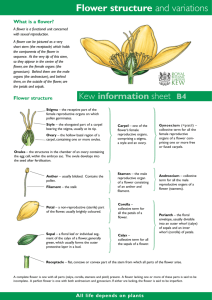
Flower is the reproductive unit in the angiosperms. It is meant for sexual reproduction. A typical flower has four different kinds of whorls calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium arranged successively on the swollen end of the stalk or pedicel called thalamus or receptacle. A flower may be bisexual (contain both androecium and gynoecium) or unisexual (contain either androecium or gynoecium) Flower may be actinomorphic (radial symmetry) or zygomorphic (bilateral symmetry). Based on the position of calyx, corolla, androecium in respect of the ovary on thalamus flowers are of three types. Hypogynous, Epigynous and Perigynous. Number, size, shape, colour and union of calyx and corolla are vary from plant species to species. Stamen and pistil also shows variation in number, arrangement and union. Flower is an organ of sexual reproduction. A complete flower contain all the four whorls. Calyx and corolla are known as accessory whorls of a flower since they indirectly involved in sexual reproduction. Androecium and gynoecium are known as essential whorl of a flower since they are directly involved in sexual reproduction. Calyx made of sepals which are generally green in colour and provide protection to flower during bud. Corolla made of petals which are variously coloured in order to attract pollinators. Androecium made of stamens which produce pollen grains are of yellow dusty powder released after maturation of anther. Gynoecium made of pistils/carpels which contain ovules are attached to the ovary wall with help of cushion like tissue called placenta. Based on the position of ovary in relation to calyx, corolla and androecium flowers are of 3 typesHypogynous, Epigynous and Perigynous. Flower is meant for reproduction in plants and not the object of expressing human feelings or used for human welfare. A flower may be with or without stake known as sessil or pedicellate respectively. Calyx –outer most whorl made of sepals may be free(polysepalous) or fused (gamosepalous) Corolla – second whorl from outer made of petals may be free(polypetalous) of fused (gamopetalous). In some plants calyx appear like petals called Petaloid sepals and corolla appear like sepals called sepaloid petals. Arrangement of sepals and petals in bud stage is called aestivation. There are four types of aestivation- Valvate, Twisted, Vexillary and imprecate. Androecium - third whorl made of stamens with long stalk called filament and top chambered structure called anther. Stamens may be free or fused to bundles(fused to single unit-monoadelphous, fused to two units-diadelphous and fused to more than two units- polyadelphous). If the filaments are fused and anthers are free it is called syngenesious and anthers are fused and filaments are free it is called synandrous. The filament connected to the anther at different levels. Anther made of single or double chamber called monothecus or dithecous. Proximal end of the filament connected to either base of the flower or inner surface of the petal which is known as epipetalous stamens. Gynoecium made of Pistils/Carpels. Flower with single carpel- Monocarpellary more than one carpel Polycarpellary. In polycarpellary ovary if the carpels are free-apocarpous, are fused- syncarpous. Ovary contain one or more ovules. Arrangement of ovules inside the ovary is called Placentation. Types of placentation are axile, marginal, parietal, basal and free central. 1. Field visit to observe the variations in number,adhesion, cohesion and attachement of members of floral whorls. 2. Floral dissection to display the floral whorl members to understand the floral morphology. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Name the whorls of a complete flower? Distinguish between the term polypetalous and gamopetalous? Define aestivation? Give an example of diadelphous stamens? What is Placentation? 1. Why androecium and gynoecium is known as essential whorl of a flower? 2. Name and explain different types of aestivation observed in angiosperms? 3. Distinguish between syngenesious and synandrous condition? 4. Explain different types of placentation with an example each? 5. Draw and label the parts of a complete flower. 1. Name the part of a flower which produce pollen grains? 2. What is aestivation? 3. Write the parts of a gynoecium/pistil ? 1. Which whorls of a flower called accessory whorl? Why? 2. What do you mean by the term monoadelphous and diadelphous? 3. Differentiate between (a) Unisexual and bisexual flower (b) Apocarpous and syncarpous (c) Zygomorphic and actinomorphic flower. 1. Distinguish between syngenesious and synadrous condition? 2. Explain hypogynous, perigynous and epigynous flower with examples?