Lecture 7: ELISA
advertisement

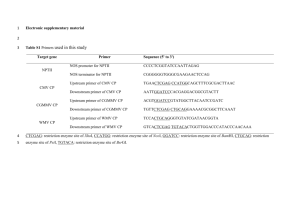
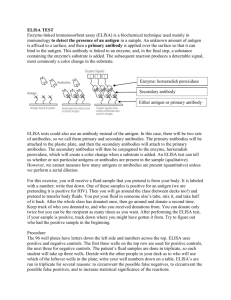
Which plant is transgenic? Determination using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay transgenic plants / GMOs • A transgenic plant has incorporated gene(s) from another species. • Transgenics are useful for engineering a specific phenotype or studying a gene’s function. transgenic selection: NPTII • Selection of plants that incorporated the transgene can be performed by simultaneously introducing a drug resistance gene into the plant (just like we do with E. coli). • nptII (most common) codes for the enzyme aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (NPTII) that phosphorylates (inactivates) aminoglycoside antibiotics including kanamycin, neomycin geneticin (G418) and paromomycin. transgenic selection: kanamycin resistance due to NPTII kanamycin WT kanamycin Transgenic NPTII Which plant is transgenic? Which plant is transgenic? WT WT WT transgenic • Need both WT and transgenic plants for experiment (today) so kanamycin selection is out. • Perform test for transgene or transgene protein? • ELISA is a fast way to test for the presence and amount of a protein such as NPTII. ELISA understanding the acronym • EL Enzyme-linked – An enzyme’s activity is used as a “reporter” to test for the presence/amount of a protein of interest. – The enzymatic reaction will produce a colored species. ELISA understanding the acronym • EL Enzyme-linked • IS Immunosorbent – An antibody or antigen (“immuno”) is adsorbed (“sorbent”) onto the polystyrene wells in which we conduct the test. – One antibody is already adsorbed added to the wells and a second antibody with our enzyme will be added in the type of ELISA we will perform today. ELISA understanding the acronym • EL Enzyme-linked • IS Immunosorbent • A Assay – We will could determine the amount of NPTII (quantitative assay). – We will use NPTII concentration standards to construct a standard curve. ELISA: uses antibodies • What is an antibody? • What types of antibodies exist? • What kinds of antibodies are used in our lab today? • What is an antibody? Protein secreted by B-cells that specifically bind a foreign substance (antigen) • Immunoglobulin domains • Complementarity-determining Regions (CDRs) • Fab= Fragment antigen binding • Hinge • Fc= Fragment crystalline • F(ab)’2= Protease digestion still useful to bind antigen producing polyclonal antibodies producing monoclonal antibodies 1 2 3 Antibody-based assays Types of immunodetection systems 2. Indirect immunodetection 1. Direct immunodetection Secondary antibody conjugated with enzyme system Primary antibody conjugated with enzyme system HRP HRP HRP HRP Ag Ag antigen Ag Ag Ag horseradish HRP peroxidase 3. Sandwich indirect immunodetection streptavidin Antigen applied in soluble form HRP HRP HRP 4. Indirect immunodetection with biotin linkers Biotinylated primary antibodies HRP HRP HRP HRP HRP HRP Ag Ag Ag Ag Streptavidin Today’s assay Sandwich indirect Antigen appliedimmunodetection in soluble form Substrate Substrate HRP HRP HRP Substrate HRP Substrate Sandwich ELISA protocol 1. Coat primary antibody onto microplate. 1a. Allow antibody adsorption and block unoccupied sites with neutral protein (BSA). 2. Add antigen sample to be detected into each well. Incubate 30 min at 370 C. 3. Add second primary antibody against antigen and HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (antibody mix) into each well. Incubate 30 min at 370 C. 4. Develop colorimetric reaction with appropriate substrate. Incubate 15 min at room temperature. 5. Stop reaction with 3M H2SO4. Read absorbance in ELISA spectrophotometer and quantitate relative antigen levels. What you will do today (1): – Collect and weigh tissue sample plant A, B and C. – Repeat for second and third plants. – Add 400 μL PEBX1 buffer to each microcentrifuge tube and grind plant tissue using pestle. – Add 100 μL of PEBX1 to wells A and B. – Add 100 μL of one sample to wells C and D. – Add 100 μL of second sample to wells E and F. – Add 100 μL of third sample to wells G and H. – HANDLE THE WELLS LIKE A CUVETTE (read at bottom) A H B C D E F G • What you will do today (2): Incubate 30 minutes at 37 °C. – Place wells in a zip-close bag to prevent them from drying out in the oven. • Wash wells 3 times with PBST • Add antibody-enzyme conjugate (MRS-2 Ab) – Note the dilution factor for the conjugate • Incubate 30 minutes at 37 °C. – Place wells in a zip-close bag to prevent them from drying out in the oven. • Wash 4 times with PBST. What you will do today (3): Add substrate and allow blue color to develop. • • Stop the enzymatic reaction with 3M H2SO4. • Presence of NPTII will result in color change from blue to yellow. How we will detect: read absorbance at 450 nm Data 1 W E L L A B C D E F G H 2 3 4 5 Absorbance 450 nm 6 7 8 9 10 11 NPTII Std Data analysis (due 4/23/12) 0.8 y = 0.3631x - 0.0025 R² = 0.995 absorbance at 450 nm 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 W E L L A Blank B Blank C Plant __ D Plant __ E Plant __ F Plant __ G Plant __ H Plant __ Total amount of plant tissue (mg) Your Sample N/A N/A A450 Your Sample 0.5 1 NPTII standard (ng/mL) 1.5 2 NPTII NPTII amount concentration (ng protein (ng/mL) /mg tissue) Transgenic? A 450 NPTII concentration (ng/mL) Your Sample 0 0 Your Sample N/A N/A Your sample N/A N/A Standard Standard Average Average Yes/No Average Average Yes/No Average Average Yes/No 2 1 0.5 0.25 0.125 0.0625 0.03125 0.015625