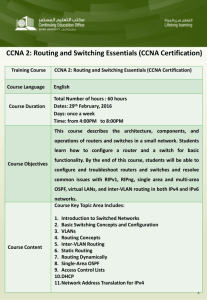
Cisco CCNA (200-120) Practice Exams
advertisement

Lesson Plans LabSim Routing and Switch Pro Table of Contents Course Overview .................................................................................................. 4 Course Introduction for Instructors ........................................................................ 8 Section 1.1: ICND1 Introduction.......................................................................... 11 Section 2.1: Networking Fundamentals .............................................................. 12 Section 2.2: Network Devices ............................................................................. 14 Section 2.3: TCP/IP Networking Model ............................................................... 16 Section 2.4: Data Encapsulation ......................................................................... 18 Section 2.5: OSI Networking Model .................................................................... 19 Section 2.6: Data Communications ..................................................................... 21 Section 2.7: Ethernet Networking........................................................................ 22 Section 2.8: WAN Fundamentals ........................................................................ 24 Section 3.1: Cisco Device Access....................................................................... 26 Section 3.2: System Startup ............................................................................... 28 Section 3.3: Command Line Interface (CLI) ........................................................ 30 Section 3.4: Command Line Help ....................................................................... 32 Section 3.5: Basic Device Settings ..................................................................... 33 Section 3.6: Device Passwords .......................................................................... 35 Section 4.1: Layer 2 Switching Overview ............................................................ 37 Section 4.2: Spanning Tree Overview ................................................................. 39 Section 4.3: Switch Interface Configuration ........................................................ 41 Section 4.4: Switch IP Configuration ................................................................... 43 Section 4.5: Virtual LANs (VLANs)...................................................................... 46 Section 4.6: Trunking .......................................................................................... 48 Section 4.7: Switch Security ............................................................................... 50 Section 4.8: Remote Switch Access ................................................................... 53 Section 4.9: Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) ..................................................... 55 Section 5.1: IPv4 Overview ................................................................................. 57 Section 5.2: IPv4 Address Classes ..................................................................... 58 Section 5.3: Subnetting ....................................................................................... 60 Section 5.4: Variable Length Subnet Masking (VSLM) ....................................... 61 Section 5.5: Subnet Planning and Design........................................................... 62 Section 6.1: IP Routing ....................................................................................... 64 Section 6.2: Routing Implementations ................................................................ 66 Section 6.3: Static Routing .................................................................................. 68 Section 6.4: Dynamic Routing ............................................................................. 70 Section 6.5: Route Summarization...................................................................... 72 Section 6.6: Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Overview .................................... 74 Section 6.7: OSPF Configuration ........................................................................ 76 Section 6.8: InterVLAN Routing Overview .......................................................... 78 Section 6.9: InterVLAN Routing Configuration .................................................... 80 Section 7.1: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) ................................ 82 Section 7.2: Access Control Lists (ACLs) ........................................................... 84 Section 7.3: ACL Commands .............................................................................. 86 ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 1 Section 7.4: ACL Configuration ........................................................................... 88 Section 7.5: Extended ACL Configuration ........................................................... 90 Section 7.6: Network Address Translation (NAT) Overview ................................ 92 Section 7.7: NAT Configuration........................................................................... 94 Section 7.8: Network Time Protocol (NTP) ......................................................... 96 Section 8.1: IPv6 Addressing Overview .............................................................. 97 Section 8.2: IPv6 Host Configuration .................................................................. 99 Section 8.3: IPv6 Routing ................................................................................. 101 Section 9.1: Network Communications Troubleshooting................................... 103 Section 9.2: Switch Troubleshooting ................................................................. 105 Section 9.3: ACL Troubleshooting .................................................................... 108 Section 10.1: ICND2 Introduction...................................................................... 109 Section 11.1: Router Configuration Files .......................................................... 110 Section 11.2: IOS Licensing .............................................................................. 112 Section 12.1: Spanning Tree Overview............................................................. 114 Section 12.2: Spanning Tree Protocol Configuration ........................................ 116 Section 12.3: Switch Troubleshooting ............................................................... 118 Section 13.1: IPv4 Routing Troubleshooting ..................................................... 120 Section 13.2: InterVLAN Routing Troubleshooting ........................................... 122 Section 13.3: Default Gateway Redundancy .................................................... 124 Section 14.1: WAN Types ................................................................................. 127 Section 14.2: Leased Line WAN Links .............................................................. 129 Section 14.3: PPP WAN Links .......................................................................... 131 Section 14.4: Frame Relay WAN Concepts ...................................................... 133 Section 14.5: Frame Relay Configuration ......................................................... 135 Section 14.6: PPPoE Configuration .................................................................. 137 Section 14.7: Virtual Private Networks .............................................................. 139 Section 14.8: WAN Troubleshooting ................................................................. 141 Section 15.1: OSPF for IPv4 Review ................................................................ 143 Section 15.2: OSPF Areas and LSA Types ...................................................... 145 Section 15.3: EIGRP for IPv4 Routing .............................................................. 147 Section 15.4: EIGRP for IPv4 Configuration ..................................................... 149 Section 15.5: IPv4 Protocol Troubleshooting .................................................... 151 Section 16.1: IPv6 Protocol Overview ............................................................... 154 Section 16.2: OSPF for IPv6 ............................................................................. 156 Section 16.3: EIGRP for IPv6 ........................................................................... 158 Section 17.1: Simple Network Management Protocol ....................................... 160 Section 17.2: System Message Log.................................................................. 162 Section 17.3: NetFlow ....................................................................................... 163 TestOut Switching Pro Practice Exams ............................................................ 164 TestOut Routing Pro Practice Exams ............................................................... 165 Cisco ICND1 (100-101) Practice Exams ........................................................... 166 Cisco ICND2 (200-101) Practice Exams ........................................................... 167 Cisco CCNA (200-120) Practice Exams ........................................................... 168 Appendix A: Approximate Time for the Course ................................................. 169 ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 2 Appendix B: Exam 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Objectives ......................................................................................................... 175 Appendix C: Exam 200-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Objectives ......................................................................................................... 181 Appendix D: Exam 200-120: Cisco Certified Network Associate Objectives ..... 186 Appendix E: TestOut Routing Pro Exam Objectives ......................................... 195 Appendix F: TestOut Routing Pro Exam Objectives ......................................... 198 ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 3 Course Overview This course prepares students for Cisco’s Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices (ICND1) and (ICND2) certification exams. 100-101 ICND1 Module 1 – ICND1 Introduction This module introduces the students to the certification options that this course prepares the students for. Module 2 – Networking Concepts In this module students will learn about basic elements of networking. This includes networking hardware, TCP/IP and OSI networking models, data encapsulation, Ethernet architecture, and the fundamentals of WAN services. Module 3 – Cisco Device Basics This module teaches students about the basics of managing Cisco routers and switches. This includes understanding the system startup, using the CLI, and configuring banners and passwords. Module 4 – LAN Switching This module teaches students about LAN switching and all the elements that are used for LAN switching: Layer 2 switching, Spanning Tree, VLANs, trunking, security, accessing remote switches, and CDP. Module 5 – IPv4 Addressing This module examines using the essentials of IPv4 Addressing. Students will become familiar with subnetting, classful and classless addresses, VLAM, and CIDR. They will learn how to design and configure subnets. Module 6 – IP Routing Technologies In this module students will learn concepts about technologies that are used for configuring IP routing, including static and dynamic routing, route summarization, OSPF, and InterVLAN routing. Module 7 – IP Services This module discusses IP services, which includes discussions on Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), Access Control Lists (ACLs), Network Address Translation (NAT) and Network Time Protocol (NTP). Module 8 – IPv6 Addressing This module teaches students about IPv6 addressing, host configuration, and IPv6 routing. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 4 Module 9 – Troubleshooting This module examines troubleshooting network communications, switches, and ACLs. The ICND1 modules also prepare students for the Cisco Certified Entry Networking Technician (CCENT) exam. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 5 200-101 ICND2 Module 10 – ICND2 Introduction This module introduces the students to the certification options that this portion of the course prepares the students for. Module 11 – Router Configuration and Management In this module students will learn about configuring router files. Students will become familiar with router passwords and router memory and how to install licenses on a Cisco device. Module 12 – Spanning Tree Protocol This module teaches students about the Spanning Tree Protocol, configuring STP, and troubleshooting LAN switches. Module 13 – Advanced IPv4 Routing This module examines troubleshooting IPv4 and InterVLAN routing, and using the First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP) family of protocols. Module 14 – Wide Area Networks In this module students will learn about following Wide Area Networks (WANs) concepts: PPP WAN links, Frame Relay WANs, configuring a PPPoE client, VPNs, and troubleshooting WAN issues. Module 15 – IPv4 Routing Protocols This module discusses using IPv4 routing protocols: OSPF for IPv4 and EIGRP for IPv4. Module 16 – IPv6 Routing Protocols This module teaches students about the IPv6 routing protocols: OSPF for IPv6 and EIGRP for IPv6. Module 17 – Network Management Using Cisco Devices This module teaches students about managing the network using Cisco devices: SNMP, system message log, and NetFlow. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 6 Practice Exams In Practice Exams students will have the opportunity to test themselves and verify that they understand the course concepts and are ready to take certification exams. The practice exams contain the types of questions that a student will find on the actual exams. The following practice exams are provided: TestOut Switching Pro TestOut Routing Pro Cisco ICND1 (100-101) Cisco ICND2 (200-101) Cisco CCNA (200-120) ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 7 Course Introduction for Instructors This course provides students with the knowledge to become industry certified as a Cisco professional. It prepares the student for the following CCNA exams: 100-101 ICND1 200-101 ICND2 200-120: Cisco Certified Network Associate Cisco offers two options for obtaining the CCNA certification: Pass Exam 200-120 (covers both ICND1 and ICND2) Pass Exam 100-101 (ICND1) AND Exam 200-101 (ICND2) For Cisco certifications the course has been organized as follows: Sections 1 through 9 prepare students for ICND1. Sections 10 through 17 prepare students for ICND2. Cisco’s 100-101 ICND1 certification measures the student’s ability to install, operate, and troubleshoot a small branch office network. The following knowledge domains are addressed: Operation of IP Data Networks LAN Switching Technologies IP Addressing (IPv4 & IPv6) IP Routing Technologies IP Services Network Device Security Troubleshooting Cisco’s 200-101 ICND1 certification measures the student’s ability to install, operate, and troubleshoot a small or medium–sized enterprise branch network. The following knowledge domains are addressed: LAN Switching Technologies IP Routing Technologies IP Services Troubleshooting WAN Technologies Cisco’s 200-120: Cisco Certified Network Associate certification measures the student’s ability to select, install, configure, and troubleshoot Cisco routers and switches. It covers all the information in both the ICND1 and ICND2 exams. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 8 Note: The objectives for the following exams are included in the appendices: 100-101 ICND1 200-101 ICND2 200-120 CCNA (covers both ICND1 and ICND2) This course also prepares students for two of TestOut’s certifications: TestOut Routing Pro TestOut Switching Pro TestOut’s Routing Pro certification measures the student’s ability to configure, manage and troubleshoot router connections. The following knowledge domains are addressed: Router Setup and Configuration Router Setup and Configuration IP Routing Implementation OSPF Routing Configuration EIGRP Routing Configuration Access Control List Configuration Frame Relay Configuration NAT Configuration DHCP Server Configuration Router Security Configuration High Availability Configuration TestOut’s Switching Pro certification measures the student’s ability to configure, manage, secure, and troubleshoot switches. The following knowledge domains are addressed: Switch Setup and Configuration Switch Interface Configuration TCP/IP Configuration VLAN Configuration InterVLAN Configuration Spanning Tree Configuration Switch Configuration EtherChannel Configuration The section introductions in LabSim and the lesson plans list the objectives that are met for each of the exams in that section. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 9 The following icons are placed in front of lesson items in LabSim to help students quickly recognize the items in each section: = Demonstration = Exam = Lab/Simulation = Text lesson or fact sheet = Video The video and demonstration icons are used throughout the lesson plans to help instructors differentiate between the timing for the videos and demonstrations. In the lesson plans the Total Time for each section is calculated by adding the approximate time for each section which is calculated using the following elements: Video/demo times Approximate time to read the text lesson (the length of each text lesson is taken into consideration) Simulations (5 minutes is assigned per simulation. This is the amount of time it would take for a knowledgeable student to complete the lab activity. Plan that the new students will take much longer than this depending upon their knowledge level and computer experience.) Questions (1 minute per question) Note: Appendix A: Approximate Time for the Course contains the approximate times for each section, which are totaled for the entire course. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 10 Section 1.1: ICND1 Introduction Summary In this section students will learn how to use the Cisco Simulator. They should be familiar with launching the lab, completing the instructions in the scenario, and reviewing the lab report. Details include: The process to complete the simulation Elements of the lab report Features of the TestOut lab engine Limitations of the TestOut simulator Cisco Device Icons used to represent network devices and connections Experiment with the router simulations so you will be able to demonstrate them in class. Video/Demo 1.1.1 ICND1 Introduction Time 00:39 Total Time About 5 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 11 Section 2.1: Networking Fundamentals Summary This section provides fundamentals about twisted pair and fiber optic cables. Details include: Twisted Pair Cables: o Components of twisted pair cables o UTP cable types and connectors o UTP cable substitution o Characteristics of a RJ-45 connector o Ethernet specifications for pins on RJ-45 connectors o Ethernet cables used for LAN connections: Straight-through Crossover Ethernet cable o Considerations when making LAN connections Fiber Optics: o Components of fiber optic cables o Advantages and disadvantages o Single mode o Multi-mode o Connector types: ST connector SC connector LC connector MT-RJ connector Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 1.2 Select the components required to meet a given network specification. 1.6 Identify the appropriate media, cables, ports, and connectors to connect Cisco network devices to other network devices and hosts in a LAN. 2.1 Determine the technology and media access control method for Ethernet networks. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 12 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the two classifications of twisted pair cable? What are the characteristics of the Cat 5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable type? How do the Cat 5 and Cat 5e types differ? What is the general rule for substituting UTP cable types? How does data transmission on straight-through Ethernet cables differ from data transmission on crossover cables? Which devices should you connect using straight-through Ethernet cable? For which devices should you use crossover? What is the purpose of cladding in fiber optic cabling? What are the advantages of fiber optic cabling? How do single mode fiber cables differ from multi-mode? What connector types are used with fiber optic cable? Video/Demo Time 2.1.1 Network Design Overview 3:37 2.1.2 Cables and Connectors 7:36 Total 11:13 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 13 Section 2.2: Network Devices Summary This section discusses network devices used within a LAN. Common connectivity devices: o Hub o Bridge o Switch Routers: o Routing table o Routing protocol o Convergence LAN segmentation: o Collision domain o Broadcast domain o Broadcast storm o Connection devices: Hub Bridge or switch Router o Considerations for a network expansion solution using a: Router Switch Bridge o Guidelines to select the appropriate connectivity device o Supporting VoIP Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 1.1 Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices, such as routers, switches, bridges, and hubs. 1.2 Select the components required to meet a given network specification. 1.3 Identify common applications and their impact on the network. 2.1 Determine the technology and media access control method for Ethernet networks. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 14 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the disadvantages to using a hub for connecting network components? How does a switch differ from a bridge? What is the 80/20 rule for designing the placement of bridges on the network? How does a unicast transmission differ from a broadcast transmission? How do routers handle broadcast transmissions? What is convergence? What network requirements would indicate the use of a router instead of a switch or hub? Video/Demo Time 2.2.1 Hubs 3:57 2.2.2 Switches 8:24 2.2.4 Routers 10:13 2.2.6 Internetworks Total 3:24 25:58 Number of Exam Questions 14 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 15 Section 2.3: TCP/IP Networking Model Summary This section provides details about the role of the TP/IP networking model. Details covered include: The advantages of the TCP/IP model Limitations of the TCP/IP model Layers of the TCP/IP model: o Application layer (Process-to-Process) o Transport layer (Host-to-Host) o Internet layer o Link layer Functions performed at each TCP/IP model layer: o Application (Process-to-Process) o Transport (Host-to-Host) o Internet o Link Network ports ICANN specifies three categories for ports: o Well Known o Registered o Dynamic (Private or High) Well known ports that correspond to common Internet services Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 1.4 Describe the purpose and basic operation of the protocols in the OSI and TCP/IP models. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the purpose of a network model? How does the TCP protocol differ from the UDP protocol? What functions are performed by Application layer protocols? How does TCP negotiate a connection with a remote host? What role do port assignments play in application-to-application communications? What functions are provided by the Internet layer? What are MAC addresses? How are they used by the Link layer? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 16 Video/Demo Time 2.3.1 Network Models Overview 5:19 2.3.2 TCP/IP Model 9:17 2.3.4 Application Layer 3:25 2.3.5 Transport Layer 5:48 2.3.6 Internet Layer 7:32 2.3.7 Link Layer 2:28 Total 33:49 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 17 Section 2.4: Data Encapsulation Summary This section discusses the steps to the data encapsulation process: Application layer—data Transport layer—segments Internet layer—packets containing logical addresses Link layer—framing that adds physical address and bits that are transmitted on the network medium Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 1.4 Describe the purpose and basic operation of the protocols in the OSI and TCP/IP models. Lecture Focus Questions: How does data encapsulation facilitate data transmission? What are the TCP/IP encapsulation process steps on a sending host? What are the TCP/IP de-encapsulation process steps? What information does the Transport layer add to data being transmitted? What is a PDU? How do PDUs relate to TCP/IP layers? Video/Demo 2.4.1 Data Encapsulation and PDUs Time 8:29 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 15 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 18 Section 2.5: OSI Networking Model Summary This section examines the OSI model. Concepts covered include: OSI model: o Advantages o Limitations o Layer names: Layer 7 Application Layer 6 Presentation Layer 5 Session Layer 4 Transport Layer 3 Network Layer 2 Data Link Layer 1 Physical Characteristics of the lower OSI model layers: o Physical o Data Link: Media Access Control Logical Link control (LLC) o Network o Transport Characteristics of the upper OSI model layers: o Application o Presentation o Session Comparison of the functions performed at each OSI model layer Protocols in the TCP/IP protocol suite: o File Transfer Protocol (FTP) o Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) o Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) o Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) o Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) o Telnet o Network File System (NFS) o Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) o Domain Name System (DNS) o Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) o User Datagram Protocol (UDP) o Internet Protocol (IP) o Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) o Internet Group Membership Protocol (IGMP) o Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) o Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP and Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 19 o Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP o Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) o Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 1.4 Describe the purpose and basic operation of the protocols in the OSI and TCP/IP models. Lecture Focus Questions: How does the OSI model differ from the TCP/IP model? How are they similar? What is the function of the Physical layer of the OSI model? What is the corresponding layer in the TCP/IP model? How does the Presentation layer ensure that data presented to the Application layer is in a compatible form? Which protocols are used by the Data Link layer? How are host-to-host connections managed? Which protocols are used to determine the IP address from a known MAC address? Video/Demo Time 2.5.1 OSI Comparison to TCP/IP 2:50 2.5.2 OSI Layers 6:09 2.5.7 Network Applications 5:40 Total 14:39 Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 20 Section 2.6: Data Communications Summary In this section students will learn details about the process of data communications between network hosts. Concepts covered include: Source host encapsulation Network transmission Destination host de-encapsulation Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 1.4 Describe the purpose and basic operation of the protocols in the OSI and TCP/IP models. 1.5 Predict the data flow between two hosts across a network. Lecture Focus Questions: Which destination address and source address is identified in a frame header? When are ARP requests used? What information is contained in the unicast response to an ARP broadcast? What action does a router perform when it receives frames? What happens if there are missing or damaged packets? Video/Demo Time 2.6.1 Packets and Frames 6:23 2.6.2 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) 5:40 2.6.3 IP Communications 6:58 Total 19:01 Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 21 Section 2.7: Ethernet Networking Summary This section discusses the following details about using an Ethernet network: Specifics of Ethernet architecture: o Topology o Media access o Transmission media o Frame type o Physical address Collision problems with original Ethernet standards we solved with: o Twisted pair cable o Switches Modes to control collision detection: o Half-duplex – collision detection is turned on o Full-duplex -- collision detection is turned off Ethernet frames contain the following components: o Preamble o Destination o Source address o Data o Optional bit to pad the frame o CRC (cyclic redundancy check) Comparison the Ethernet categories, standards, and requirements: o Ethernet: 10BaseT 10BaseFL o Fast Ethernet: 100BaseTX 100BaseFX o Gigabit Ethernet: 1000BaseT 1000BaseCX (short copper) 1000BaseSX (short) 1000BaseLX (long) o 10 Gigabit Ethernet: 10GBaseT 10GBaseSR/10GBaseSW 10GBaseLR/10GBaseLW 10GBaseER/10GBaseEW Ethernet facts ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 22 Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 1.4 Describe the purpose and basic operation of the protocols in the OSI and TCP/IP models. 1.6 Identify the appropriate media, cables, ports, and connectors to connect Cisco network devices to other network devices and hosts in a LAN. 2.1 Determine the technology and media access control method for Ethernet networks. Lecture Focus Questions: What functions does a network access technology provide? Which topologies are supported by Ethernet? What is a disadvantage of the linear topology? What are the components of a chassis-based switch? What function does each perform? What is switch layering? How does it work? How does the CSMA/CD network access method help to ensure data delivery? How do the four Ethernet frame types differ? What are the hardware requirements to use full-duplex mode? Video/Demo Time 2.7.1 History of Access Technologies 2:53 2.7.2 Network Topologies 5:32 2.7.3 Network Access (CSMA/Cx) 9:19 2.7.6 Frame Format 4:49 2.7.8 Ethernet Standards 3:37 Total 26:10 Number of Exam Questions 12 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 23 Section 2.8: WAN Fundamentals Summary This section discusses the basics of WAN connectivity. Details include: WAN types: o Point-to-Point o Circuit switching o Packet switching Components of a WAN structure: o Consumer Premises Equipment (CPE) o Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) o Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit (CSU/DSU) o Demarcation point (demarc) o Local loop o Central Office (CO) o Data Communication Equipment (DCE) o WAN cloud o Packet-Switching Exchange (PSE) Common WAN transmission media: o Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) o T1 (a.k.a. DS1) o T3 (a.k.a. DS3) o E1 o E3 o J1 o J3 o Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) satellite WAN connectivity service options: o Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) o Leased lines o X.25 o Frame Relay o Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) o Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) o DSL Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) WAN connector types and ports: o DB-6 Connector – Serial WIC port o Smart Serial Connector – Smart Serial WIC port o RJ-48 Connector – Integrated T1 DSU/DSU WIC port o RJ-11 Connector – DSL WIC port ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 24 Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 1.4 Describe the purpose and basic operation of the protocols in the OSI and TCP/IP models. 8.1 Identify different WAN Technologies. o Metro Ethernet o Cellular 3G/4G o T1/E1 o ISDN o DSL o Frame relay o Cable o VPN Lecture Focus Questions: How does using leased lines for a WAN differ from using MPLS? What are the advantages to using MPLS? What is an Ethernet handoff? What advantage does it have in WAN communication? How does circuit switching WAN system differ from a packet switching implementation? What components are included in a CPE? What role does a DCE play in WAN communications? Video/Demo 2.8.1 WAN Overview Time 3:34 Number of Exam Questions 13 questions Total Time About 25 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 25 Section 3.1: Cisco Device Access Summary This section discusses how to access a Cisco router or switch. Concepts covered include: Connection types used to manage a Cisco device: o Console o Virtual Terminal VTY o Security Device Manager (SDM) Cable types to make the initial connection to the switch or router for device management: o Rollover cable o Straight-through Ethernet cable o Crossover Ethernet cable Students will learn how to: Use HyperTerminal to connect to a Cisco device console. Use Telnet to create a virtual terminal connection to a Cisco device. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.3 Configure and verify initial switch configuration, including remote access management: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic switch setup Lecture Focus Questions: What HyperTerminal settings should you use to connect to the router console? What are the requirements for using a VTY (virtual terminal) connection to a Cisco device? What types of cable can you use to connect a PC to a router console port? If an SDM connection to a new router fails, what should you do to connect to the router? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 26 Video/Demo 3.1.1 Device Access Time 4:36 Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 10 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 27 Section 3.2: System Startup Summary In this section students will learn about the Cisco configuration files, types of memory on Cisco devices, and the boot sequence of a Cisco switch or router. Concepts covered include: Types of storage on Cisco devices: o ROM (read-Only Memory) o Flash o RAM (Random Access Memory) o NVRAM (Non-Volatile RAM) Non-volatile memory (such as ROM, flash, and NVRAM) remains when the device is powered off Volatile memory (RAM) is lost when the device is powered down The startup sequence used to boot a Cisco device Students will learn how to: Load an IOS image from an alternate location. Upgrade the IOS image. Save configuration changes. Cisco Exam 200-101 (ICND2) Objectives: 2.1 Describe the boot process of Cisco IOS routers. TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 1.0 Router setup and configuration: o Manage router configuration o Manage router IOS files TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 1.0 Switch setup and configuration: o Manage switch configuration files o Manage switch IOS files ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 28 Lecture Focus Questions: Where is the startup-config file stored? Where is the running-config file stored? What happens to unsaved configuration changes when the system is powered down or loses power? What is stored in ROM? How does flash memory differ from NVRAM (non-Volatile RAM)? In which locations does the system check for the IOS image if the start-up config file is missing or the location is not specified? Video/Demo 3.2.1 Device Startup Sequence Time 3:41 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 10 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 29 Section 3.3: Command Line Interface (CLI) Summary This section discusses how to access a Cisco router or switch. Concepts covered include: Connection types used to manage a Cisco device: o Console o Virtual Terminal VTY o Security Device Manager (SDM) Cable types to make the initial connection to the switch or router for device management: o Rollover cable o Straight-through Ethernet cable o Crossover Ethernet cable Students will learn how to: Enter and move between basic command mode prompts. Use show commands to find information about the device configuration. Use the copy command to save configuration changes, and load different versions of the configuration files. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.3 Configure and verify initial switch configuration, including remote access management: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic switch setup 4.2 Configure and verify utilizing the CLI to set basic router configuration: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic router setup 4.3 Configure and verify the operation status of a device interface, both serial and Ethernet. TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 1.0 Router setup and configuration: o View router configuration information o Manage router configuration o Manage router IOS files ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 30 TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 1.0 Switch setup and configuration: o View switch configuration information o Manage switch configuration files o Manage switch IOS files Lecture Focus Questions: What router mode is indicated by the # prompt? When would you use ROM Monitor mode? How do you get to EXEC mode from this mode? When would you boot into RXBoot mode? How do you enter RXBoot mode? What is the difference between using exit or Ctrl + Z when changing confirmation mode? How are switches with multiple banks numbered? What is the slot/port numbering scheme for routers without built-in ports or built-in WIC slots? Video/Demo Time 3.3.1 Command Modes 2:36 3.3.2 Using the Command Line Interface (CLI) 7:16 Total 9:52 Lab/Activity Find Device Information Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 25 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 31 Section 3.4: Command Line Help Summary This section provides details of using command line Help in device modes. Using the Help command Managing the command history Using advanced editing features of the CLI Students will learn how to: Use help commands to find information about the commands available. Use the Cisco command history to select previously used commands. Lecture Focus Questions: Using CLI Help, how would you display commands that start with a specific letter? Using CLI Help, how would you display the keywords for a specific command? When using command history, how could you display a command you typed previously? How do you display all the commands in the command history? Video/Demo 3.4.1 Using Command History, Editing, and Help Time 6:35 Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 32 Section 3.5: Basic Device Settings Summary This section discusses configuring basic device settings for Cisco switches and routers. Details include: Hostname and description commands Screen output management problems and solutions Commands to display banners that will display during login Students will learn how to: Name a host and designate a description for an interface. Use commands to control response messages. Create banners. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.3 Configure and verify initial switch configuration, including remote access management: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic switch setup 4.2 Configure and verify utilizing the CLI to set basic router configuration: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic router setup TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 1.0 Router setup and configuration: o Configure router hostnames and interface descriptions o Configure router banners TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 1.0 Switch setup and configuration: o Configure switch hostnames and interface descriptions o Configure switch banners ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 33 Lecture Focus Questions: What command do you use to set a description for a specific interface? How do you remove the interface description? What does the no logging console command accomplish? How can you change the disconnect time? If you enter a banner command without a keyword, which type of banner is created? How do you create multiple-line banners? Lab/Activity Configure Hostnames and Descriptions Configure Banners Modify Banners Video/Demo 3.5.1 Configuring Basic Device Settings Time 10:32 Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 34 Section 3.6: Device Passwords Summary This section discusses configuring device passwords. Details include: Common password types: o Console o VTY o EXEC mode Recommendations for configuring router passwords Basic password commands Conditions to allow access to the console through a Telnet session Password recovery steps for the 2960 switch Password recovery steps for the 1800 series routers Students will learn how to: Configure router passwords including enable, console, and VTY. Restrict console and VTY access to a Cisco device. Recover device passwords. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.3 Configure and verify initial switch configuration, including remote access management: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic switch setup 4.2 Configure and verify utilizing the CLI to set basic router configuration: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic router setup 4.3 Configure and verify the operation status of an Ethernet interface. 6.1 Configure and verify network device security features, such as: o Device password security o Enable secret vs. enable o Transport: Disable telnet SSH o VTYs o Physical security o Service password o Describe external authentication methods ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 35 TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 10.0 Router security configuration: o Restrict router access o Configure router passwords TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 7.0 Switch security: o Restrict access to a switch o Configure switch passwords Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between the enable and the enable secret passwords? Which one is more secure? How would you require a password when logging on through the console? You have configured the VTY lines on a router with a password but you did not use the login command. Will VTY login be allowed? Will a password be required? What must you do to disable VTY login? Why is the login command in line mode important? Video/Demo Time 3.6.1 Password Levels 4:25 3.6.2 Configuring Line Level Passwords 2:57 3.6.4 Configuring Enable Mode Passwords 3:29 Total 10:51 Lab/Activity Set Console and VTY Passwords Exploring Enable Passwords Modify System Passwords Number of Exam Questions 13 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 36 Section 4.1: Layer 2 Switching Overview Summary This section provides overview of Layer 2 switching. Concepts covered include: Bridges and switches build a forwarding database Conditions required for transparent bridges to forward packets Comparisons of methods to switch uses to forward packets: o Store-and-forward o Cut-through o Fragment-free Frame types that can be created by network hosts and transmitted by network switches: o Unicast o Broadcast o Multicast Collision domain Broadcast domain Connection devices and membership within collision or broadcast domains: o Hub o Bridge or switch o Router Guidelines for appropriate connectivity devices: o Router o Switch o Bridge Conditions to provide support for VoIP Internal processing methods that a switch may use when it is forwarding frames: o Cut-through o Fragment-free o Store-and-forward Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.2 Identify basic switching concepts and the operation of Cisco switches: o Collision Domains o Broadcast Domains o Types of switching o CAM Table ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 37 Lecture Focus Questions: What is the function of a CAM table? How does a switch learn information to populate the CAM table? When is a CAM table complete? When does a switch use flooding? What happens when a switch floods the frame? In what circumstance does a switch filter a frame? When do transparent bridges forward packets? How does the store and forward method of switching differ from the fragment-free method? What conditions can lead to a broadcast storm? Video/Demo Time 4.1.1 Switching Operations 7:09 4.1.3 Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast Frames 6:12 4.1.5 Collision and Broadcast Domains 5:18 4.1.7 Switching Methods 5:13 Total 23:52 Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 38 Section 4.2: Spanning Tree Overview Summary This section discusses the following concepts about Spanning Tree: Definition of a bridging loop The Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) standard Benefits of spanning tree algorithm Bridge roles: o Root bridge o Designated bridge o Backup bridge Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) port states: o Disabled o Blocking o Listening o Learning o Forwarding Ports on each switch are configured as the following port types: o Root port o Designated port o Blocking port The process used by devices participating in the spanning tree algorithm STP is slow to respond to topology changes Proprietary features to improve convergence: o Port Fast o Uplink Fast The process to identify the state of each port with the bridge ID and MAC addresses Spanning Tree example of a switched network with redundant paths Spanning Tree example showing how ports are labeled after spanning tree converges Students will learn how to: Given the MAC Address of a switch, configure it to be the root bridge. Configure a switch to be a primary root bridge. Configure a switch to be a secondary root bridge. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 39 Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.8 Identify enhanced switching technologies: o RSTP o PVSTP o EtherChannels 2.9 Configure and verify PVSTP operation: o Describe root bridge election o Spanning Tree mode TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 6.0 Spanning Tree configuration: o View STP configuration information Lecture Focus Questions: What is a bridging loop? How does the spanning tree protocol eliminate bridging loops? What advantages does the spanning tree protocol provide? How is the root bridge determined? How do designated bridges differ from backup bridges? What is the function of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs)? How do bridges recover from the loss of a bridge on the network? Which ports become root ports? Which port state builds the bridge database with MAC addresses? Video/Demo 4.2.1 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Time 5:08 Number of Exam Questions 11 questions Total Time About 25 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 40 Section 4.3: Switch Interface Configuration Summary This section provides information about switch interface configuration. Details include: Details of switch configuration modes: o Interface configuration o Config-vlan o VLAN configuration o Line configuration Switch configuration commands Students will learn how to: Configure a switch interface. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.3 Configure and verify initial switch configuration, including remote access management: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic switch setup 4.3 Configure and verify the operation status of a device interface, both serial and Ethernet. TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 2.0 Router interface configuration: o View the status of router interfaces o Configure Ethernet and serial router interfaces TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 2.0 Switch interface configuration: o Configure interface speed and duplex settings o View the status of switch interfaces 7.0 Switch security: o Disable switch interfaces ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 41 Lecture Focus Questions: How does the VLAN interface configuration mode differ from Ethernet, FastEthernet and GigabitEthernet interface configuration modes? What must you consider if you manually configure the speed or duplex setting? What happens when autonegotiation fails for the Ethernet interface on a Cisco device? What is the default setting for a switch? How does port numbering differ from switch numbering? Video/Demo Time 4.3.1 Switch Configuration Overview 4:12 4.3.2 Configuring Switch Interfaces 5:42 Total 9:54 Lab/Activity Configure Switch Ports Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 25 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 42 Section 4.4: Switch IP Configuration Summary In this section students will learn about configuring switch IP settings. Concepts covered in this section include: Key host configuration settings on a TCP/IP network: o IP address o Subnet mask o Default gateway o Host name o DNS server o MAC address Methods used to assign TCP/IP configuration settings: o Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) o Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) o Static (manual assignment) Considerations when configuring IP addresses on switches The role of the Domain Name System (DNS): o The differences when resolving a logical hostname to an IP address using a: Router or Switch Workstation Commands to configure DNS services on a router or switch Status lights used on the 2960 series switch: o SYST (System) o RPS (Redundant Power Supply) o Port: Stat (Port status) Duplex (Port duplex mode) Speed (Port speed) To customize the switch configuration, connect to the switch in one of the following ways: o Console connection o Telnet session o Web management software (connect through the LAN through a Web browser) Students will learn how to: Configure workstation TCP/IP settings. Configure an IP address and default gateway on a switch. Configure a router interface with an IP address. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 43 Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.3 Configure and verify initial switch configuration, including remote access management: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic switch setup 4.2 Configure and verify utilizing the CLI to set basic router configuration: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic router setup TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 2.0 Router interface configuration: o Configure TCP/IP settings on a router interface 10.0 Router security configuration: o Configure remote access to a router using SSH TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 2.0 Switch interface configuration: o View the status of switch interfaces 3.0 TCP/IP configuration: o Configure switch TCP/IP settings o Troubleshoot LAN communications 4.0 VLAN configuration: o Manage default VLAN configuration settings Lecture Focus Questions: What is the minimum amount of information a workstation needs in order to communicate on a single subnet? What additional configuration values are required for inter-network communications? What address range indicates an APIPA address assignment? What are the drawbacks to using manual IP address assignments? Why does a switch have an IP address? Which interface is assigned the IP address? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 44 Video/Demo Time 4.4.1 IP Address and Default Gateway Configuration 3:32 4.4.8 Verifying Switch Configuration and Operation 5:41 Total 9:13 Lab/Activity Configure Management VLAN Settings Configure Switch IP Settings Configure Device IP Settings Exploring Switch Port Status Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 45 Section 4.5: Virtual LANs (VLANs) Summary This section discusses configuring Virtual LANS (VLANs). Details include: Definition of a virtual LAN (VLAN) Example of a single-switch VLAN configuration By default, switches come configured with several default VLANs: o VLAN1 o VLAN 1002 o VLAN 1003 o VLAN 1004 o VLAN 1005 By default all ports are members of VLAN 1 The administrative benefits of creating VLANs with switches Creating VLANs with switches vs. using routers to create distinct networks Routers are still needed to: o Filter WAN traffic o Route traffic between separate networks o Route packets between VLANs VLAN configuration commands Students will learn how to: Create VLANs and assign switch ports to a VLAN. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.5 Describe how VLANs create logically separate networks and the need for routing between them: o Explain network segmentation and basic traffic management concepts 2.6 Configure and verify VLANs. 2.8 Identify enhanced switching technologies: o RSTP o PVSTP o EtherChannels 6.2 Configure and verify Switch Port Security features, such as: o Assign unused ports to an unused VLAN o Setting native VLAN to other than VLAN1 ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 46 TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 4.0 VLAN configuration: o View information about VLANs configured on a switch o Configure VLANs on a switch Lecture Focus Questions: What are two advantages to creating VLANs on your network? You have two VLANs configured on a single switch. How many broadcast domains are there? How many collision domains are there? What happens if two devices on the same switch are assigned to different VLANs? Video/Demo Time 4.5.1 VLAN Overview 5:24 4.5.3 Configuring VLANs 6:19 Total 11:43 Lab/Activity Create VLANs Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 47 Section 4.6: Trunking Summary This section discusses configuring trunking. The following details are covered: Definition of trunking Trunking and VLANs VLAN ID number frame tag Cisco devices support two trunking protocols: o Inter-Switch Link (ISL) o 802.1Q Default Switch Configuration for Catalyst 2960 switch Commands for configuring and monitoring trunking on a switch Students will learn how to: Configure a switch port as an access port or a trunk port. Configure dynamic trunking modes. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.7 Configure and verify trunking on Cisco switches: o DTP o Auto negotiation 2.8 Identify enhanced switching technologies: o RSTP o PVSTP o EtherChannels 6.2 Configure and verify Switch Port Security features, such as: o Sticky MAC o MAC address limitation o Static / dynamic o Violation modes: Err disable Shutdown Protect restrict o Shutdown unused ports o Err disable recovery o Assign unused ports to an unused VLAN o Setting native VLAN to other than VLAN1 TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 4.0 VLAN configuration: o Extend VLANs to multiple switches using trunking ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 48 Lecture Focus Questions: Why is trunking important to VLAN configuration? Which trunking protocols are supported on a Cisco 2960 switch? Which protocol is an industry standard? What protocol does a Cisco switch use to automatically detect trunk ports? By default, traffic from which VLANs are allowed on trunk ports? A trunk port is set to dynamic desirable. What configurations on other switches are allowed so the port enters a trunking state? What is the default configuration of most Cisco switches? Video/Demo Time 4.6.1 Access and Trunk Ports 5:58 4.6.4 Configuring Trunking 3:13 4.6.7 Configuring the Native VLAN 5:59 Total 15:10 Lab/Activity Configure Trunking Configure the Native VLAN Configure Allowed VLANs Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 49 Section 4.7: Switch Security Summary This section discusses configuring switch security. Concepts covered include: Switch port security Port security uses three MAC address types: o SecureConfigured o SecureDynamic o SecureSticky Port violation Action to take when a violation occurs Considerations when using port security Action to configure port security Commands to manage switch port security Commands to verify port security operations Description of entries from output from the show port-security interface command: o Port Security o Port Status o Violation Mode o Maximum MAC Addresses o Total MAC Addresses o Configured MAC Addresses o Sticky MAC Addresses o Security Violation Count Students will learn how to: Configure remote switch access. Configure VTY passwords. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.3 Configure and verify initial switch configuration, including remote access management: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic switch setup 4.2 Configure and verify utilizing the CLI to set basic router configuration: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic router setup 6.1 Configure and verify network device security features, such as: o Device password security o Enable secret vs. enable o Transport: Disable telnet SSH ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 50 o VTYs o Physical security o Service password o Describe external authentication methods 6.2 Configure and verify Switch Port Security features, such as: o Sticky MAC o MAC address limitation o Static/dynamic o Violation modes: Err disable Shutdown Protect restrict o Shutdown unused ports o Err disable recovery o Assign unused ports to an unused VLAN o Setting native VLAN to other than VLAN 1 TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 7.0 Switch security: o Enable switch port security Lecture Focus Questions: How do you configure a range of incoming concurrent connections for VTY? What two commands are used to activate Telnet connectivity? What command is used to verify the enabled version of SSH? What are the two requirements of the crypto key generate rsa command? Video/Demo Time 4.7.1 Port Security 4:21 4.7.3 Configuring Port Security 3:42 Total ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 8:03 51 Lab/Activity Configure Port Security 1 Configure Port Security 2 Configure Port Security 3 Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 52 Section 4.8: Remote Switch Access Summary This section discusses actions and commands to secure remote switch access. Students will learn how to: Configure a device to allow access by either Secure Shell and/or Telnet. Configure SSH with a username and password. Generate a key pair for encryption. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.3 Configure and verify initial switch configuration, including remote access management: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic switch setup 4.2 Configure and verify utilizing the CLI to set basic router configuration: o Cisco IOS commands to perform basic router setup 6.1 Configure and verify network device security features, such as: o Device password security o Enable secret vs. enable o Transport Disable telnet SSH o VTYs o Physical security o Service password o Describe external authentication methods TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 7.0 Switch security: o Restrict access to a switch o Configure remote access to a switch using SSH ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 53 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the prerequisites to generate a key pair? Video/Demo 4.8.1 Configuring Remote Access Time 3:27 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 10 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 54 Section 4.9: Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) Summary This section discusses the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) information used by Cisco devices to learn and share information about each other. Students will learn how to: Customize and view CDP information. Enable and disable CDP on an interface. Change CDP configuration. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.4 Verify router configuration and network connectivity: o Cisco IOS commands to review basic router information and network connectivity TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 2.0 Switch interface configuration: o View directly-connected network devices using CDP o Manage the CDP configuration Lecture Focus Questions: What is the default state of Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on supported interfaces? How do you view information about CDP configuration? How can you access information about all CDP neighbor devices? What command specifies how often CDP packets are exchanged? What is the requirement for CDP? What types of devices does it discover information about? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 55 Video/Demo 4.9.1 Configuring Basic Device Settings Time 6:41 Lab/Activity Exploring CDP Configure CKP Modify the CDP Configuration Find CDP Information Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 56 Section 5.1: IPv4 Overview Summary This section provides an overview of IPv4. Concepts covered include: Characteristics of IPv4 addresses: o 32-bit binary number represented as four octets (four 8-bit values) o Can be represented in two ways: Decimal Binary o Includes both the network and host address o Address class o The subnet mask identifies the network portion of the address Converting an IP address from binary to decimal Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 3.1 Describe the operation and necessity of using private and public IP addresses for IPv4 addressing. Lecture Focus Questions: What information does the IP address provide? What is the binary form of the IPv4 address 192.168.46.20? What is the role of a subnet mask? Video/Demo Time 5.1.1 IP Address 5:18 5.1.3 Binary Math 14:18 5.1.5 IP Address Format Total 6:32 26:08 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 57 Section 5.2: IPv4 Address Classes Summary This section examines IPv4 address classes. Concepts covered include: Default classes for IP addresses (including the address range, first octet range, default subnet mask, and default routing prefix): o Class A o Class B o Class C o Class D o Class E Considerations of special addresses: o Network o Host o Broadcast o Local host Determining the number of hosts for a given network address and subnet mask Private and public IP addresses: o Private o Public Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 3.1 Describe the operation and necessity of using private and public IP addresses for IPv4 addressing. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the purpose of the IP address default class? What is the default address class of the IP address 132.11.166.5? What three address ranges are used for private IP addresses? Using IPv4, how is the host portion of a network address expressed? What is the network address used by routers to specify the default route? What are commonly used broadcast address formats? What is a commonly used loopback address? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 58 Video/Demo Time 5.2.1 IP Address Classes 7:07 5.2.4 Public vs. Private IP Addresses 8:11 Total 15:18 Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 25 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 59 Section 5.3: Subnetting Summary This section examines subnetting. Concepts covered include: Converting binary to decimal numbers Calculate the number of hosts per subnet The role of subnetting Reasons to create subnets Subnetting to break a single class A network ID into multiple network IDs Subnetting a class B address Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 3.1 Describe the operation and necessity of using private and public IP addresses for IPv4 addressing. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the formula for determining the decimal value of a binary number? What is the purpose of a subnet? How do subnets enable network implementation? What does a subnet mask identify? Given IP addresses and subnet masks, how do you determine if two workstations are on the same subnet? Video/Demo 5.3.1 Subnetting Overview 5.3.2 Subnetting Math Total Time 8:22 12:55 21:17 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 60 Section 5.4: Variable Length Subnet Masking (VSLM) Summary This section discusses using Variable Length Subnet Masking (VSLM). Concepts covered include: The role of classful addressing Vary the number of bits in a variable length subnet mask (VLSM) using a: o Subnet o Supernet Definitions needed when working with subnets: o Classful addresses o Classless addresses o VLSM o Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR) o Route aggregation (also called route summarization) Solutions to common subnetting tasks Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 3.3 Identify the appropriate IPv4 addressing scheme using VLSM and summarization to satisfy addressing requirements in a LAN/WAN environment. Lecture Focus Questions: What is the relationship between the number of subnets on a network and the number of hosts on each subnet? How are classful addresses different from classless addresses? What information do CIDR routers use to identify networks? What is route aggregation? Video/Demo 5.4.1 VLSM Time 17:51 Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 61 Section 5.5: Subnet Planning and Design Summary This section discusses planning a subnet design. Details covered include: Process to identify and assign IP addresses throughout a network Create a table to quickly identify subnet masks, subnet addresses, and host addresses consisting of: o Bits in the mask o Magic number o Decimal mask value o Hosts per subnet o Number of subnets possible (subnet zero) Students will learn how to: Given a scenario, select and configure subnet addresses, masks, and host addresses. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 3.1 Describe the operation and necessity of using private and public IP addresses for IPv4 addressing. TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 3.0 IP routing implementation: o Calculate and configure subnet masks for network hosts Lecture Focus Questions: If you use 8 bits for host addressing, how many host can you have on each subnet? How do you determine the number of subnets you will need for the network? If you want to increase the number of host on each subnet, how do you change the subnet mask? What is this process called? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 62 Video/Demo Time 5.5.1 Subnet Design 8:05 5.5.2 Configuring Subnets 7:53 Total 15:58 Lab/Activity Configure Subnet Masks 1 Configure Subnet Masks 2 Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 63 Section 6.1: IP Routing Summary This section discusses understanding the routing table and the processes used to send packets between networks. Details covered include: The role of the routing table Viewing the routing table Important information shown in the command output: o Gateway of last resort o Route type o Network o Administrative distance and cost o Next hop router o Last update o Out interface The process to send a message from one host to another on a different network Additional considerations about communications Internal routing methods to process packets between networks: o Process Switching o Fast Switching o Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) Students will learn how to: View information in a routing table. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.1 Describe basic routing concepts: o CEF o Packet forwarding o Router lookup process 4.5 Configure and verify routing configuration for a static or default route given specific routing requirements. 4.6 Differentiate methods of routing and routing protocols: o Static vs. Dynamic o Link state vs. Distance Vector o Administrative distance o Split horizon o Metric o Next hop o IP routing table o Passive interfaces ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 64 Lecture Focus Questions: How does a router choose between two routes to the same destination network? What happens to a packet that does not match any of the routes in a routing table? What happens when a match is found? What command do you use to view the routing table? What does an asterisk ( * ) on a route indicate? Video/Demo 6.1.1 Routing Overview Time 8:19 Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 65 Section 6.2: Routing Implementations Summary This section provides the basics of static and dynamic routing. Details covered include: The role of static routing Drawbacks to static routing Common types of static routes: o Default route o Floating The role of dynamic routing Common dynamic routing protocols: o BGP o EIGRP o IS-IS o OSPF o RIP The main drawback to dynamic routing is the burden it places on network bandwidth and router resources Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.5 Configure and verify routing configuration for a static or default route given specific routing requirements. 4.6 Differentiate methods of routing and routing protocols: o Static vs. Dynamic o Link state vs. Distance Vector o Administrative distance o Split horizon o Metric o Next hop o IP routing table o Passive interfaces ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 66 Lecture Focus Questions: You want to configure an automatic backup for a dynamic route. Which type of static route would you configure? What are the sources of the routing information that is used to calculate administrative distance? What criteria does a router use for choosing between multiple routes? Under which circumstances would you choose static routing over dynamic routing? What is the main purpose of a floating static route? Video/Demo Time 6.2.1 Static vs. Dynamic Routing 9:56 6.2.4 Routing Metrics 4:06 6.2.5 Administrative Distance (AD) 4:14 Total 18:16 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 25 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 67 Section 6.3: Static Routing Summary This section discusses configuring static routing. Details include: Situations to configure static routes Details about a default route Commands to configure static routes Students will learn how to: Configure static routes. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.5 Configure and verify routing configuration for a static or default route given specific routing requirements. 4.6 Differentiate methods of routing and routing protocols: o Static vs. Dynamic o Link state vs. Distance Vector o Administrative distance o Split horizon o Metric o Next hop o IP routing table o Passive interfaces TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 3.0 IP routing implementation: o Configure static routes on a router Lecture Focus Questions: Under what circumstances would you use the ip default-gateway command to configure a default gateway? What is the most common method of configuring a default gateway? What are advantages to configuring a default route? In which situations would static routes be useful? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 68 Video/Demo 6.3.1 Configuring Static Routing Time 7:03 Lab/Activity Configure Static Routes Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 69 Section 6.4: Dynamic Routing Summary This section provides details about dynamic routing. Details covered include: The role of Autonomous Systems The role of routers within Autonomous Systems Routing protocol classifications: o Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) o Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) o Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Commonly used interior gateway protocols: o Routing Information Protocol version 2 (RIPv2) o Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) o Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Principles about the distance vector method Methods to minimize the effects of a routing loop: o Split horizon o Split horizon with poison reverse o Triggered updates o Hold-downs The advantages of the distance vector method Disadvantages of the distance vector method The role of the link-state method Advantages of using the link-state method over the distance vector method Problems with the link-state method Solutions to overcome the effects of inconsistent LSP information Comparison of the characteristics of the following routing protocols: o RIP o OSPF o EIGRP Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.5 Configure and verify routing configuration for a static or default route given specific routing requirements. 4.6 Differentiate methods of routing and routing protocols: o Static vs. Dynamic o Link state vs. Distance Vector o Administrative distance o Split horizon o Metric o Next hop o IP routing table ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 70 o Passive interfaces TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 3.0 IP routing implementation: o View the routing table on a router Lecture Focus Questions: What is the function of a BGP protocol? How does split horizon reduce network traffic? What effect does poison reverse have on convergence? Network traffic? When are Link-State Packets (LSPs) sent? How is the Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm used? What is a potential problem when using LSPs on a large network? How does the convergence time of the routing protocols RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP compare? Video/Demo Time 6.4.1 Internal vs. External Routing 4:53 6.4.3 Distance Vector vs. Link-State Routing Overview 3:49 6.4.4 Distance Vector Routing Operation 6:28 6.4.6 Link-State Routing Operation 7:18 Total 22:28 Lab/Activity Finding Routing Table Information Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 71 Section 6.5: Route Summarization Summary This section examines using route summarization to make routing updates more efficient. Details covered include: Summarization: o Reduces the size of the routing table o Speeds convergence o Retains all necessary routing information o Can happen in one of two ways: Automatic Manual Automatic summarization Identifying a summarized route for a group of subnets Commands to configure route summarization Students will learn how to: Given a scenario, select the appropriate subnet addresses and masks to prepare for summarization. Given a scenario, identify the summarized route. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 3.3 Identify the appropriate IPv4 addressing scheme using VLSM and summarization to satisfy addressing requirements in a LAN/WAN environment. TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 3.0 IP routing implementation: o Manage auto-summarization between networks Lecture Focus Questions: What benefits are provided by route summarization? If automatic route summarization is used, how does the router determine which routes to summarize? What route becomes the summarized network? Which routing protocol does not support automatic route summarization? Why do discontiguous networks pose a problem for route summarization? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 72 Video/Demo Time 6.5.1 Route Summarization Overview 4:05 6.5.2 Route Summarization Network Design 4:37 6.5.4 Configuring Route Summarization 4:15 Total 12:57 Lab/Activity Explore Auto-Summarization Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 73 Section 6.6: Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Overview Summary This section provides an overview of the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. Concepts covered include: The role of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) To help minimize traffic caused by routing updates, OSPF defines the following router roles: o Designated Router (DR) o Backup Designated Router (BDR) o DROTHER Considerations about DR and BDR Adjacent neighbor routers are required for OSPF routers to share route information Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.7 Configure and verify OSPF: o Benefit of single area o Neighbor adjacencies o OSPF states o Discuss multi-area OSPF o Configure OSPF v2 o Configure OSPF v3 o Router ID o Passive interface o LSA types Lecture Focus Questions: How do the DR and the BDR reduce network traffic? When is the DR not used? How is the DR elected? How can you ensure that a specific device becomes the DR? What conditions must be met before two routers running OSPF will share information? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 74 Video/Demo Time 6.6.1 OSPF Concepts and Terminology 8:19 6.6.2 OSPF Areas and Border 5:30 6.6.3 OSPF Passive Interfaces and Default Routes 6:15 Total 20:04 Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 75 Section 6.7: OSPF Configuration Summary This section discusses commands to configure OSPF and identify the networks that will participate in OSPF routing. Students will learn how to: Configure OSPF routing. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.7 Configure and verify OSPF: o Benefit of single area o Neighbor adjacencies o OSPF states o Discuss multi-area OSPF o Configure OSPF v2 o Configure OSPF v3 o Router ID o Passive interface o LSA types TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 4.0 OSPF routing configuration: o Enable OSPF routing o Configure and manage OSPF routing Lecture Focus Questions: What is the significance of the router ID? What is Area 0 in an OSPF implementation? How many areas can a single subnet be in? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 76 Video/Demo Time 6.7.1 Configuring OSPF 5:20 6.7.2 Configuring Passive Interfaces and Default Routes 6:26 6.7.3 Verifying OSPF Operation 4:57 Total 16:43 Lab/Activity Enable OSPF Exploring OSPF Configure OSPF Routing Number of Exam Questions 11 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 77 Section 6.8: InterVLAN Routing Overview Summary This section provides an overview of using interVLAN routing to enable communications between workstations located in different VLANs. Details include: Devices capable of providing interVLAN routing: o Router o Multilayer switch Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.5 Describe how VLANs create logically separate networks and the need for routing between them: o Explain network segmentation and basic traffic management concepts. Lecture Focus Questions: To provide interVLAN routing, a device must have which layer of functionality? What are two implementations of interVLAN routing? Why doesn't trunking enable interVLAN communication? What method is used to allow a single router to perform interVLAN routing using a single physical interface? What function includes the concept of route once, switch many? What are the requirements for interVLAN routing? What is upstream routing? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 78 Video/Demo Time 6.8.1 Routing Between VLANs 7:21 6.8.2 Router-on-a-Stick InterVLAN Routing 8:43 6.8.3 Layer 3 Switch InterVLAN Routing 7:17 Total 23:21 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 79 Section 6.9: InterVLAN Routing Configuration Summary This section discusses commands used to configure and verify interVLAN routing. Students will learn how to: Configure a router on a stick interVLAN routing. Configure Layer 3 switch interVLAN routing. Configure subinterfaces and ISL encapsulation to enable interVLAN routing on a router. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.8 Configure and verify interVLAN routing (router on a stick): o Sub interfaces o Upstream routing o Encapsulation 4.9 Configure SVI interfaces. 6.2 Configure and verify Switch Port Security features, such as: o Assign unused ports to an unused VLAN o Setting native VLAN to other than VLAN 1 TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 3.0 IP routing implementation: o Configure router-on-a-stick interVLAN routing TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 5.0 InterVLAN routing: o Configure interVLAN routing Lecture Focus Questions: What is a subinterface? What is its role in an interVLAN configuration? How do you configure an interface as a trunk? What commands are used? How do you enable management of a switch from a remote network? What information does the show running-config command display? What command is used to verify that an adjacency exists for a connected device? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 80 Video/Demo Time 6.9.1 Configuring Router-on-a-Stick InterVLAN Routing 4:06 6.9.2 Configuring Layer 3 Switch InterVLAN Routing 4:11 Total 8:17 Lab/Activity Configure InterVLAN Routing 1 Configure InterVLAN Routing 2 Configure InterVLAN Routing 3 Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 81 Section 7.1: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Summary In this section students will learn about the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Details include: Protocols that can perform address resolution: o Address Resolution Protocol o Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) o Bootstrap Protocol (BootP) o Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) DHCP configuration parameters include: o Address pool o Lease o DHCP option o Binding o Interface The process to obtain an IP address Enabling DHCP across subnets Prerequisites to configuring a Cisco router as a DHCP server Commands to configure the DHCP service on a Cisco router Students will learn how to: Use the SDM interface to configure the DHCP service on a router. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 5.1 Configure and verify DHCP (IOS router): o Configuring router interfaces to use DHCP o DHCP options o Excluded addresses o Lease time TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 9.0 DHCP server configuration: o Configure the DHCP service on a router o Configure DHCP bindings o Configure a DHCP relay agent ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 82 Lecture Focus Questions: What is the difference between the ARP and RARP protocols? What is the difference between the BootP and DHCP protocols? What type of information is delivered by DHCP options? How can you make sure a specific host gets the same IP address from the DHCP server each time it boots? How does the router determine which interfaces will respond to DHCP requests? How can you enable DHCP messages to work across subnets? Video/Demo 7.1.1 DHCP Overview 7.1.4 Configuring DHCP Total Time 13:27 4:07 17:34 Lab/Activity Configure a DHCP Server Configure DHCP Manual Bindings Configure a DHCP Relay Agent Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 55 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 83 Section 7.2: Access Control Lists (ACLs) Summary This section examines Access Control Lists (ACLs). Details in this section include: Characteristics of an access list An access list requires at least one permit statement General types of access lists: o Standard ACL o Extended ACL An access list can be designed to provide security to both the router and any connected networks Considerations when applying an access list to an interface Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 5.2 Describe the types, features, and applications of ACLs: o Standard: Sequence numbers Editing o Extended o Named o Numbered o Log option Lecture Focus Questions: You want to create an access list that restricts traffic from host 12.0.15.166. What type of access list can you use? You want to create an access list that restricts ICMP traffic. What type of access list would you use? How many access lists can be applied to a single interface? When can you have two access lists for the same direction applied to an interface? Where in the access list should you place the most restrictive statements? How does standard ACL differ from an extended ACL? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 84 Video/Demo Time 7.2.1 ACL Overview 7:05 7.2.2 Standard ACLs 7:17 7.2.3 Extended ACLs 6:30 7.2.4 Named ACLs 2:56 Total 23:48 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 85 Section 7.3: ACL Commands Summary This section presents the ACL command formats. Details include: The role of the wildcard mask How to calculate the wildcard mask Examine the subnet address, subnet mask, and wildcard mask in binary values Students will learn how to: Create a wildcard mask. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 5.3 Configure and verify ACLs in a network environment: o Named o Numbered o Log option TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 6.0 Access Control List configuration: o Use wildcard masks in ACLs Lecture Focus Questions: What is the purpose of a wildcard mask? How is a wildcard mask related to the subnet mask? What does a 0 in a wildcard mask indicate? How are bits identified with a 1 handled? How do you calculate the wildcard mask? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 86 Video/Demo Time 7.3.1 ACL Command Format 7:31 7.3.2 Inverse Wildcard Masking 4:34 Total 12:05 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 87 Section 7.4: ACL Configuration Summary This section covers configuring ACLs. Details include: Steps to configure access lists: o Create the list and list entries o Apply the list to a specific interface or line Considerations when constructing access list statements Examples of configuring access lists Commands to use for viewing specific access list information on the router Students will learn how to: Based on filtering requirements, construct access list statements. Create an access list and apply it to an interface. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 5.3 Configure and verify ACLs in a network environment: o Named o Numbered o Log option 6.3 Configure and verify ACLs to filter network traffic. 6.4 Configure and verify ACLs to limit telnet and SSH access to the router. 7.4 Troubleshoot and resolve ACL issues: o Statistics o Permitted networks o Direction o Interface TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 6.0 Access Control List configuration: o Implement standard, extended, and named ACLs o Use ACLs to manage network traffic: Permit allowed traffic Block disallowed traffic ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 88 Lecture Focus Questions: When viewing an access list statement, how can you determine if the list is a standard or extended list? After creating an ACL list and the list entries, what is the next step in configuring an ACL? How are access list statements associated with an access list? What happens when you delete an access list statement? Video/Demo Time 7.4.1 Configuring Basic ACLs 6:04 7.4.2 Configuring Standard ACLs 9:20 7.4.3 Filtering Inbound Remote Access 2:36 Total 18:00 Lab/Activity Restrict Telnet and SSH Access Permit Traffic Block Source Hosts Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 89 Section 7.5: Extended ACL Configuration Summary This section covers methods to back up and restore a CA. Details include: Configuring standard and extended access lists Standard access lists can be used to control traffic based only on source IP addresses Extended access lists can be used to control traffic based on: o Source IP address and port number o Destination IP address and port number o Protocol designations, such as IP, TCP, UDP, and ICMP Considerations when constructing access list statements Commands to create and implement extended ACLs Students will learn how to: Control traffic using extended ACLs. Create a rule to deny specific traffic. Create a rule to permit all other IP traffic. Create rules to permit traffic in a single direction. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 6.3 Configure and verify ACLs to filter network traffic. TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 6.0 Access Control List configuration: o Implement standard, extended, and named ACLs o Use ACLs to manage network traffic: Permit allowed traffic Block disallowed traffic Lecture Focus Questions: What command is used to add an access list to an interface? How many access lists can be applied to an interface per protocol per direction? What does a mask value of 0 mean? What does a value of 255 mean? How is the wildcard mask value calculated? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 90 Video/Demo 7.5.1 Configuring Extended ACLs Time 5:21 Lab/Activity Configure Allowed Networks Create Access List Statements Block Invalid Addresses Allow Only Specific Services Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 91 Section 7.6: Network Address Translation (NAT) Overview Summary This section provides an overview of Network Address Translation (NAT). Concepts covered include: The role of NAT NAT terminology: o Inside o Outside o Inside local address o Inside global address o Outside global address o Outside local address Methods when configuring NAT: o Static o Overloaded with PAT o Dynamic Configuring NAT on a Cisco router may be done through the: o Command line interface (CLI) o Security Device Manager Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 5.4 Identify the basic operation of NAT: o Purpose o Pool o Static o 1 to 1 o Overloading o Source addressing o One-way NAT ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 92 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the benefits of using NAT? What is the difference between an inside global address and an outside global address? What is overloading, and why is it important in a NAT configuration? How is an access list used in NAT configuration? Video/Demo 7.6.1 NAT Overview Time 4:41 Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 15 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 93 Section 7.7: NAT Configuration Summary This section provides details about configuring NAT. Concepts covered include: Options available when configuring NAT: o Static o Overloaded with PAT o Dynamic Configuration steps for: o Static NAT Configure static mappings (mapping inside local addresses to outside local addresses) Identify inside and outside interfaces o Overloaded with PAT Identify allowed translated inside local addresses Associate the allowed list with the outside interface and identify the translation type as overloaded Identify inside and outside interfaces o Dynamic NAT Define an inside global address pool Identify allowed translated inside local addresses Associate the allowed list with the pool Identify inside and outside interfaces Commands to monitor NAT Students will learn how to: Configure NAT inside and outside interfaces. Configure static NAT and NAT pools. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 5.5 Configure and verify NAT for given network requirements. TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 8.0 NAT configuration: o Configure static NAT on a router o Configure dynamic NAT on a router o Configure overloaded PAT on a router ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 94 Lecture Focus Questions: How do you link a NAT address pool to an access list and an interface? What parameter must you use in your NAT configuration if you have more private hosts than public IP addresses? Which NAT configuration method associates a specific outside IP address with an inside host? Video/Demo Time 7.7.1 Dynamic NAT 9:19 7.7.2 Configuring Dynamic NAT 4:05 7.7.4 Static NAT 3:46 7.7.5 Configuring Static NAT 2:25 7.7.7 Configuring Port Address Translation (PAT) 2:58 Total 22:33 Lab/Activity Configure Dynamic NAT Configure Static NAT Configure Overloaded PAT Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 95 Section 7.8: Network Time Protocol (NTP) Summary This section discusses using the Network Time Protocol (NTP) to timesynchronize a network of machines. Concepts covered include: Facts about NTP: o NTP Service o NTP Host Roles o NTP Terminology o NTP Stratum Commands to implement NTP Students will learn how to: Implement NTP. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 5.6 Configure and verify NTP as a client. Lecture Focus Questions: How does NTP handle time drift? What is the function of an NTP time client? How does slam differ from slew in correcting time? How is the concept of stratum implemented by NTP? Video/Demo 7.8.1 NTP Overview Time 3:03 Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 15 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 96 Section 8.1: IPv6 Addressing Overview Summary This section provides an overview of IPv6 Addressing. IPv6 features: o Geographic assignment of addresses o Efficient route summarization o No need for Network Address Translation (NAT) or Port Address Translation (PAT) o Native Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) o Header improvements o Built-in Quality of Service (QoS) o Flow label Features of an IPv6 address: o 32 hexadecimal numbers into 8 quartets o Quartets are separated by colons o Quartets are represented by 0 and FFFF o Leading zeros can be omitted o The 128-bit address contains two parts: Prefix is the first 64 bits Interface ID is the last 64 bits Example of how the IPv6 prefix could be divided: o Regional Internet Registry (RIR) o Internet Service Provider (ISP) o Site o Subnet ID IPv6 identifies the following types of addresses: o Unicast: Link-local Unique local Global unicast o Multicast o Anycast o Loopback o Unspecified Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 3.1 Describe the operation and necessity of using private and public IP addresses for IPv4 addressing. 3.2 Identify the appropriate IPv6 addressing scheme to satisfy addressing requirements in a LAN/WAN environment. 3.5 Describe IPv6 addresses: o Global unicast ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 97 o o o o o Multicast Link local Unique local Eui 64 Autoconfiguration Lecture Focus Questions: Why was it necessary to implement IPv6? How many bits of data does each quartet represent in an IPv6 address? How do you properly abbreviate an IPv6 address? What two 64-bit parts are contained in an IPv6 address, and what does each part represent? What is the difference between an anycast address and a unicast address? What is the function of the local loopback address? How can you easily identify IPv6 multicast addresses? What does the special address FF02::2 mean? When is address ::1 used? Video/Demo Time 8.1.1 IPv6 Overview 3:16 8.1.3 IPv6 Addressing 8:53 8.1.5 IPv6 Address Types 3:54 Total 16:03 Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 98 Section 8.2: IPv6 Host Configuration Summary In this section students will learn about configuring the IPv6 host. Concepts covered include: It is a good practice to ensure that all IPv6 addresses are globally unique Methods for deploying IPv6: o Dual stack o Tunneling: Manually configured tunnel 6-to-4 tunneling Intra-site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) Teredo tunneling o Network Address Translation-Protocol Translation (NAT-PT) Methods to configure an IPv6 address: o Static full assignment o Static partial assignment o Stateless autoconfiguration o DHCPv6 The process a host uses at startup to configure the IPv6 address for each interface Commands used for configuring IPv6 addresses Students will learn how to: Implement IPv6 on a network by configuring IPv6 addresses on the interfaces. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 3.4 Describe the technological requirements for running IPv6 in conjunction with IPv4, such as dual stack. 3.5 Describe IPv6 addresses: o Global unicast o Multicast o Link local o Unique local o Eui 64 o Autoconfiguration ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 99 Lecture Focus Questions: How is the EUI-64 format applied? When would you use dual stack? Which tunneling methods use NAT? How does 6-to-4 tunneling differ from the Intra-site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) method of tunneling? Which is easier to implement? How does Teredo tunneling enable host-to-host communication between IPv6 devices through an IPv4 network? How are IPv6 addresses created using static partial assignment? What is the next step to configure an IPv6 address if the host receives a neighbor advertisement (NA) message? Video/Demo Time 8.2.1 EUI-64 and Auto-Configuration 3:36 8.2.3 Configuring IPv6 2:43 Total 6:19 Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 25 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 100 Section 8.3: IPv6 Routing Summary This section provides information about configuring IPv6 routing. Concepts covered include: Changes made to OSPFv2 to accommodate IPv6 with OSPFv3: o Default Router ID o Multicast address o LSA Types o Commands o Graceful restart Functions of OSPF for IPv6: o Shortest Path First (SPF) Throttling o Load balancing o IPsec authentication o Secure socket states Considerations about OSPF for IPv6 Commands for configuring IPv6 OSPF routing Students will learn how to: Configure IPv6 OSPF unicast routing between subnets. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.7 Configure and verify OSPF: o Benefit of single area o Neighbor adjacencies o OSPF states o Discuss multi-area OSPF o Configure OSPF v2 o Configure OSPF v3 o Router ID o Passive interface o LSA types ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 101 Lecture Focus Questions: Which major OSPFv2 changes accommodate IPv6 in OSPFv3? What is the main difference between the commands used with OSPF in IPv4 and those used in IPv6? How does OSPFv3 handle IPv6 authentication? How many IPv6 address prefixes can be configured on a single interface? How is the SPF calculation interval determined? How do periods of network topology instability affect SPF? How does interface enabling differ between OSPF for IPv6 and OSPFv2? When configuring IPv6 OSPF routing, you discover an IPv4 address is not configured on any interface. What action must you take? Video/Demo Time 8.3.1 IPv6 Routing 3:31 8.3.3 Configuring OSPFv3 Routing 6:18 Total 9:49 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 102 Section 9.1: Network Communications Troubleshooting Summary This section provides details about troubleshooting network communications. Concepts covered include: Types of ICMP messages: o Echo o Destination unreachable o Time exceeded o Redirect o Source quench o Router discovery Utilities to test network connectivity between devices: o Ping o Traceroute o Telnet Considerations when using ping, traceroute, and telnet on Cisco devices Utilities to verify the configuration of the workstation: o Ipconfig o Arp o Nslookup Considerations when troubleshooting IP Common problems, symptoms, and solutions to correct communication problems Students will learn how to: Use ping and traceroute to verify connectivity between devices. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.4 Verify network status and switch operation using basic utilities, such as ping, telnet, and SSH. 4.4 Verify router configuration and network connectivity: o Cisco IOS commands to review basic router information and network connectivity 7.1 Troubleshoot and correct common problems associated with IP addressing and host configurations. 7.6 Identify and correct common network problems. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 103 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the differences and similarities between ping and traceroute? You can ping a device but can't open a Telnet session with that device. What is the problem? What are possible uses of extended mode for ping and traceroute? In which situations can you receive a traceroute time exceeded message? What information does the ipconfig command provide? What action should you take if you suspect a routing failure is the result of cache that hasn't been updated? What should you check for if all hosts on a local network can communicate with each other, but not with hosts outside the local network? Video/Demo Time 9.1.1 Network Communications Troubleshooting 8:52 9.1.2 Troubleshooting Network Communications 7:37 Total 16:29 Lab/Activity Exploring TCP/IP Communications Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 104 Section 9.2: Switch Troubleshooting Summary This section provides information about how to troubleshoot switches. Concepts covered include: Commands to view the interface status Possible conditions indicated by the interface status: o Administratively down o Down o Up o Up Commands to display VLAN configuration information for verification and troubleshooting The fields and descriptions for output generated from the show interfaces fa 0/1 switchport command: o Name o Switchport o Administrative Mode, Operational Mode o Administrative Trunking Encapsulation, Operational Trunking Encapsulation, Negotiation of Trunking o Access Mode VLAN o Trunking Native Mode VLAN o Trunking VLANs Enabled o Pruning VLANs Enabled The values and description for output generated from the show interfaces fa 0/1 trunk command: o Mode o Encapsulation o Status o Native VLAN o VLANs allowed on trunk o VLANs allowed and active in management domain o VLANs in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Students will learn how to: Troubleshoot problems with switches. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 105 Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 7.2 Troubleshoot and resolve VLAN problems: o Identify that VLANs are configured o Verify port membership correct o Correct IP address configured 7.3 Troubleshoot and resolve trunking problems on Cisco switches: o Correct trunk states o Correct encapsulation configured o Correct VLANs allowed 7.5 Troubleshoot and resolve Layer 1 problems: o Framing o CRC o Runts o Giants o Dropped packets o Late collision o Input/Output errors 7.12 Troubleshoot and resolve WAN implementation issues: o PPP TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 4.0 VLAN configuration: o View information about VLANs configured on a switch o Troubleshoot VLAN issues o Troubleshoot trunking issues Lecture Focus Questions: What should you look for if the line status is up and the protocol status is down? How can you view a single line of information about each IP interface? What types of problems are the result of collisions? What are late collisions? What is a probable cause? What steps do you take to verify connectivity at the Physical layer? How do you verify that trunking is enabled correctly on a switch? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 106 Video/Demo 9.2.1 Troubleshooting Switches Time 8:17 Lab/Activity Find VLAN Information Troubleshooting VLANs 1 Troubleshooting VLANs 2 Number of Exam Questions 11 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 107 Section 9.3: ACL Troubleshooting Summary This section discusses guidelines to troubleshooting and resolving issues with ACLs, and commands to view ACL information. Students will learn how to: Troubleshoot and resolve issues with ACLs. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 7.4 Troubleshoot and resolve ACL issues: o Statistics o Permitted networks o Direction o Interface Lecture Focus Questions: Why is it a good idea to use a text editor to build and evaluate ACLs before implementing them? What type of information does the show log command display? How can you view log messages that identify which line in an ACL is being matched? What happens to a packet that does not match any line in an ACL? Why? Video/Demo 9.3.1 Troubleshooting ACLs Time 5:57 Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 108 Section 10.1: ICND2 Introduction Summary This section introduces the students to the ICND2 materials. The remaining sections of this course contain information relating to the Cisco 200-101 (ICND2) exam. While students can use the remaining sections of this TestOut product to prepare them for the 200-101 (ICND2) exam, the product is geared towards passing the 200-120 CCNA exam that covers both ICND1 and ICND2. Video/Demo 10.1.1 ICND2 Introduction Time 0:59 Total Time About 1 minute ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 109 Section 11.1: Router Configuration Files Summary This section provides details of managing Cisco IOS software. Details include: Different types of router memory: o Random-access memory (RAM) o Flash o Read-only memory (ROM) o Non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM) The four-step boot process: o The POST is performed o The router runs the bootstrap program o The bootstrap program launches the OS o The router loads the startup configuration files from NVRAM Steps to upgrade a router’s IOS Boot system commands Students will learn how to: Recover a router password. Change a router's boot configuration. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.10 Manage Cisco IOS Files: o Boot preferences o Cisco IOS image(s) o Licensing Show license Change license Cisco Exam 200-101 (ICND2) Objectives: 2.1 Describe the boot process of Cisco IOS routers. TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 1.0 Router setup and configuration: o Manage router configuration files o Manage router IOS files ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 110 TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 1.0 Switch setup and configuration: o Manage switch configuration files o Manage switch IOS files Lecture Focus Questions: If the router can't find an IOS image in flash, where will it look next? What happens if the router can't find a configuration file at startup? What is the role of the configuration register? What configuration register value tells the router to skip the startup-config file? Video/Demo Time 11.1.1 IOS Boot Process 10:54 11.1.2 Booting a Router 5:23 11.1.3 Router Configuration Files 7:43 11.1.4 Modifying Configuration Files 4:23 11.1.5 Router Password Recovery 6:18 11.1.6 Recovering a Forgotten Password 4:51 Total 39:32 Number of Exam Questions 7 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 111 Section 11.2: IOS Licensing Summary This section discusses managing IOS licensing. Concepts covered include: In the past, Cisco created different IOS images to address each possible combination of parameters Recently, Cisco has switched to a universal image model Important features sets (called technology packages) that are provided in IOS images for Cisco devices: o IP Base (ipbaedk9) o Data (datak9) o Unified Communications (uck9) o Security (securityk9) Product Authorization Key (PAK) Unique Device Identifier (UDI) is composed of two parts: o Product ID (PID) o Serial number (SN) Steps to obtain a license key for a feature Making the license key accessible Commands to install license on a Cisco device Commands to view installed licenses on a Cisco device Downloading IOS images Students will learn how to: View the current IOS license status. Add a package license. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.10 Manage Cisco IOS Files: o Boot preferences o Cisco IOS image(s) o Licensing: Show license Change license ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 112 TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 1.0 Router setup and configuration: o Manage router IOS files TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: Switch setup and configuration: o Manage switch IOS files Lecture Focus Questions: How does a version differ from a release? What is a feature set? In what two ways can the licensing keys for the Cisco IOS be activated? What is the UDI? What command do you use to display it? Video/Demo Time 11.2.1 IOS Universal Image Model 4:53 11.2.2 Package Licensing and Activation 5:18 11.2.3 Viewing the Current License Status 3:18 11.2.4 Adding a Package License 4:08 Total 17:37 Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 113 Section 12.1: Spanning Tree Overview Summary This section discusses the basic concepts of Spanning Tree Protocol. Details covered include: STP concepts: o Switching forward logic o Forwarding state o Bridge ID o Bridge and root port election Using EtherChannel to combine multiple switch ports into a single, logical link between two stitches Protocols used by Cisco Catalyst switches for EtherChannel configuration: o Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP) o Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) Commands to configure EtherChannel Guidelines to troubleshoot an EtherChannel configuration Students will learn how to: View the MAC table. Change interface states. Configure EtherChannels. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.8 Identify enhanced switching technologies: o RSTP o PVSTP o EtherChannels 7.14 Troubleshoot EtherChannel problems. TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 8.0 EtherChannel configuration: o Configure EtherChannel using the following: PAGP LACP ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 114 Lecture Focus Questions: A switch port is identified as a backup port. What state is it in? What advantages are added to spanning tree with the edge port type definition? How does this improve performance? How does PVST+ differ from Rapid PVST+? What advantages does the EtherChannel feature provide? Why must EtherChannel be used to create multiple links between switches that can be used at the same time? How does EtherChannel interact with spanning tree? What function does BPDU guard provide? Video/Demo 12.1.1 Key Switch Functions 12.1.2 Spanning Tree Protocol Concepts 12.1.3 Viewing a Switch’s MAC Table 12.1.4 STP Topology Time 6:02 19:59 6:32 13:00 12.1.5 Advanced STP Features 8:17 12.1.7 Configuring EtherChannels 8:18 Total 62:08 Lab/Activity Configure EtherChannel with PAGP Configure EtherChannel with LACP Number of Exam Questions 10 questions Total Time About 90 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 115 Section 12.2: Spanning Tree Protocol Configuration Summary This section discusses configuring and managing spanning tree protocol. Details covered include: By default, spanning tree is enabled on all Cisco switches Many LANs will benefit from configuration changes to spanning tree Spanning tree configuration tasks Commands to configure spanning tree Tasks to troubleshoot STP The action of switches during STP convergence Students will learn how to: Configure STP. Select a Root Bridge. Troubleshoot SPT. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.8 Identify enhanced switching technologies: o RSTP o PVSTP o EtherChannels 2.9 Configure and verify PVSTP operation: o Describe root bridge election o Spanning Tree mode 7.6 Troubleshoot and resolve Spanning Tree operation issues: o Root switch o Priority o Mode is correct o Port states TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 6.0 Spanning Tree configuration: o View STP configuration information o Manually configure a switch as a root bridge o Configure Rapid PVST+ o Troubleshoot STP issues ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 116 Lecture Focus Questions: Why will a tie breaker never be necessary for the root switch selection? When would you modify an STP mode? How does PVST+ differ from Rapid PVST+? How do ports work in a multiple VLAN environment? How are root bridges designated in a multiple VLAN environment? What happens during STP convergence? Video/Demo 12.2.1 STP Design and implementation Time 10:16 12.2.2 Configuring STP 5:38 12.2.3 Selecting a Root Bridge 5:18 12.2.8 STP Troubleshooting 6:30 Total 27:42 Lab/Activity Configure the Root Bridge Configure the Primary and Secondary Root Bridge Configure Rapid PVST+ Find STP Info 1 Find STP Info 2 Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Total Time About 65 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 117 Section 12.3: Switch Troubleshooting Summary This section discusses guidelines for troubleshooting LAN switching. Details include: Systematic troubleshooting approach: o Analyze and predict the normal operations. o Isolate the problem. o Determine the root cause. Problems associated with LAN switching Troubleshooting planes used to identify processing: o Data plane o Control plane o Management plane A reliable troubleshooting process: o Tasks to be performed in the data plane o Tasks to be performed in the control plane o Begin problem isolation by examining the Layer 3 data plane o Identify the first major routing step that fails o Analyze the system until the root cause is found Students will learn how to: Use CLI commands to troubleshoot LAN switching problems. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 7.6 Identify and correct common network problems. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 118 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the most common issues that cause STP problems? What are characteristics of the data plane? What are characteristics of the control plane? What should you do to isolate VLAN and trunking problems? Video/Demo Time 12.3.1 Troubleshooting Models 7:53 12.3.2 Layered Troubleshooting Approach 5:13 12.3.3 Troubleshooting Command List 6:39 Total 19:45 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 25 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 119 Section 13.1: IPv4 Routing Troubleshooting Summary This section discusses the following utilities used for troubleshooting IPv4 routing: Ping Extended ping Traceroute Extended traceroute Students will learn how to: Use the ping and traceroute commands to troubleshoot IPv4 routing problems. View the routing table. Use show ip protocols commands to verify routing protocol configuration. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 2.4 Verify network status and switch operation using basic utilities, such as ping, Telnet, and SSH. 7.6 Identify and correct common network problems. 7.8 Troubleshoot and resolve routing issues: o Routing is enabled o Routing table is correct o Correct path selection Lecture Focus Questions: What does a successful ping verify? How does the ping command differ from the traceroute command? What are common problems that occur between hosts and routers? What causes a port to be in an err-disabled state? What are overlapping routes? What can cause an overlapping route? What should you do to troubleshoot routing problems caused by ACLs? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 120 Video/Demo 13.1.1 IPv4 Routing Overview 13.1.2 Viewing the Routing Table 13.1.3 Routing Troubleshooting Tools Time 10:20 4:09 17:32 13.1.4 Using Ping and Traceroute 4:48 13.1.5 Host Configuration Issues 11:07 13.1.6 Router Configuration Issues 11:09 13.1.7 Using Show Commands on the Router Total 8:46 67:51 Number of Exam Questions 13 questions Total Time About 85 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 121 Section 13.2: InterVLAN Routing Troubleshooting Summary This section provides information about how to troubleshoot interVLAN routing. Details covered include: Elements to check to verify the configuration when problems arise when implementing interVLAN routing in a router-on-a-stick or SVI configuration check the following: o Connectivity at the Physical layer o IP settings on network hosts and routers o Appropriate subinterface has been created and configured on the router for each VLAN o Native option is used with the encapsulation command on the router o Trunking is enabled correctly on the switch Commands to display interVLAN routing configuration settings for verification and troubleshooting: o Show vlan brief o Show ip route o Show run o Show interfaces trunk Students will learn how to: Use the ping command to verify access to interVLAN components. Use the show vlan brief command to display VLANs in the VLAN database. Use the show run command to view interVLAN routing information on a Layer 3 switch. Use the show interfaces trunk command to display trunk information. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 7.11 Troubleshoot and resolve interVLAN routing problems: o Connectivity o Encapsulation o Subnet o Native VLAN o Port mode trunk status ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 122 TestOut Switching Pro Objectives: 5.0 InterVLAN routing: o Troubleshoot interVLAN routing issues Lecture Focus Questions: Which command would you use to display the port types? What information does the show interface command provide? What is a trunk port? How do you create a trunk? Video/Demo 13.2.1 Troubleshooting InterVLAN Routing Time 9:04 Lab/Activity Troubleshoot InterVLAN Routing 1 Troubleshoot InterVLAN Routing 2 Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 123 Section 13.3: Default Gateway Redundancy Summary This section provides information about creating redundant first-hop routers. Details covered include: The role of the First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP) FHRP identifies a family of protocols: o Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) o Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) o Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) HSRP is a Cisco proprietary redundancy protocol for establishing a faulttolerant default gateway: o An HSRP group consists of the following entities or roles: Active router Standby router Virtual router Additional HSRP member routers o HSRP router states: Initial Learn Listen Speak Standby Active o Routers configured with HSRP exchange three types of multicast messages: Hello Coup Resign o Elements that effect which router is the active router o HSRP details o Commands used to configure and verify HSRP Details of VRRP: o Differences between VRRP and HSRP o VRRP uses the following timers: Advertisement interval Master-down interval o Commands used to configure and verify VRRP Details of GLBP: o Modes for load balancing that GLBP supports: Round-robin Weighted Host-dependent o Commands to configure and verify GLBP ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 124 Students will learn how to: Implement HSRP on a network. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 5.7 Recognize High availability (FHRP): o VRRP o HSRP o GLBP TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 11.0 High availability configuration: o Configure GLBP o Configure VRRP o Configure HSRP Lecture Focus Questions: What function does the First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP) provide? How does VRRP differ from HSRP? What is a virtual router? What tasks do additional HSRP member routers perform? How does the speak router state differ from the active router state? What type of router sends a coup message? Video/Demo 13.3.1 Default Gateway Router Redundancy Time 13:04 13.3.3 Configuring HSRP 6:57 13.3.6 Configuring VRRP 4:53 13.3.9 Configuring GLBP 6:07 Total ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 31:01 125 Lab/Activity Configure HSRP Configure VRRP Configure GLBP Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 75 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 126 Section 14.1: WAN Types Summary This section discusses different types of WANs that are typically implemented. Details include: Types of WANs: o Private o Public Descriptions and details about carriers: o Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) o Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) o Cable o Cellular o Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) o Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 8.1 Identify different WAN Technologies: o Metro Ethernet o VSAT o Cellular 3G/4G o MPLS o T1/E1 o ISDN o DSL o Frame relay o Cable o VPN Lecture Focus Questions: How do private WANs differ from public WANs? What type of line does PPPoE use to connect to the ISP's router? What are the advantages of using PPPoE? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 127 Video/Demo 14.1.1 Common WAN Technologies Time 16:52 Number of Exam Questions 15 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 128 Section 14.2: Leased Line WAN Links Summary In this section students will learn about leased line WAN links. Details include: Layer 1 leased lines are sometimes referred to using the following names: o A leased circuit o A serial link o A point-to-point link o T1 line o A generic WAN link Facts about WAN leased lines HDLC is often used as the data link protocol for WAN leased line connections Requirements of the following physical components of a leased line implementation: o CPE o CSU/DSU o Serial cable o Supported lines Routers in a back-to-back configuration: o The router providing clocking is known as the DCE (Data Communications Equipment) o The router not providing clocking is known as the DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) Commands to configure routers Students will learn how to: Configure and implement a leased line WAN link. Identify WAN technologies available for leased line WAN links. Configure a leased line WAN link to use the HDLC protocol. Configure back-to-back routers to simulate a leased line WAN link test environment. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.3 Configure and verify the operation status of a device interface, both serial and Ethernet. 8.1 Identify different WAN technologies. 8.2 Configure and verify a basic WAN serial connection. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 129 TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 2.0 Router interface configuration: o View the status of router interfaces o Configure Ethernet and serial router interfaces Lecture Focus Questions: What is a leased line WAN link? What is HDLC and what benefits does it provide? How do you configure your routers to use HDLC over a leased line? What is the purpose of the FCS field used in the HDLC protocol? What are the roles of DCEs, DTEs, and CSUs in a leased line WAN link? What types of telecommunication lines are available for a leased line WAN link? Video/Demo Time 14.2.1 Leased Line Overview 9:54 14.2.2 Exploring HDLC Links 3:21 14.2.5 Configuring Back-to-back Routers 3:35 Total 16:50 Lab/Activity Explore Serial Interface Status Configure Back-to-back Routers Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 130 Section 14.3: PPP WAN Links Summary This section discusses Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) WAN links. Details include: The role of Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) The main protocols used by PPP to establish and maintain the link: o Link Control Protocol (LCP) o Network Control Protocol (NCP) PPP established communication in three phases: o LCP phase o Authenticate phase o NCP phase Tasks to configure PPP on the router Configuring username and passwords for PAP or CHAP authentication PPP commands Understanding the results of using the show interface command Students will learn how to: Configure a link to use the HDLC protocol. Use the CLI to troubleshoot a serial link. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.3 Configure and verify the operation status of a device interface, both serial and Ethernet. 8.3 Configure and verify a PPP connection between Cisco routers. TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 2.0 Router interface configuration: o View the status of router interfaces o Configure Ethernet and serial router interfaces o Configure a PPP connection between routers ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 131 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the advantages of using PPP? What is PPP and how do you configure your routers to use it on a leased line WAN link? What is LCP responsible for in PPP communication? What is NCP used for in PPP communication? Which authentication method is more secure, PAP or CHAP? How do you configure the password used with PPP authentication? Video/Demo Time 14.3.1 PPP Overview 8:27 14.3.3 Configuring a PPP Link 4:52 Total 13:19 Lab/Activity Configure PPP Number of Exam Questions 12 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 132 Section 14.4: Frame Relay WAN Concepts Summary In this section students will gain an understanding of Frame Relay concepts. Details include: The role of Frame Relay networks Frame Relay terms: o Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) o Data Communication Equipment (DCE) o Virtual Circuit (VC) o Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC) o Switched Virtual Circuit o Access Link o Access Rate o Committed Information Rate (CIR) o Data Link Connection Identifier (DLCI) o Nonbroadcast Multiaccess (NBMA) o Local Management Interface (LMI) Frame Relay transmission concepts: o Data flow o Corrupt packet handling o Network congestion o Header and trailer o Protocol identification Options for assigning subnets and IP addresses on Frame Relay interfaces Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 8.1 Identify different WAN Technologies: o Metro Ethernet o VSAT o Cellular 3G/4G o MPLS o T1/E1 o ISDN o DSL o Frame relay o Cable o VPN ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 133 TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 2.0 Router interface configuration: o View the status of router interfaces o Configure Ethernet and serial router interfaces Lecture Focus Questions: What is the CIR? What does locally significant mean in relation to the DLCI number? What functions are performed by LMI? What is the difference between a point-to-point and a multipoint link? When are the FECN and BECN bits set? What does each one mean? How does inverse ARP simplify Frame Relay configuration? What is a subinterface? Video/Demo 14.4.1 Frame Relay WANs 14.4.2 Frame Relay Addressing Total Time 18:29 9:19 27:48 Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 134 Section 14.5: Frame Relay Configuration Summary This section discusses configuring Frame Relay. Concepts include: Designing Frame Relay: Configuration options for multipoint connections: o Inverse ARP o Manual mapping o Subinterfaces Tasks to configure Frame Relay on an interface Commands to configure a simple Frame Relay Using the frame-relay map command Students will learn how to: Set Frame Relay encapsulation on a serial interface. Configure Frame Relay to use inverse ARP for address discovery. Use show commands to monitor Frame Relay on a router. Troubleshoot a Frame Relay configuration. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 7.12 Troubleshoot and resolve WAN implementation issues: o Serial interfaces o PPP o Frame relay 8.4 Configure and verify frame relay on Cisco routers. TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 2.0 Router interface configuration: o View the status of router interfaces o Configure Ethernet and serial router interfaces 7.0 Frame Relay configuration: o Enable Frame Relay on a router o Configure Frame Relay static mappings o Configure point-to-point Frame Relay o Configure multipoint Frame Relay ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 135 Lecture Focus Questions: When might you use inverse ARP? What are subinterfaces and why would you use them? Which command would you use to view the DLCI numbers for each interface? Why wouldn't you use the DLCI number included in the show interfaces command to identify assigned DLCIs? Which commands can you use to view the LMI type used on your router? Which Frame Relay encapsulation type should you use when connecting to routers from different vendors? Video/Demo Time 14.5.1 Frame Relay Design and Implementation 7:15 14.5.2 Configuring Frame Relay Links 4:10 14.5.6 Configuring Static Mappings 3:53 14.5.9 Configuring Subinterfaces for Frame Relay 5:03 Total 20:21 Lab/Activity Configure Frame Relay Configure Static Mappings Configure Point-to-Point Frame Relay Configure Multipoint Frame Relay Number of Exam Questions 12 questions Total Time About 60 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 136 Section 14.6: PPPoE Configuration Summary This section provides information about configuring PPPoE. Details include: Considerations when configuring a PPPoE client Commands to configure a PPPoE client router Examples Students will learn how to: Configure a PPPoE client. Use the CLI to configure PPPoE settings. Troubleshoot issues with PPPoE. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 8.5 Implement and troubleshoot PPPoE. TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 2.0 Router interface configuration: o Configure PPPoE connections on a router Lecture Focus Questions: On which interfaces can PPPoE be configured? How do you enable a router to use one global address for many local addresses? What does the callin keyword do when using CHAP or PAP authentication? How do you enable PPP encapsulation on the dialer interface? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 137 Video/Demo 14.6.1 Configuring a PPPoE Client Time 4:42 Lab/Activity Configure PPPoE 1 Configure PPPoE 2 Number of Exam Questions 3 questions Total Time About 25 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 138 Section 14.7: Virtual Private Networks Summary In this section students will learn about virtual private networks. Details include: The role of a Virtual Private Network (VPN) Benefits provided by VPNs: o Confidentiality o Authentication o Integrity o Anti-replay o Non-repudiation Common VPN security technologies: o Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) o Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) o Transport Layer Security (TLS) o Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) o Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F) o Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Basic types of Cisco VPNs: o Site-to-site o Remote access Devices that may be used in a VPN connection: o Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) o Routers o PIX Firewalls o VPN accelerator cards o VPN concentrators o VPN client-side software o VPN client-side hardware IPsec includes protocols for authentication, data encryption, and connection negotiation: o Authentication Header (AH) o Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) o Internet Key Exchange (IKE) IPsec modes of operation: o Tunnel mode o Transport mode Modes of Cisco SSL VPNs: o Clientless o Thin-Client o Full tunnel Client requirements for SSL VPNs include: o An SSL VPN account (username and password) ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 139 o An SSL VPN supported browser (such as Internet Explorer, Firefox, or Safari o Local administrative privileges for the Thin-Client and full tunnel installation requirements Students will learn how to: Configure a GRE tunnel. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 8.1 Identify different WAN Technologies: o VPN Lecture Focus Questions: What function do routers between two GRE endpoints provide? What function do VPN tunnel endpoints provide? What protocols are supported by a GRE tunnel? How do site-to-site VPNs differ from remote access VPNs? How are extranets typically used? How does IPsec implement security? Video/Demo 14.7.1 VPN Overview Time 13:13 14.7.2 GRE Tunneling for VPNs 8:03 14.7.3 Configuring a GRE Tunnel 5:50 Total 27:06 Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 140 Section 14.8: WAN Troubleshooting Summary This section discusses troubleshooting WAN. Details include: Commands that may help troubleshoot router connections Possible conditions indicated by the interface status: o Administratively down/down o Down/down o Up/down o Up/up Troubleshoot TCP/IP connectivity Considerations when troubleshooting connectivity Students will learn how to: Troubleshoot and repair WAN issues relating to frame relay and serial link issues. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 7.12 Troubleshoot and resolve WAN implementation issues: o Serial interfaces o PPP o Frame relay TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 2.0 Router interface configuration: o Troubleshoot router connections 3.0 IP routing implementation: o Troubleshoot WAN communication issues using utilities such as ping and tracert Lecture Focus Questions: What are some possible causes of Layer 1 problems? If a ping or traceroute fails, what can you examine to rule out Layer 1 and Layer 2 issues? At which layer is there a problem if a Telnet test fails? What does an interface status of down/down indicate? What does up/down indicate? What should you verify when troubleshooting TCP/IP connectivity? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 141 Video/Demo Time 14.8.1 Serial WAN Link Troubleshooting 5:52 14.8.2 Troubleshooting WAN Issues 7:18 14.8.8 Troubleshooting Frame Relay 5:37 Total 18:47 Lab/Activity View Serial Interface Status Troubleshoot a Serial Connection 1 Troubleshoot a Serial Connection 2 Troubleshoot a Serial Connection 3 Troubleshoot a Serial Connection 4 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 142 Section 15.1: OSPF for IPv4 Review Summary This section provides a review of OSPF for IPv4. Details include: OSPF uses the following methods: o Neighbor discovery o Topology exchange o Route determination Details about Router IDs (RID)s OSPF communication process: o Down o Attempt o Init o 2-way o Exstart o Exchange o Loading state o Full state A router will monitor each neighbor’s relationship using: o Hello packets o Hello interval o Dead interval Students will learn how to: Configure OSPF routing. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.7 Configure and verify OSPF: o Benefit of single area o Neighbor adjacencies o OSPF states o Discuss multi-area OSPF o Configure OSPF v2 o Configure OSPF v3 o Router ID o Passive interface o LSA types ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 143 TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 4.0 OSPF routing configuration: o Enable OSPF routing o Configure and manage OSPF routing Lecture Focus Questions: Must the process ID number used on different OSPF routers match? What is Area 0 in an OSPF implementation? How many areas can a single subnet be in? How do the DR and BDR reduce network traffic? When is the DR not used? How is the DR elected? How can you ensure that a specific device becomes the DR? What conditions must be met before two routers running OSPF will share information? Video/Demo Time 15.1.1 OSOPF Review 7:38 15.1.2 Configuring OSPF 9:24 15.1.3 Verifying OSPF 6:05 Total 23:07 Number of Exam Questions 5 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 144 Section 15.2: OSPF Areas and LSA Types Summary This section discusses OSPF areas and LSA types. Concepts covered include: Configuring OSPF Terms regarding OSPF areas: o Area o Backbone area o Area Border Router (ABR) o Backbone router o Internal router o Inter-area route o Intra-area route LSA types: o Type 1 o Type 2 o Type 3 OSPF databases: o Adjacency o Topology o Routing table Facts about the SPF algorithm and routers Default administrative costs for different route types: o Connected 0 o Static 1 o BGP 20 o EIGRP 90 o OSPF 110 o RIP 120 Students will learn how to: View OSPF settings. Explore OSPF areas. Verify OSPF configuration. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.7 Configure and verify OSPF: o Benefit of single area o Neighbor adjacencies o OSPF states o Discuss multi-area OSPF o Configure OSPF v2 ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 145 o o o o Configure OSPF v3 Router ID Passive interface LSA types TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 4.0 OSPF routing configuration: o Enable OSPF routing o Configure and manage OSPF routing Lecture Focus Questions: What are the different types of LSAs? What is the role of an Area Border Router (ABR)? How does a router choose between competing connected and static OSPF routes? What are the three databases that OSPF uses? When would you use an OSPF multi-area configuration? What are backbone routers? What are internal routers? Video/Demo Time 15.2.1 OSPF Area Design 5:25 15.2.2 Exploring OSPF Areas 4:53 15.2.3 OSPF LSA Types 3:23 15.2.4 Exploring LSA Types 5:21 15.2.5 OSPF Databases 6:10 15.2.6 Exploring OSPF Databases 3:17 Total 28:29 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 35 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 146 Section 15.3: EIGRP for IPv4 Routing Summary This section discusses EIGRP concepts. Details covered include: Enhanced IGRP is a Cisco-proprietary balanced hybrid routing protocol The EIGRP process that results in the creation of a routing table Requirements for EIGRP communication between neighbors The role of EIGRP once the routing table has been established EIGRP offers a number of operating efficiencies Concepts to understand how EIGRP can provide load balancing and fast recovery for failed links: o Advertised distance (AD) o Feasible distance (FD) o Successor o Feasible successor o Diffusing Update Algorithm Considerations regarding the EIGRP and routes Conditions that must be met for an EIGRP router to share information with a neighbor Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.11 Configure and verify EIGRP (single AS): o Feasible distance/feasible successors/administrative distance o Feasibility condition o Metric composition o Router ID o Auto summary o Path selection o Load balancing: Equal Unequal o Passive interface Lecture Focus Questions: What type of routing protocol is EIGRP? What is the metric used with EIGRP? How does the router calculate the feasible distance? What condition must be met for a route to become a feasible successor route? What is the difference between a feasible successor and a successor? How does EIGRP determine how many paths to keep in its topology database? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 147 Video/Demo Time 15.3.1 EIGRP Routing Overview 7:02 15.3.2 EIGRP Routing Processes 7:21 15.3.3 EIGRP Convergence 6:48 Total 21:11 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 148 Section 15.4: EIGRP for IPv4 Configuration Summary This section discusses configuring, managing, and monitoring EIGRP for IPv4. Details include: Facts about equal load balancing Auto-summarization and summarized networks: o Contiguous o Discontiguous Commonly used EIGRP commands: o router eigrp number o network n.n.n.n o auto-summary o maximum-paths Commands to manage and monitor EIGRP: o show ip route o show ip eigrp neighbors o show ip eigrp interfaces Students will learn how to: Configure EIGRP. Use CLI commands to verify EIGRP settings. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.11 Configure and verify EIGRP (single AS): o Feasible distance/feasible successors/administrative distance o Feasibility condition o Metric composition o Router ID o Auto summary o Path selection o Load balancing: Equal Unequal o Passive interface TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 5.0 EIGRP routing configuration: o Enable EIGRP routing o Configure and manage EIGRP routing ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 149 Lecture Focus Questions: What are the core steps for configuring EIGRP? What is the importance of the autonomous system (AS) number? How is EIGRP different than OSPF? What are the differences between a contiguous and discontiguous network? How does EIGRP choose the bandwidth metrics for the optimal route calculation? With load balancing, what is the default number of paths? What is the maximum number of paths? Video/Demo Time 15.4.1 EIGRP Design and Implementation 5:10 15.4.2 Enabling EIGRP Routing 5:15 15.4.3 Verifying EIGRP Routing 4:17 15.4.5 Exploring EIBRP Convergence 6:48 15.4.6 EIGRP Load Balancing, Metrics, and Autosummarization 6:08 15.4.7 Exploring Auto-Summary, Load Balancing, and Passive Interface 6:22 Total 34:00 Lab/Activity Enable EIGRP Number of Exam Questions 6 questions Total Time About 45 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 150 Section 15.5: IPv4 Protocol Troubleshooting Summary In this section students will learn about troubleshooting the IPv4 routing protocols. Details include: OSPF: o Conditions that must be met for OSPF routers to become fully adjacent o Commands for monitoring and troubleshooting OSPF: show ip protocols show ip ospf show ip ospf neighbor show ip ospf interface debug ip ospf events o Error messages that display with the debug ip ospf events command: OSPF: mismatched hello parameters from 10.0.0.1 OSPF: Dead R 20 C 40, Hello R 5 C 5 Mask R 255.255.255.0 C 255.255.255.0 OSPF: help packet with mismatched E bit Neighbor Down: Dead timer expired EIGRP: o Conditions that must be met for an EIGRP router to share information with a neighbor o Commands to verify EIGRP: show ip protocols show ip eigrp interfaces show ip eigrp neighbors show ip eigrp topology o Error messages that display with the show ip eigrp topology alllinks command: Destination network Known routes Successor routes Feasible successor routes Students will learn how to: Use CLI commands to analyze neighbor relationships. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 151 Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 7.8 Troubleshoot and resolve routing issues: o Routing is enabled o Routing table is correct o Correct path selection 7.9 Troubleshoot and resolve OSPF problems: o Neighbor adjacencies o Hello and Dead timers o OSPF area o Interface MTU o Network types o Neighbor states o OSPF topology database 7.10 Troubleshoot and resolve EIGRP problems: o Neighbor adjacencies o AS number o Load balancing o Split horizon TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 4.0 OSPF routing configuration: o Troubleshoot OSPF routing 5.0 EIGRP routing configuration: o Troubleshoot EIGRP routing Lecture Focus Questions: Why is it important to analyze neighbor relationships when troubleshooting IPv4 routing protocols? What should you look for when analyzing neighbor relationships? How do neighbor relationship requirements differ from OSPF and EIGRP? What information is included in the topology table for EIGRP? What is the E bit? If you get a message that indicates a mismatched E bit, what is the problem? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 152 Video/Demo Time 15.5.1 Adjacency Issues 5:25 15.5.2 Exploring Adjacency Issues 8:12 Total 13:37 Lab/Activity Troubleshoot OSPF 1 Troubleshoot OSPF 2 Troubleshoot EIGRP 1 Troubleshoot EIGRP 2 Number of Exam Questions 12 questions Total Time About 50 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 153 Section 16.1: IPv6 Protocol Overview Summary This section discusses the following concepts of troubleshooting IPv6 routing: Unicast addressing: o Link-local addresses o Global addresses o Unique local unicast addressing DHCP: o Static address assignment o Modes of an updated version of DHCP (DHCPv6): Stateful DHCPv6 Stateless DHCPv6 o Stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC) IPv6 Configuration Problem areas when troubleshooting IPv6: o Between hosts and routers o Router-specific o Filters Commands to troubleshoot IPv6 networks: o ping o traceroute o show ipv6 route o show ipv6 neighbors Students will learn how to: Use ping and traceroute to troubleshoot IPv6 problems. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 3.2 Identify the appropriate IPv6 addressing scheme to satisfy addressing requirements in a LAN/WAN environment. 3.5 Describe IPv6 addresses: o Global unicast o Multicast o Link local o Unique local o Eui 64 o Autoconfiguration 7.8 Troubleshoot and resolve routing issues: o Routing is enabled o Routing table is correct o Correct path selection ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 154 Lecture Focus Questions: How do link-local addresses differ from unique local addresses? How are stateless addresses generated with stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC)? What types of problems are indicated by a failed ping? What possible causes should you look for when hosts cannot communicate with a router? Video/Demo 16.1.1 IPv6 Protocol Review Time 17:31 16.1.2 Common IPv6 Troubleshooting Issues 9:35 16.1.3 Exploring IPv6 Addressing on Routers 6:05 Total 33:11 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 155 Section 16.2: OSPF for IPv6 Summary This section discusses configuring and managing OSPF for IPv6. Details include: Changes between OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 Comparison of OSPFv3 LSAs and OSPFv2 LSAs Key LSAs that are created by each router: o Type 1 Router LSA o Type 2 Network LSA o Type 3 Inter-area Prefix LSA Commands for configuring IPv6 OSPF routing Students will learn how to: Configure OSPF routing. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.7 Configure and verify OSPF: o Benefit of single area o Neighbor adjacencies o OSPF states o Discuss multi-area OSPF o Configure OSPF v2 o Configure OSPF v3 o Router ID o Passive interface o LSA types TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 4.0 OSPF routing configuration: o Configure and manage OSPF routing Lecture Focus Questions: How do LSAs differ between OSPFv2 and OSPFv3? How do mismatched MTUs affect OSPFv3 routing? What are common interface subcommand configuration problems? What is the function of a type 3 Inter-area Prefix LSA? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 156 Video/Demo Time 16.2.1 OSPFv3 Routing Overview 8:47 16.2.2 Configuring OSPFv3 Routing 3:08 16.2.3 Verifying OSPFv3 Routing Functionality 2:47 Total 14:42 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 25 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 157 Section 16.3: EIGRP for IPv6 Summary In this section students will learn about configuring and managing EIGRP for IPv6. Concepts covered include: Modes EIGRPv6 uses for configuration commands to create the EIGRPv6 process: o EIGRP mode o Interface mode Differences between EIGRPv4 and EIGRPv6 Similarities between EIGRPv4 and EIGRPv6 Elements to review when troubleshooting EIGRPv6 Commands that can be used to verify and troubleshoot EIGRPv6: o show ipv6 eigrp interfaces o show ipv6 eigrp neighbors o show ipv6 protocols o show ipv6 eigrp topology Students will learn how to: Configure EIGRPv6. Use CLI commands to verify EIGRPv6 settings. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 4.11 Configure and verify EIGRP (single AS): o Feasible distance/feasible successors/administrative distance o Feasibility condition o Metric composition o Router ID o Auto summary o Path selection o Load balancing: Equal Unequal o Passive interface TestOut Routing Pro Objectives: 5.0 EIGRP routing configuration: o Configure and manage EIGRP routing o Troubleshoot EIGRP routing ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 158 Lecture Focus Questions: In which ways does EIGRPv6 differ from EIGRPv4? In which situation is it easy to overlook an EIGRPv6 interface enabled without an AS number? How does EIGRP choose the bandwidth metrics for the optimal route calculation? Video/Demo Time 16.3.1 EIGRPv6 Routing Overview 4:10 16.3.2 Configuring EIGRPv6 Routing 3:05 16.3.3 Common EIGRPv6 Routing Issues 4:07 16.3.4 Verifying EIGRPv6 Routing Functionality 3:50 Total 15:12 Number of Exam Questions 4 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 159 Section 17.1: Simple Network Management Protocol Summary This section provides information about the Simple Network Management Protocol. Concepts covered include: Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP): o Components SNMP uses: SNMP Manager SNMP Agents Management Information Base (MIB) o Ways SNMP communication can occur: Poll Trap o SNMPv3 is more secure than earlier version o Features that SNMPv3 uses to implement three levels of security: noAuthnoPriv authNoPriv authPriv o Setting up SNMP communications o Comparison of the security of SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3 o Commands to implement SNMPv3 Students will learn how to: Configure SNMP. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 5.9 Describe SNMP v2 and v3. Lecture Focus Questions: What is SNMP? What roles do SNMP Managers and SNMP Agents play? How does SNMP use the MIB? In what ways can SNMP communication take place? How is SNMPv3 different from prior SNMP versions? How do you configure SNMP servers? ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 160 Video/Demo Time 17.1.1 SNMP Overview 14:39 17.1.2 Enabling SNMP on Cisco Devices 13:14 Total 27:53 Number of Exam Questions 9 questions Total Time About 40 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 161 Section 17.2: System Message Log Summary This section provides details of system message logs. Details include: The role of syslog messages Understanding the components that comprise a log message: o Timestamp o Facility o Severity level o Mnemonic o Message text Commands to implement log redirection Students will learn how to: Configure Syslog. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 5.8 Configure and verify syslog: o Utilize syslog output Lecture Focus Questions: What is the function of syslog messages? What are the components of log messages? Under what situation would you redirect log messages to a syslog server? What are the system logging message severity levels? Video/Demo Time 17.2.1 Syslog Overview 7:11 17.2.2 Configuring Centralized Logging with Cisco Devices 1:38 Total 8:49 Number of Exam Questions 8 questions Total Time About 20 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 162 Section 17.3: NetFlow Summary This section discusses NetFlow. Concepts covered include: The role of NetFlow to track monitor IP communications on the network. Network flows Considerations to be aware of when using NetFlow Commands to configure NetFlow and view flow information on a Cisco router Students will learn how to: Configure NetFlow. Cisco Exam 200-120 (CCNA) Objectives: 7.13 Monitor NetFlow statistics. Cisco Exam 200-101 (ICND2) Objectives: 4.2 Utilize NetFlow data. Lecture Focus Questions: What IP communication issues can be monitored using NetFlow? What is a network flow? What are the features and benefits of NetFlow? How do you configure NetFlow on a Cisco router? Video/Demo Time 17.3.1 NetFlow Overview 9:44 17.3.2 Enabling NetFlow on Cisco Devices 2:50 Total 12:34 Number of Exam Questions 11 questions Total Time About 30 minutes ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 163 TestOut Switching Pro Practice Exams Summary This section provides information to help prepare students to take the TestOut Switching Pro certification exam. Students will have the opportunity of testing their mastery of the concepts presented in this course to reaffirm that they are ready for the certification exam. Students will typically take about 5-10 minutes (depending upon the complexity and their level of knowledge) to complete each simulation question in the following practice exams. There is no time limit on the amount of time a student can take to complete the practice exams for the following domains. Objective 1: Switch Setup and Configuration (4 simulation questions) Objective 2: Switch Interface Configuration (4 simulation questions) Objective 3: TCP/IP Configuration (3 simulation questions) Objective 4: VLAN Configuration (11 simulation questions) Objective 5: InterVLAN Routing (4 simulation questions) Objective 6: Spanning Tree Configuration (5 simulation questions) Objective 7: Switch Security (3 simulation questions) Objective 8: EtherChannel Configuration (2 simulation questions) The TestOut Switching Pro Certification Practice Exam consists of 15 simulation questions that are randomly selected from the above practice exams. Each time the Certification Practice Exam is accessed different questions may be presented. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 164 TestOut Routing Pro Practice Exams Summary This section provides information to help prepare students to take the TestOut Routing Pro certification exam. Students will have the opportunity of testing their mastery of the concepts presented in this course to reaffirm that they are ready for the certification exam. Students will typically take about 5-10 minutes (depending upon the complexity and their level of knowledge) to complete each simulation question in the following practice exams. There is no time limit on the amount of time a student can take to complete the practice exams for the following domains. Objective 1: Router Setup and Configuration (4 simulation questions) Objective 2: Router Interface Configuration (13 simulation questions) Objective 3: IP Routing Implementation (6 simulation questions) Objective 4: OSPF Routing Configuration (4 simulation questions) Objective 5: EIGRP Routing Configuration (3 simulation questions) Objective 6: Access Control List Configuration (7 simulation questions) Objective 7: Frame Relay Configuration (6 simulation questions) Objective 8: NAT Configuration (4 simulation questions) Objective 9: DHCP Server Configuration (3 simulation questions) Objective 10: Router Security Configuration (1 simulation question) Objective 11: High Availability Configuration (3 simulation questions) The TestOut Routing Pro Certification Practice Exam consists of 15 simulation questions that are randomly selected from the above practice exams. Each time the Certification Practice Exam is accessed different questions may be presented. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 165 Cisco ICND1 (100-101) Practice Exams Summary This section provides information to help prepare students to take the Cisco ICND1 (100-101) certification exam. Students will have the opportunity of testing their mastery of the concepts presented in this course to reaffirm that they are ready for the certification exam. Students will typically take about 5-10 minutes (depending upon the complexity and their level of knowledge) to complete each simulation question in the following practice exams. There is no time limit on the amount of time a student can take to complete the practice exams for the following domains. Objective 1.0: Operation of IP Data Networks (56 questions) Objective 2.0: LAN Switching Technologies (85 questions) Objective 3.0: IP Addressing (IPv4/IPv6) (98 questions) Objective 4.0: IP Routing Technologies (104 questions) Objective 5.0: IP Services (53 questions) Objective 6.0: Network Device Security (60 questions) Objective 7.0: Troubleshooting (39 questions) The Cisco ICND1 (100-101) Certification Practice Exam consists of 60 simulation questions that are randomly selected from the above practice exams. Each time the Certification Practice Exam is accessed different questions may be presented. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 166 Cisco ICND2 (200-101) Practice Exams Summary This section provides information to help prepare students to take the Cisco ICND2 (200-101) certification exam. Students will have the opportunity of testing their mastery of the concepts presented in this course to reaffirm that they are ready for the certification exam. Students will typically take about 5-10 minutes (depending upon the complexity and their level of knowledge) to complete each simulation question in the following practice exams. There is no time limit on the amount of time a student can take to complete the practice exams for the following domains. Objective 1.0: LAN Switching Technologies (20 questions) Objective 2.0: IP Routing Technologies (83 questions) Objective 3.0: IP Services (50 questions) Objective 4.0: Troubleshooting (46 questions) Objective 5.0: WAN Technologies (79 questions) The Cisco ICND2 (200-101) Certification Practice Exam consists of 60 simulation questions that are randomly selected from the above practice exams. Each time the Certification Practice Exam is accessed different questions may be presented. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 167 Cisco CCNA (200-120) Practice Exams Summary This section provides information to help prepare students to take the Cisco CCNA (200-120) certification exam. Students will have the opportunity of testing their mastery of the concepts presented in this course to reaffirm that they are ready for the certification exam. Students will typically take about 5-10 minutes (depending upon the complexity and their level of knowledge) to complete each simulation question in the following practice exams. There is no time limit on the amount of time a student can take to complete the practice exams for the following domains. Objective 1.0: Operation of IP Data Networks (56 questions) Objective 2.0: LAN Switching Technologies (104 questions) Objective 3.0: IP Addressing (IPv4/IPv6) (98 questions) Objective 4.0: IP Routing Technologies (169 questions) Objective 5.0: IP Services (103 questions) Objective 6.0: Network Device Security (60 questions) Objective 7.0: Troubleshooting (84 questions) Objective 8.0: WAN Technologies (79 questions) The Cisco CCNA (200-120) Certification Practice Exam consists of 60 simulation questions that are randomly selected from the above practice exams. Each time the Certification Practice Exam is accessed different questions may be presented. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 168 Appendix A: Approximate Time for the Course The total time for the LabSim Routing and Switching Pro course is approximately 88 hours and 17 minutes. The time is calculated by adding the approximate time for each section which is calculated using the following elements: Video/demo times Approximate time to read the text lesson (the length of each text lesson is taken into consideration) Simulations (5 minutes assigned per simulation, of course many students may take longer depending upon their knowledge level and experience) Questions (1 minute per question) The breakdown for this course is as follows: Module Sections Time Minute HR:MM 5 5 :05 20 45 45 15 35 30 45 25 260 4:20 10 5 25 20 35 45 140 2:20 1.0 ICND1 Introduction 1.1 ICND1 Introduction 2.0 Cisco Devices 2.1 Networking Fundamentals 2.2 Network Devices 2.3 TCP/IP Networking Model 2.4 Data Encapsulation 2.5 OSI Networking Model 2.6 Data Communications 2.7 Ethernet Networking 2.8 WAN Fundamentals 3.0 Cisco Device Basics 3.1 Cisco Device Access 3.2 System Startup 3.3 Command Line Interface (CLI) 3.4 Command Line Help 3.5 Basic Device Settings 3.6 Device Passwords 4.0 LAN Switching 4.1 Layer 2 Switching Overview 4.2 Spanning Tree Overview 4.3 Switch Interface Configuration 4.4 Switch IP Configuration ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 45 25 25 50 169 4.5 Virtual LANs (VLANs) 4.6 Trunking 4.7 Switch Security 4.8 Remote Switch Access 4.9 Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) 30 50 45 10 35 315 5:15 30 25 30 35 45 165 2:45 30 25 20 50 30 35 45 30 40 305 5:05 55 30 20 45 45 15 40 15 265 4:25 35 25 20 80 1:20 5.0 IPv4 Addressing 5.1 IPv4 Overview 5.2 IPv4 Address Classes 5.3 Subnetting 5.4 Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) 5.5 Subnet Planning and Design 6.0 IP Routing Technologies 6.1 IP Routing 6.2 Routing Implementations 6.3 Static Routing 6.4 Dynamic Routing 6.5 Route Summarization 6.6 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Overview 6.7 OSPF Configuration 6.8 InterVLAN Routing Overview 6.9 InterVLAN Routing Configuration 7.0 IP Services 7.1 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 7.2 Access Control Lists (ACLs) 7.3 ACL Commands 7.4 ACL Configuration 7.5 Extended ACL Configuration 7.6 Network Address Translation (NAT) Overview 7.7 NAT Configuration 7.8 Network Time Protocol (NTP) 8.0 IPv6 Addressing 8.1 IPv6 Addressing Overview 8.2 IPv6 Host Configuration 8.3 IPv6 Routing ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 170 9.0 Troubleshooting 9.1 Network Communications Troubleshooting 9.2 Switch Troubleshooting 9.3 ACL Troubleshooting 45 45 20 110 1:50 1 1 :01 50 30 80 1:20 90 65 25 180 3:00 85 35 75 195 3:15 35 35 35 45 50 200 3:20 35 35 35 40 60 25 45 50 325 5:25 10.0 ICND2 Introduction 10.1 ICND2 Introduction 11.0 Router Configuration and Management 11.1 Router Configuration Files 11.2 IOS Licensing 12.0 Spanning Tree Protocol 12.1 Spanning Tree Overview 12.2 Spanning Tree Protocol Configuration 12.3 Switch Troubleshooting 13.0 Advanced IPv4 Routing 13.1 IPv4 Routing Troubleshooting 13.2 InterVLAN Routing Troubleshooting 13.3 Default Gateway Redundancy 14.0 Wide Area Networks 15.1 OSPF for IPv4 Review 15.2 OSPF Areas and LSA Types 15.3 EIGRP for IPv4 Routing 15.4 EIGRP for IPv4 Configuration 15.5 IPv4 Routing Protocol Troubleshooting 14.0 Wide Area Networks 14.1 WAN Types 14.2 Leased Line WAN Links 14.3 PPP WAN Links 14.4 Frame Relay WAN Concepts 14.5 Frame Relay Configuration 14.6 PPPoE Configuration 14.7 Virtual Private Networks 14.8 WAN Troubleshooting ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 171 15.0 IPv4 Routing Protocols 15.1 OSPF for IPv4 Review 15.2 OSPF Areas and LSA Types 15.3 EIGRP for IPv4 Routing 15.4 EIGRP for IPv4 Configuration 15.5 IPv4 Routing Protocol Troubleshooting 30 35 30 45 50 190 3:10 40 25 20 85 1:25 40 20 30 90 1:30 255 4:15 16.0 IPv6 Routing Protocols 16.1 IPv6 Protocol Overview 16.2 OSPF for IPv6 16.3 EIGRP for IPv6 17.0 Network Management Using Cisco Devices 17.1 Simple Network Management Protocol 17.2 System Message Log 17.3 NetFlow TestOut Switching Pro Practice Exams 1. Switch Setup and Configuration (4 simulation questions) 2. Switch Interface Configuration (4 simulation questions) 3. TCP/IP Configuration (3 simulation questions) 4. VLAN Configuration (11 simulation questions) 5. InterVLAN Routing (4 simulation questions) 6. Spanning Tree Configuration (5 simulation questions) 7. Switch Security (3 simulation questions) 8. EtherChannel Configuration (2 simulation questions) TestOut Switching Pro Certification Practice Exam (15 questions) ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 20 20 15 55 20 25 15 10 75 172 TestOut Routing Pro Practice Exams 1. Router Setup and Configuration (4 simulation questions) 2. Router Interface Configuration (13 questions) 20 65 3. IP Routing Implementation (6 simulation questions) 30 4. OSPF Routing Configuration (4 simulation questions) 20 5. EIGRP Routing Configuration (3 simulation questions) 15 6. Access Control List Configuration (7 simulation questions) 35 7. Frame Relay Configuration (6 simulation questions) 8. NAT Configuration (4 simulation questions) 30 20 9. DHCP Server Configuration (3 simulation questions) 15 10. Router Security Configuration (1 simulation question) 5 11. High Availability Configuration (3 simulation questions) 15 TestOut Routing Pro Certification Practice Exam (15 simulation questions) 75 345 5:45 555 9:15 Cisco ICND1 (100-101) Practice Exams 1.0 Operation of IP Data Networks (56 questions) 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies (85 questions) 3.0 IP Addressing (IPv4 / IPv6) (98 questions) 4.0 IP Routing Technologies (104 questions) 5.0 IP Services, (53 questions) 6.0. Network Device Security (60 questions) 7.0 Troubleshooting (39 questions) Cisco ICND1 (100-101) Certification Practice Exam (60 questions) ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 56 85 98 104 53 60 39 60 173 Cisco ICND2 (200-101) Practice Exams 1.0 LAN Switching Technologies (20 questions) 2.0 IP Routing Technologies (83 questions) 3.0 IP Services (50 questions) 4.0 Troubleshooting (46 questions) 5.0 WAN Technologies (79 questions) 20 83 50 46 79 Cisco ICND2 (200-101) Certification Practice Exam (60 questions) 60 338 5:38 56 104 98 169 103 60 84 79 60 813 13:33 5297 88:17 Cisco CCNA (200-120) Practice Exams 1.0 Operations of IP Data Networks (56 questions) 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies (104 questions) 3.0 IP Addressing (IPv4 / IPv6) (98 questions) 4.0 IP Routing Technologies (169 questions) 5.0 IP Services (103 questions) 6.0 Network Device Security (60 questions) 7.0 Troubleshooting (84 questions) 8.0 WAN Technologies (79 questions) Certification Practice Exam (60 questions) Total Time ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 174 Appendix B: Exam 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 Objectives Exam 100-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1. For up-to-date information about this exam, visit www.cisco.com. Cisco offers two options for obtaining the CCNA certification: Pass Exam 200-120 OR Pass Exam 100-101 AND Exam 200-101 While you can use this TestOut product to prepare for either exam, the product is geared towards passing the Cisco 200-120 (CCNA) exam. We recommend you study all of the material and take the single exam option rather than taking two exams. This specific certification exam measures your ability to pass the 100101: ICND1 exam. Before taking the exam, you should be proficient in the job skills listed below. In the spread sheet below the column to the right lists the sections where the information is located in the course: # Exam Objective Module.Section 1.0 Operation of IP Data Networks 1.1 Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices, such as routers, switches, bridges, and hubs. 1.2 Select the components required to meet a given network specification. 1.3 Identify common applications and their impact on the network. 1.4 Describe the purpose and basic operation of the protocols in the OSI and TCP/IP models. 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8 1.5 Predict the data flow between two hosts across a network. 2.6 1.6 Identify the appropriate media, cables, ports, and connectors to connect Cisco network devices to other network devices and hosts in a LAN. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 2.2 2.1, 2.2 2.2 2.1, 2.7 175 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies 2.1 Determine the technology and media access control method for Ethernet networks. 2.1, 2.2, 2.7 Identify basic switching concepts and the operation of Cisco switches: 2.2 Collision Domains Broadcast Domains Types of switching CAM Table Configure and verify initial switch configuration, including remote access management: 2.3 Cisco IOS commands to perform basic switch setup 2.4 Verify network status and switch operation using basic utilities, such as ping, Telnet, and SSH. 4.1 3.1, 3.3, 3.5, 3.6 4.3, 4.4, 4.7, 4.8 9.1 13.1 Describe how VLANs create logically separate networks and the need for routing between them: 2.5 2.6 Explain network segmentation and basic traffic management concepts. Configure and verify VLANs. 4.5 6.8 4.5 Configure and verify trunking on Cisco switches: 2.7 DTP Auto negotiation ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 4.6 176 3.0 IP Addressing (IPv4/IPv6) 3.1 Describe the operation and necessity of using private and public IP addresses for IPv4 addressing. 3.2 Identify the appropriate IPv6 addressing scheme to satisfy addressing requirements in a LAN/WAN environment. 8.1 16.1 3.3 Identify the appropriate IPv4 addressing scheme using VLSM and summarization to satisfy addressing requirements in a LAN/WAN environment. 5.4 6.5 3.4 Describe the technological requirements for running IPv6 in conjunction with IPv4, such as dual stack. 8.2 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.5 8.1 Describe IPv6 addresses: 3.5 4.0 Global unicast Multicast Link local Unique local Eui 64 Autoconfiguration 8.1, 8.2 16.1 IP Routing Technologies Describe basic routing concepts: 4.1 CEF Packet forwarding Router lookup process Configure and verify utilizing the CLI to set basic router configuration: 4.2 Cisco IOS commands to perform basic router setup 4.3 Configure and verify the operation status of an Ethernet interface. 6.1 3.3, 3.5, 3.6 4.4, 4.7, 4.8 3.3, 3.6 4.3 Verify router configuration and network connectivity: 4.4 Cisco IOS commands to review basic router information and network connectivity ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 4.9 9.1 177 4.5 Configure and verify routing configuration for a static or default route given specific routing requirements. 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4 Differentiate methods of routing and routing protocols: 4.6 Static vs. Dynamic Link state vs. Distance Vector Next hop IP routing table Passive interfaces 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4 Configure and verify OSPF (single area): 4.7 Benefit of single area Configure OSPF v2 in a single area Configure OSPF v3 in a single area Router ID Passive interface 6.6, 6.7 8.3 Configure and verify interVLAN routing (router on a stick): 4.8 Sub interfaces Upstream routing Encapsulation 4.9 Configure SVI interfaces. 5.0 IP Services 6.9 6.9 Configure and verify DHCP (IOS router): 5.1 Configuring router interfaces to use DHCP DHCP options Excluded addresses Lease time 7.1 Describe the types, features, and applications of ACLs: 5.2 Standard o Sequence numbers o Editing Extended Named Numbered Log option ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 7.2 178 Configure and verify ACLs in a network environment: 5.3 Named Numbered Log option 7.3, 7.4 Identify the basic operation of NAT: 5.4 Purpose Pool Static 1 to 1 Overloading Source addressing One-way NAT 7.6 5.5 Configure and verify NAT for given network requirements. 7.7 5.6 Configure and verify NTP as a client. 7.8 6.0 Network Device Security Configure and verify network device security features, such as: 6.1 Device password security Enable secret vs. enable Transport o Disable Telnet o SSH VTYs Physical security Service password Describe external authentication methods 3.6 4.7, 4.8 Configure and verify Switch Port Security features, such as: 6.2 Sticky MAC MAC address limitation Static/dynamic Violation modes o Err disable o Shutdown o Protect restrict Shutdown unused ports Err disable recovery Assign unused ports to an unused VLAN Setting native VLAN to other than VLAN 1 ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 4.5, 4.6, 4.7 6.9 179 6.3 Configure and verify ACLs to filter network traffic. 6.4 Configure and verify ACLs to limit Telnet and SSH access to the router. 7.0 Troubleshooting 7.1 Troubleshoot and correct common problems associated with IP addressing and host configurations. 7.4, 7.5 7.4 9.1 Troubleshoot and resolve VLAN problems: 7.2 Identify that VLANs are configured Verify port membership correct Correct IP address configured 9.2 Troubleshoot and resolve trunking problems on Cisco switches: 7.3 Correct trunk states Correct encapsulation configured Correct VLANs allowed 9.2 Troubleshoot and resolve ACL issues: 7.4 Statistics Permitted networks Direction Interface 7.4 9.3 Troubleshoot and resolve Layer 1 problems: 7.5 Framing CRC Runts Giants Dropped packets Late collision Input/Output errors ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 9.2 180 Appendix C: Exam 200-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 Objectives Exam 200-101: Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2. For up-to-date information about this exam, visit www.cisco.com. Cisco offers two options for obtaining the CCNA certification: Pass Exam 200-120 OR Pass Exam 100-101 AND Exam 200-101 While you can use this TestOut product to prepare for either exam, the product is geared towards passing the Cisco 200-120 (CCNA) exam. We recommend you study all of the material and take the single exam option rather than taking two exams. This specific certification exam measures your ability to pass the 200101: ICND2 exam. Before taking the exam, you should be proficient in the job skills listed below. In the spread sheet below the column to the right lists the sections where the information is located in the course: # 1.0 Exam Objective Module.Section LAN Switching Technologies Identify enhanced switching technologies: 1.1 RSTP PVSTP EtherChannels 4.2, 4.5, 4.6 12.1, 12.2 Configure and verify PVSTP operation: 1.2 Describe root bridge election Spanning Tree mode 2.0 IP Routing Technologies 2.1 Describe the boot process of Cisco IOS routers. 2.2 Configure and verify the operation status of a serial interface. 2.3 Differentiate methods of routing and routing protocols: ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 4.2, 12.2 3.2 11.1 14.2, 14.3 6.1 6.2, 6.3, 6.4 181 Administrative distance Split horizon Metric Next hop Configure and verify OSPF (multi area): 2.4 Neighbor adjacencies OSPF states Discuss multi-area OSPF Configure OSPF v2 Configure OSPF v3 Router ID LSA types 6.6, 6.7 8.3 15.1, 15.2 16.2 Manage Cisco IOS Files: 2.5 Boot preferences Cisco IOS image(s) Licensing o Show license o Change license 11.1, 11.2 Configure and verify EIGRP (single AS): 2.6 2.7 Feasible distance/feasible successors/administrative distance Feasibility condition Metric composition Router ID Auto summary Path selection Load balancing o Equal o Unequal Passive interface. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 15.3, 15.4 16.3 15.3, 15.4 16.3 182 3.0 IP Services Recognize High availability (FHRP): 3.1 VRRP HSRP GLBP 13.3 Configure and verify syslog: 3.2 Utilize syslog output 17.2 3.3 Describe SNMP v2 and v3. 17.1 4.0 Troubleshooting 4.1 Identify and correct common network problems. 9.1 12.3 13.1 4.2 Utilize NetFlow data. 17.3 Troubleshoot and resolve Spanning Tree operation issues: 4.3 Root switch Priority Mode is correct Port states 12.2 Troubleshoot and resolve routing issues: 4.4 Routing is enabled Routing table is correct Correct path selection 13.1 15.5 16.1 Troubleshoot and resolve OSPF problems: 4.5 Neighbor adjacencies Hello and Dead timers OSPF area Interface MTU Network types Neighbor states OSPF topology database ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 15.5 183 Troubleshoot and resolve EIGRP problems: 4.6 Neighbor adjacencies AS number Load balancing Split horizon 15.5 Troubleshoot and resolve interVLAN routing problems: 4.7 Connectivity Encapsulation Subnet Native VLAN Port mode trunk status 13.2 Troubleshoot and resolve WAN implementation issues: 4.8 Serial interfaces PPP Frame relay 9.2 14.5, 14.8 4.9 Monitor NetFlow statistics. 17.3 4.10 Troubleshoot EtherChannel problems. 12.1 5.0 WAN Technologies Identify different WAN Technologies: 5.1 Metro Ethernet VSAT Cellular 3G/4G MPLS T1/E1 ISDN DSL Frame relay Cable VPN ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 2.8 14.1 14.2 14.4, 14.7 184 5.2 Configure and verify a basic WAN serial connection. 14.2 5.3 Configure and verify a PPP connection between Cisco routers. 14.3 5.4 Configure and verify frame relay on Cisco routers. 14.5 5.5 Implement and troubleshoot PPPoE. 14.6 ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 185 Appendix D: Exam 200-120: Cisco Certified Network Associate Objectives Exam 200-120: Cisco Certified Network Associate. For up-to-date information about this exam, visit www.cisco.com. Cisco offers two options for obtaining the CCNA certification: Pass Exam 200-120 OR Pass Exam 100-101 AND Exam 200-101 While you can use this TestOut product to prepare for either exam, the product is geared towards passing the Cisco 200-120 (CCNA) exam. We recommend you study all of the material and take the single exam option rather than taking two exams. This certification exam measures your ability to select, install, configure, and troubleshoot Cisco routers and switches. Before taking the exam, you should be proficient in the job skills listed below. In the spread sheet below the column to the right lists the sections where the information is located in the course: # Exam Objective Module.Section 1.0 Operation of IP Data Networks 1.1 Recognize the purpose and functions of various network devices, such as routers, switches, bridges, and hubs. 1.2 Select the components required to meet a given network specification. 1.3 Identify common applications and their impact on the network. 1.4 Describe the purpose and basic operation of the protocols in the OSI and TCP/IP models. 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8 1.5 Predict the data flow between two hosts across a network. 2.6 1.6 Identify the appropriate media, cables, ports, and connectors to connect Cisco network devices to other network devices and hosts in a LAN. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 2.2 2.1, 2.2 2.2 2.1, 2.7 186 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies 2.1 Determine the technology and media access control method for Ethernet networks. 2.1, 2.2, 2.7 Identify basic switching concepts and the operation of Cisco switches: 2.2 Collision Domains Broadcast Domains Types of switching CAM Table 4.1 Configure and verify initial switch configuration, including remote access management: 2.3 2.4 Cisco IOS commands to perform basic switch setup Verify network status and switch operation using basic utilities, such as ping, Telnet, and SSH. 3.1, 3.3, 3.5, 3.6 4.3, 4.4, 4.7, 4.8 9.1, 13.1 Describe how VLANs create logically separate networks and the need for routing between them: 2.5 2.6 Explain network segmentation and basic traffic management concepts. Configure and verify VLANs. 4.5 6.8 4.5 Configure and verify trunking on Cisco switches: 2.7 DTP Auto negotiation 4.6 Identify enhanced switching technologies: 2.8 RSTP PVSTP EtherChannels ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 4.2, 4.5, 4.6 12.1, 12.2 187 Configure and verify PVSTP operation: 2.9 Describe root bridge election Spanning Tree mode 4.2 12.2 3.0 IP addressing (IPv4/IPv6) 3.1 Describe the operation and necessity of using private and public IP addresses for IPv4 addressing. 3.2 Identify the appropriate IPv6 addressing scheme to satisfy addressing requirements in a LAN/WAN environment. 8.1 16.1 3.3 Identify the appropriate IPv4 addressing scheme using VLSM and summarization to satisfy addressing requirements in a LAN/WAN environment. 5.4 6.5 3.4 Describe the technological requirements for running IPv6 in conjunction with IPv4, such as dual stack. 8.2 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.5 8.1 Describe IPv6 addresses: 3.5 4.0 Global unicast Multicast Link local Unique local Eui 64 Autoconfiguration 8.1, 8.2 16.1 IP Routing Technologies Describe basic routing concepts: 4.1 CEF Packet forwarding Router lookup process Configure and verify utilizing the CLI to set basic router configuration: 4.2 Cisco IOS commands to perform basic router setup ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 6.1 3.3, 3.5, 3.6 4.4, 4.7, 4.8 188 4.3 Configure and verify the operation status of a device interface, both serial and Ethernet. 3.3, 3.6 4.3 14.2, 14.3 Verify router configuration and network connectivity: 4.4 4.5 Cisco IOS commands to review basic router information and network connectivity Configure and verify routing configuration for a static or default route given specific routing requirements. 4.9 9.1 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4 Differentiate methods of routing and routing protocols: 4.6 Static vs. Dynamic Link state vs. Distance Vector Administrative distance Split horizon Metric Next hop IP routing table Passive interfaces 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4 Configure and verify OSPF: 4.7 Benefit of single area Neighbor adjacencies OSPF states Discuss multi-area OSPF Configure OSPF v2 Configure OSPF v3 Router ID Passive interface LSA types 6.6, 6.7 8.3 15.1, 15.2 16.2 Configure and verify interVLAN routing (router on a stick): 4.8 4.9 Sub interfaces Upstream routing Encapsulation Configure SVI interfaces. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 6.9 6.9 189 Manage Cisco IOS Files: 4.10 Boot preferences Cisco IOS image(s) Licensing o Show license o Change license 11.1, 11.2 Configure and verify EIGRP (single AS): 4.11 5.0 Feasible distance/feasible successors/administrative distance Feasibility condition Metric composition Router ID Auto summary Path selection Load balancing o Equal o Unequal Passive interface 15.3, 15.4 16.3 IP Services Configure and verify DHCP (IOS router): 5.1 Configuring router interfaces to use DHCP DHCP options Excluded addresses Lease time 7.1 Describe the types, features, and applications of ACLs: 5.2 Standard o Sequence numbers o Editing Extended Named Numbered Log option 7.2 Configure and verify ACLs in a network environment: 5.3 Named Numbered Log option ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 7.3, 7.4 190 Identify the basic operation of NAT: 5.4 Purpose Pool Static 1 to 1 Overloading Source addressing One-way NAT 7.6 5.5 Configure and verify NAT for given network requirements. 7.7 5.6 Configure and verify NTP as a client. 7.8 Recognize High availability (FHRP): 5.7 VRRP HSRP GLBP 13.3 Configure and verify syslog: 5.8 Utilize syslog output 5.9 Describe SNMP v2 and v3. 6.0 Network Device Security 17.2 17.1 Configure and verify network device security features, such as: 6.1 Device password security Enable secret vs. enable Transport o Disable Telnet o SSH VTYs Physical security Service password Describe external authentication methods ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 3.6 4.7, 4.8 191 Configure and verify Switch Port Security features, such as: 6.2 Sticky MAC MAC address limitation Static/dynamic Violation modes o Err disable o Shutdown o Protect restrict Shutdown unused ports Err disable recovery Assign unused ports to an unused VLAN Setting native VLAN to other than VLAN 1 6.3 Configure and verify ACLs to filter network traffic. 6.4 Configure and verify ACLs to limit Telnet and SSH access to the router. 7.0 Troubleshooting 7.1 Troubleshoot and correct common problems associated with IP addressing and host configurations. 4.5, 4.6, 4.7 6.9 7.4, 7.5 7.4 9.1 Troubleshoot and resolve VLAN problems: 7.2 Identify that VLANs are configured Verify port membership correct Correct IP address configured 9.2 Troubleshoot and resolve trunking problems on Cisco switches: 7.3 Correct trunk states Correct encapsulation configured Correct VLANs allowed 9.2 Troubleshoot and resolve ACL issues: 7.4 Statistics Permitted networks Direction Interface ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 7.4 9.3 192 Troubleshoot and resolve Layer 1 problems: 7.5 7.6 Framing CRC Runts Giants Dropped packets Late collision Input/Output errors Identify and correct common network problems. 9.2 9.1 12.3 13.1 Troubleshoot and resolve Spanning Tree operation issues: 7.7 Root switch Priority Mode is correct Port states 12.2 Troubleshoot and resolve routing issues: 7.8 Routing is enabled Routing table is correct Correct path selection 13.1 15.5 16.1 Troubleshoot and resolve OSPF problems: 7.9 Neighbor adjacencies Hello and Dead timers OSPF area Interface MTU Network types Neighbor states OSPF topology database 15.5 Troubleshoot and resolve EIGRP problems: 7.10 Neighbor adjacencies AS number Load balancing Split horizon ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 15.5 193 Troubleshoot and resolve interVLAN routing problems: 7.11 Connectivity Encapsulation Subnet Native VLAN Port mode trunk status 13.2 Troubleshoot and resolve WAN implementation issues: 7.12 Serial interfaces PPP Frame relay 9.2 14.5, 14.8 7.13 Monitor NetFlow statistics. 17.3 7.14 Troubleshoot EtherChannel problems. 12.1 8.0 WAN Technologies Identify different WAN Technologies: 8.1 Metro Ethernet VSAT Cellular 3G/4G MPLS T1/E1 ISDN DSL Frame relay Cable VPN 2.8 14.1 14.2, 14.4, 14.7 8.2 Configure and verify a basic WAN serial connection. 14.2 8.3 Configure and verify a PPP connection between Cisco routers. 14.3 8.4 Configure and verify frame relay on Cisco routers. 14.5 8.5 Implement and troubleshoot PPPoE. 14.6 ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 194 Appendix E: TestOut Routing Pro Exam Objectives The TestOut Routing Pro Exam covers the following objectives: Exam Objective 1.0 Router Setup and Configuration View router configuration information. Configure router hostnames and interface descriptions. Configure router banners. Manage router configuration files. Manage router IOS files. 2.0 4.3, 4.4 14.2, 14.3, 14.4, 14.5,14.6, 14.8 IP Routing Implementation Calculate and configure subnet masks for network hosts. Configure static routes on a router. View the routing table on a router. Manage auto-summarization between networks. Configure router-on-a-stick interVLAN routing. Troubleshoot WAN communication issues using utilities, such as ping and tracert. 4.0 3.2, 3.3, 3.5 11.1,11.2 Router Setup and Configuration View the status of router interfaces. View directly connected devices using CDP. Configure Ethernet and serial router interfaces. Configure TCP/IP settings on a router interface. Configure a PPP connection between routers. Configure PPPoE connections on a router. Troubleshoot router connections. 3.0 Module.Section 5.5 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.9 14.8 OSPF Routing Configuration Enable OSPF routing. Configure and manage OSPF routing. Troubleshoot OSPF routing. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 6.7 15.1, 15.2, 15.5 16.2 195 5.0 EIGRP Routing Configuration Enable EIGRP routing. Configure and manage EIGRP routing. Troubleshoot EIGRP routing. 6.0 Access Control List Configuration Implement standard, extended, and named ACLs. Use wildcard masks in ACLs. Use ACLs to manage network traffic: o Permit allowed traffic. o Block disallowed traffic. 7.0 14.5 NAT Configuration Configure static NAT on a router. Configure dynamic NAT on a router. Configure overloaded PAT on a router. 9.0 7.3, 7.4, 7.5 Frame Relay Configuration Enable Frame Relay on a router. Configure Frame Relay static mappings. Configure point-to-point Frame Relay. Configure multipoint Frame Relay. 8.0 15.4, 15.5 16.3 7.7 DHCP Server Configuration Configure the DHCP service on a router. Configure DHCP bindings. Configure a DHCP relay agent. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 7.1 196 10.0 Router Security Configuration Restrict router access. Configure router passwords. Configure remote access to a router using SSH. 3.6, 4.4 11.0 High Availability Configuration Configure GLBP. Configure VRRP. Configure HSRP. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 13.3 197 Appendix F: TestOut Routing Pro Exam Objectives The TestOut Switching Pro Exam covers the following objectives: Exam Objective 1.0 Switch Setup and Configuration View switch configuration information. Configure switch hostnames and interface descriptions. Configure switch banners. Manage switch configuration files. Manage switch IOS files. 2.0 4.4 VLAN Configuration View information about VLANs configured on a switch. Manage default VLAN configuration settings. Configure VLANs on a switch. Extend VLANs to multiple switches using trunking. Troubleshoot VLAN issues. Troubleshoot trunking issues. 5.0 4.3, 4.4, 4.9 TCP/IP Configuration Configure switch TCP/IP settings. Troubleshoot LAN communications. 4.0 3.2, 3.3, 3.5 11.1, 11.2 Switch Interface Configuration View directly connected network devices using CDP. Mange the CDP configuration. Configure interface speed and duplex settings. View the status of switch interfaces. 3.0 Module.Section 4.4, 4.5, 4.6 9.2 InterVLAN Routing Configure interVLAN routing. Troubleshoot interVLAN routing issues. ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 6.9 13.2 198 6.0 Spanning Tree Configuration View STP configuration information. Manually configure a switch as a root bridge. Configure Rapid PVST+. Troubleshoot STP issues. 7.0 Switch Security Restrict access to a switch. Configure switch passwords. Disable switch interfaces. Enable switch port security. Configure remote access to a switch using SSH. 8.0 4.2 12.2 3.6 4.3, 4.7, 4.8 EtherChannel Configuration Configure EtherChannel using the following: o PAGP o LACP ©2014 TestOut Corporation (Rev 12/14) Routing and Switching Pro 12.1 199