Routing, Switching and WAN Technologies - Kiamichi
advertisement

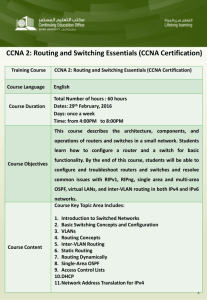
Routing, Switching, and WAN Technologies Syllabus Course Title: Routing, Switching, and WAN Technologies (Cisco Level III and IV) Course Number: 8487 Career Cluster/Pathway: Information Technology/Network Systems Career Pathway/Major(s): Enterprise Network Associate, Enterprise Network Professional, Network Systems Specialist, Network Security Specialist, Network Security Professional, Secure E-Commerce Professional, Cyber Security Professional Pre-requisite: Network and Routing Fundamentals (Cisco Level I and II) Locations: Kiamichi Technology Center, Poteau Campus Length: 1 Carnegie Unit (100 hours theory/ 50 hours lab) Course Description: Students will cover curriculum pertaining to CCNA, Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing and WAN Technologies, which is the second half of four courses leading to the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) designation. The Cisco Networking Academy Program is a comprehensive e-learning program that provides students with the Internet technology skills essential in a global economy. Specific Learning Competencies - Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Understand classless routing. 2. Define VLSM and briefly describe the reasons for its use. 3. Divide a major network into subnets of different sizes using VLSM. 4. Define route aggregation and summarization as they relate to VLSM. 5. Configure a router using VLSM. 6. Identify the key features of RIP v1 and RIP v2. 7. Identify the important differences between RIP v1 and RIP v2. 8. Configure RIP v2. 9. Verify and troubleshoot RIP v2 operation. 10. Configure default routes using the IP route and IP default-network commands. 11. Describe how link-state routing algorithms, also known as shortest path first (SPF) algorithms, maintain a complex database of topology information. 12. Explain how the EIGRP routing protocol works. 13. Outline the features of the EIGRP routing protocol. 14. Describe the algorithm the EIGRP routing protocol uses. Routing, Switching, and WAN Technologies April 2008 Page 1 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of EIGRP routing. Install switches, explain switching concepts, and perform switching configurations. Describe the five Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) states. Configure switches to create virtual LANs and perform troubleshooting as needed. Explain VLAN Trunking Protocol and Inter-VLAN routing. Demonstrate advanced IP addressing techniques. Explain WAN technology and terminology. Configure Point-to-Point Protocol. Define the ISDN standards used for addressing, concepts, and signaling. Describe how ISDN uses the physical and data link layers. List the interfaces and reference points for ISDN. Configure the router ISDN interface. Determine what traffic is allowed when configuring DDR. Configure static routes for DDR. Choose the correct encapsulation type for DDR. Be able to determine and apply an access list affecting DDR traffic. Configure dialer interfaces. Explain the scope and purpose of Frame Relay. Discuss the technology of Frame Relay. Compare point-to-point and point-to-multipoint topologies. Examine the topology of a Frame Relay network. Configure a Frame Relay Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC). Create a Frame Relay Map on a remote network. Explain the issues of a non-broadcast multi-access network. Describe the need for sub interfaces and how to configure them. Verify and troubleshoot a Frame Relay connection. Identify several potential tasks performed by a workstation. Identify several potential functions of a server. Describe the roles of equipment in a client/server environment. Describe the differences between a NOS and a desktop operating system. List several Windows operating systems and their features. List several alternatives to the Windows operating systems and their features. Identify network management tools. Identify the driving forces behind network management. Describe the OSI and network management model. Describe simple network management protocol (SNMP) and common management information protocol (CMIP). 51. Describe how management software gathers information and records problems. 52. Perform network management. 53. Understand Optical Networking. Instruction: 75 Hours Intermediate Routing and Switching (Cisco Level 3) 75 Hours WAN Technologies (Cisco Level 4) Routing, Switching, and WAN Technologies April 2008 Page 2 Methods of Instruction: Lecture, class discussions, hands-on-training, demonstrations, projects and performance evaluation. Required Certifications: (Select one of the following options) ODCTE: None Cisco: CCNA OR End-of-course exams (Level 3 and 4) Brainbench: Select 2: Cisco Network Support IP Routing and Switching Cisco Network Design Microsoft: Microsoft Certified Professional (MCP) Microsoft Certified Systems Administrator (MCSA) Recommended Certifications: Recognized Primary Course Textbooks and Instructional Resources: Cisco Networking Academy Online Curriculum Routing, Switching, and WAN Technologies April 2008 Page 3