Western Europe - Economics - Mrs. Oliver's World Geography
advertisement

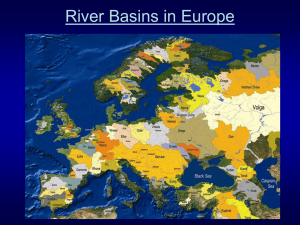
Western Europe - Economics How does cooperation among countries impact the economies of the countries? A. Trade is hurt. B. Trade is helped. C. There is no impact on trade. Physical features that aid economic development Europe has two major river systems the Rhine and Danube: • Transport goods between coastal harbors and inland regions Economic Dev Con’d What is the main source of water for the Rhine River? • The Rhine River System • 820 miles long, mouth is the North Sea • Flows from Alps through Switzerland, France, Germany, • Major industrial areas: • Ruhr Valley in Germany (iron and steel) • Alsace Lorraine (coal and iron ore) region in France Economic Dev Con’d Danube River System: • Flows West to East, 1771 miles from Alps to the Black Sea. • The chemical, food, and paper industries are amongst the main industrial polluters in the Danube River Basin • Allows trade between Eastern and Western Europe What economic impact does industrial pollution have on rivers? 6 How does the direction in which European rivers flow aid in linking Europeans to the World? Because they flow toward different seas, the rivers help Europeans to travel to other regions. Economics, Technology, and Environment Agriculture in Western Europe • 33% of all land is arable • World average 11% What does Usable for arable mean? farming • NORTHERN EUROPEAN PLAIN • One of most Fertile regions in the world • Extends through France, Belgium, Netherlands, Denmark, Germany and Poland • Crops include - Grains, Grapes, Olives PREVAILING WESTERLIES BLOW WARM WINDS OVER EUROPE LEADING TO MORE THAN ADEQUATE RAINFALL FOR AGRICULTURE PRODUCTION THE NORTH ATLANTIC DRIFT WARM WATER CURRENT Mineral Resources in Western Europe • Abundance of Coal and Iron Ore needed for an industrialized economy - needed to produce steel • North Sea Oil Fields are major source of petroleum and Natural Gas • UK, Norway, Denmark, and Netherlands • Timber and Lumber Products come from Scandinavian Forests Mineral Resources con’d •Ireland (No Coal) –Use Peat for heat and energy: •Peat is partially decayed plant matter found in bogs or swamps • The Industrial Revolution transformed Western Europe from an agricultural society to an industrial society. 6 • Manufacturing and trade are the dominant economic activities in large parts of Western Europe. • Commercial farming is practiced through most of Western Europe. • Hydroelectric power is produced in more mountainous areas. Industrial Revolution • Urbanization (movement from rural to urban living) • Western Europe was one of first regions in the world to industrialize. • Great Britain was first and remained a leader in the industrial revolution • Four top Manufacturing Countries in Western Europe– England, France, Germany and Netherlands • Products include: • Automobiles, High Speed Trains, Aero Space, Electronics, Computers, Paper Products and Food Products. • Switzerland is known for Service Industries and luxury items such as International Banking and fine watches (Rolex) Tourism Have any of you been to Europe? If not, do you want to go? If so, share your experience. Trade within Europe and between Europe and the rest of the world is changing as a result of the European Union and changes in the political and economic landscape of eastern Europe. • The goal of the EU is to make Europe’s economies competitive with the rest of the world by getting rid of restrictions on the movement of goods, services, and people across its members’ borders. DFS Trans 1 Western Europe Economic Notes • The Rhine and Danube rivers aid in economic development • The Rhine allows trade across Northern and Southern Europe • The Danube allows trade between Western and Eastern Europe • Agriculture- 33% arable land • Northern European Plain- one of the most fertile regions in world. • grapes, olives, grains • Minerals- Coal, Iron ore, Petroleum, Natural Gas, and timber • Peat-partially decayed plant matter found in bogs or swamps (used as fuel in Ireland) • Great Britain was the first in the Industrial Revolution • European Union • The goal of the EU is to make Europe’s economies competitive with the rest of the world by getting rid of restrictions on the movement of goods, services, and people across its members’ borders.