Chapter 9
advertisement

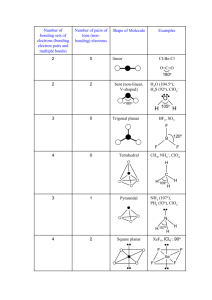
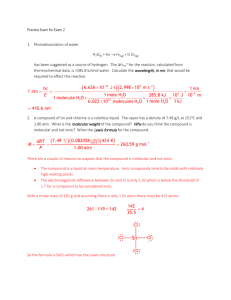
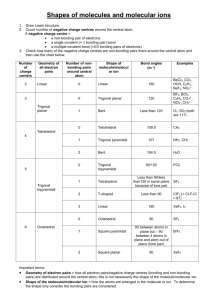
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory • based on idea that regions of electron density in valence shell of central atom will be distributed in space such that electrostatic repulsions are minimized • places regions of electron density as far apart as possible • produces molecular geometry Steps in Predicting Molecular Geometry • draw Lewis structure of substance • count regions of electron density on central atom • draw electron pair shape • derive and draw molecular geometry Regions of Electron Density • • • • • single covalent bond double covalent bond triple covalent bond lone pair unpaired electron # Regions 2 Shape linear 180° # Regions Shape 2 linear 3 trigonal planar 180° 120° # Regions Shape 2 linear 3 trigonal planar 4 tetrahedral 180° 120° 109.5° 90° 5 trigonal bypyramidal 120° 90° 5 trigonal bypyramidal 120° 6 octahedral 90° Examples Determine the electron-pair and molecular geometries of each of the following. Draw and name each. Beryllium Chloride Beryllium Chloride BeCl2 Beryllium Chloride BeCl2 1. Lewis structure Beryllium Chloride BeCl2 1. Lewis structure Cl Be Cl Beryllium Chloride BeCl2 1. Lewis structure Cl Be Cl 2. Count regions of electron density on central atom Beryllium Chloride BeCl2 1. Lewis structure Cl Be Cl 2. Count regions of electron density on central atom 2 Beryllium Chloride BeCl2 1. Lewis structure Cl Be Cl 2. Count regions of electron density on central atom 2 3. Draw and name electron-pair shape Be Cl Cl linear Beryllium Chloride BeCl2 3. Draw and name electron-pair shape Cl Be Cl linear 3. Derive and name molecular shape Cl Be Cl linear Carbon Dioxide Carbon Dioxide CO2 Carbon Dioxide CO2 O C O Carbon Dioxide CO2 O C O 2 regions Carbon Dioxide CO2 O C O 2 regions Electron-pair shape, linear O C O Carbon Dioxide CO2 O C O 2 regions Electron-pair shape, linear O C O Molecular shape, linear O C O Aluminum Bromide Aluminum Bromide AlBr3 Br Br Al Br Aluminum Bromide AlBr3 Br Br Al Aluminum Bromide AlBr3 3 regions Br Br Aluminum Bromide AlBr3 Electron-pair shape 3 regions trigonal planar Al Br Br Br Br Al Br Br Aluminum Bromide AlBr3 Electron-pair shape 3 regions trigonal planar Al Br Br Br Molecular shape Al trigonal planar Br Br Br Br Al Br Nitrite Ion Nitrite Ion NO2– O N O – Nitrite Ion NO2– O N O 3 regions – Nitrite Ion NO2– O N O 3 regions – Nitrite Ion NO2– Electron-pair shape trigonal planar – O N O O N O 3 regions – Nitrite Ion NO2– Electron-pair shape trigonal planar – O N O O N O 3 regions Nitrite Ion NO2– – Electron-pair shape trigonal planar Molecular shape bent O N – O – O N O Carbon Tetrabromide Carbon Tetrabromide CBr4 Br Br C Br Br Carbon Tetrabromide CBr4 Br Br C Br Br Carbon Tetrabromide CBr4 4 regions Br Br C Br Br Carbon Tetrabromide CBr4 4 regions Electron-pair shape tetrahedral Br C Br Br Br Br Br Carbon Tetrabromide CBr4 4 regions C Electron-pair shape Br Br tetrahedral Br Molecular shape C tetrahedral Br Br Br Arsine Arsine AsH3 Arsine AsH3 H As H H Arsine AsH3 H As H H 4 regions electron-pair shape, tetrahedral Arsine AsH3 H As 4 regions electron-pair shape, tetrahedral H H As H H H Arsine AsH3 H As 4 regions electron-pair shape, tetrahedral H H molecular shape trigonal pyramid or tripod As H H H Arsine AsH3 H As 4 regions electron-pair shape, tetrahedral H H molecular shape trigonal pyramid or tripod As H H H As H H H Water H 2O Water H 2O O H H Water H 2O O H H 4 regions electron-pair shape tetrahedral Water H 2O O H H O H H 4 regions electron-pair shape tetrahedral Water H 2O O H H molecular shape bent O H 4 regions electron-pair shape tetrahedral H Water H 2O O H H molecular shape bent O H 4 regions electron-pair shape tetrahedral H O H H Phosphorus Pentafluoride Phosphorus Pentafluoride PF5 F F F P F F Phosphorus Pentafluoride PF5 F F F 5 regions P electron-pair shape F F trigonal bipyramidal F F F P F F Phosphorus Pentafluoride PF5 F F F 5 regions P electron-pair shape F F trigonal bipyramidal F F F P F F molecular shape trigonal bipyramidal Sulfur Tetrafluoride Sulfur Tetrafluoride SF4 F F S F F Sulfur Tetrafluoride SF4 F F S F F Sulfur Tetrafluoride SF4 5 regions trigonal bipyramidal F F S F F Sulfur Tetrafluoride SF4 5 regions trigonal bipyramidal F F S F F F F S F F F F S F Sulfur Tetrafluoride SF4 5 regions trigonal bipyramidal molecular shape distorted tetrahedral F F F S F F F F S F F F F S F Sulfur Tetrafluoride SF4 5 regions trigonal bipyramidal molecular shape see saw F F S F F F Chlorine Trifluoride Chlorine Trifluoride ClF3 F Cl F F Chlorine Trifluoride ClF3 F Cl F F Chlorine Trifluoride ClF3 5 regions electron-pair shape trigonal bipyramidal Chlorine Trifluoride ClF3 F 5 regions Cl electron-pair shape F F trigonal bipyramidal F F Cl F Chlorine Trifluoride ClF3 F 5 regions Cl electron-pair shape F F trigonal bipyramidal F F Cl F Chlorine Trifluoride ClF3 F 5 regions Cl electron-pair shape F F trigonal bipyramidal F molecular shape T-shape F F Cl F F Cl F Sulfur Hexafluoride Sulfur Hexafluoride SF6 F F F S F F F Sulfur Hexafluoride SF6 Sulfur Hexafluoride SF6 F F 6 regions F S electron-pair shape F F octahedral F F F F S F F F Sulfur Hexafluoride SF6 F F 6 regions F S electron-pair shape F F octahedral F F molecular shape F F octahedral S F F F Bromine Pentafluoride Bromine Pentafluoride BrF5 Bromine Pentafluoride BrF5 F Br F F F F Bromine Pentafluoride BrF5 F Br F F F F 6 regions electron-pair shape octahedral Bromine Pentafluoride BrF5 F Br F F F F F 6 regions electron-pair shape octahedral F F Br F F Bromine Pentafluoride BrF5 F Br F F F F F 6 regions electron-pair shape octahedral F F Br F F Bromine Pentafluoride BrF5 6 regions F F electron-pair shape Br octahedral molecular shape F F square pyramidal F F F F F F F Br Br F F F F Xenon Tetrafluoride Xenon Tetrafluoride XeF4 F F Xe F F Xenon Tetrafluoride XeF4 F F Xe F F Xenon Tetrafluoride XeF4 6 regions electron-pair shape octahedral Xenon Tetrafluoride XeF4 F F Xe F F F 6 regions electron-pair shape octahedral F Xe F F Xenon Tetrafluoride XeF4 F F Xe F F 6 regions electron-pair shape octahedral F F Xe F F Xenon Tetrafluoride XeF4 F F Xe F F 6 regions electron-pair shape octahedral F F Xe F F molecular shape square planar F F Xe F F Tribromide Ion Br3– Br Br Br Tribromide Ion Br3– Br Br Br Tribromide Ion Br3– 5 regions electron-pair shape trigonal bipyramidal Br Tribromide Ion Br3– Br Br 5 regions electron-pair shape trigonal bipyramidal Br Br Br Br Tribromide Ion Br3– Br Br 5 regions electron-pair shape trigonal bipyramidal Br Br Br Br Tribromide Ion Br3– Br Br 5 regions electron-pair shape trigonal bipyramidal Br molecular shape linear Br Br Br Br Br Polarity of Molecules • molecules in which dipole moments of the bonds do not cancel are polar molecules • molecules that do not contain polar bonds or in which all dipole moments cancel are non-polar molecules CO2 O C O vs H2O O H H CO2 – O + C – O vs H2O – O H + H + CO2 – O + C – O vs H2O – O H + H + CO2 – O + C 0 – O vs H2O – O H + H + CO2 – O + C 0 – O vs H2O – O H + H + CO2 vs H2O H + – O + C – O y – O H + x y 0 x CO2 vs H2O – O H + H + – O + C – O y y x x CO2 – O + C – O nonpolar vs H2O – O H + H + polar Study and Know 9.2 Polarity of Molecules VSEPR Theory only explains molecular shapes says nothing about bonding in molecules Enter Valence Bond (VB) Theory atoms share electron pairs by allowing their atomic orbitals to overlap + H H + H H bond + H H E 1s H bond + H H E H 1s H bond + F F F2 + F F F2 bond 2p E 2s 1s F F 2p E 2s 1s F Methane CH4 2p E 2s 1s C Methane CH4 H H 2p E 2s 1s C Methane CH4 H H+ E 2p 2s 1s H C Methane CH4 H H+ E 2p 2s 1s H H– C Methane CH4 H H+ E H H– 2p H 2s H C C H 90° H 1s 90° Methane CH4 H 109.5° C H H H Tetrahedral Geometry 4 Identical Bonds Problem and Solution C must have 4 identical orbitals in valence shell for bonding solution: hybridization Methane CH4 2p E 2s 1s Methane CH4 2s 2p E 2s 1s E 1s 2p Methane CH4 2s 2p E 2s 1s E 1s 2p Methane CH4 2s 2p E 2s 1s E 1s 2p Methane CH4 2p E 2s 1s sp3 E 1s + – + + 2p 2s + – + + 2p = 2s an sp3 hybrid orbital 4 identical sp3 hybrid orbitals 4 identical sp3 hybrid orbitals tetrahedral geometry 4 identical sp3 hybrid orbitals tetrahedral geometry 4 identical sp3 hybrid orbitals tetrahedral geometry Methane CH4 H 2p E 2s 1s H H sp3 E 1s H Hybridization vs Shape (e– pair) • • • • • sp sp2 sp3 sp3d sp3d2 linear trigonal planar tetrahedral trigonal bipyramidal octahedral Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in tribromide ion Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in tribromide ion Br3– Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in tribromide ion Br3– Br Br Br 5 regions electron-pair shape trigonal bypyramidal Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in tribromide ion Br3– Br Br Br 5 regions electron-pair shape trigonal bypyramidal sp3d Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in carbon dioxide CO2 Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in carbon dioxide CO2 O C O 2 regions Electron-pair shape, linear Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in carbon dioxide CO2 O C O 2 regions Electron-pair shape, linear sp Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in aluminum bromide Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in aluminum bromide Br Br Al Br Electron-pair shape 3 regions trigonal planar Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in aluminum bromide Br Br Al Br Electron-pair shape 3 regions trigonal planar sp2 Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in xenon tetrafluoride Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in xenon tetrafluoride F F Xe F F 6 regions electron-pair shape octahedral Predict the Hybridization of the Central Atom in xenon tetrafluoride F F Xe F F 6 regions electron-pair shape octahedral sp3d2 Consider Ethylene, C2H4 Consider Ethylene, C2H4 H H C H C H Consider Ethylene, C2H4 H H C C H 3 regions trigonal planar H Consider Ethylene, C2H4 H H C C H 3 regions trigonal planar sp2 H Consider Ethylene, C2H4 H H C H C H 3 regions trigonal planar 2 sp 2p E 2s 1s 2s 2p E 2s 1s E 1s 2p 2p E 2s 1s sp2 E 1s 2p sp2 2p sp2 sp2 2p sp2 sp2 sp2 bond framework bond bond Consider Acetylene, C2H2 H C C H Consider Acetylene, C2H2 H C 2 regions linear C H Consider Acetylene, C2H2 H C C 2 regions linear sp H Consider Acetylene, C2H2 H C C H 2 regions linear sp 2s 2p E 2s 1s E 1s 2p 2p E 2s 1s sp E 1s 2p 2p sp 2p sp bond framework bonds bonds Generally • single bond is a bond • double bond consists of 1 and 1 bond • triple bond consists of 1 and 2 bonds Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory when atoms combine to form molecules, atomic orbitals overlap and are then combined to form molecular orbitals orbitals are conserved a molecular orbital is an orbital associated with more than 1 nucleus like any other orbital, an MO can hold 2 electrons consider hydrogen atoms bonding to form H2 + H H subtract add subtract antibonding add bonding subtract antibonding *1s add bonding 1s *1s E E 1s 1s 1s H H2 H *1s E E 1s 1s 1s H H2 H *1s E E 1s 1s 1s H H2 H *1s E E 1s 1s 1s H H2 H (1s ) 2 *1s E E 1s 1s 1s H H2 H (1s ) 2 total spin = 0 *1s E E 1s 1s 1s H H2 H • Diamagnetic: slightly repelled by a magnetic field total spin = 0 • paramagnetic: attracted to a magnetic fiels total spin not 0 • Bond Order = 1/2 (bonding e– – antibonding e–) (1s ) 2 total spin = 0 diamagnetic *1s E E 1s 1s 1s H H2 H BO = 1/2 ( 2 – 0) = 1 *1s E E 1s 1s 1s H H2 H Consider He2 *1s E E 1s 1s 1s He He2 He *1s E E 1s 1s 1s He He2 He (1s ) 2 ( *1s ) 2 *1s E E 1s 1s 1s He He2 He diamagnetic *1s E E 1s 1s 1s He He2 He BO = 1/2 ( 2 – 2 ) = 0 *1s E E 1s 1s 1s He He2 He Combination of p Atomic Orbitals 2p 2p subtract add antibonding MO subtract add bonding MO subtract antibonding MO *2p add bonding MO 2p 2p 2p subtract add subtract antibonding MO add bonding MO subtract *2p add 2p subtract *2p add 2p Consider Li2 *2p *2p 2p E 2p 2p E 2p *2s 2s 2s Li 2s Li2 Li *2p *2p 2p E 2p 2p E 2p *2s 2s 2s Li 2s Li2 Li *2p *2p 2p E 2p 2p E 2p *2s 2s 2s Be 2s Be2 Be *2p *2p 2p E 2p 2p E 2p *2s 2s 2s Be 2s Be2 Be *2p *2p 2p E 2p 2p E 2p *2s 2s 2s B 2s B2 B *2p *2p 2p E 2p 2p E 2p *2s 2s 2s B 2s B2 B *2p *2p 2p E 2p 2p E 2p *2s 2s 2s C 2s C2 C *2p *2p 2p E 2p 2p E 2p *2s 2s 2s N 2s N2 N *2p *2p 2p E 2p 2p E 2p *2s 2s 2s O 2s O2 O *2p *2p 2p E 2p 2p E 2p *2s 2s 2s F 2s F2 F *2p *2p 2p E 2p 2p E 2p *2s 2s 2s Ne 2s Ne2 Ne


![VSEPR [Compatibility Mode]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008210566_1-9238cc104b5d8abec6ce7a8d91d0b7ef-300x300.png)