Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks
advertisement
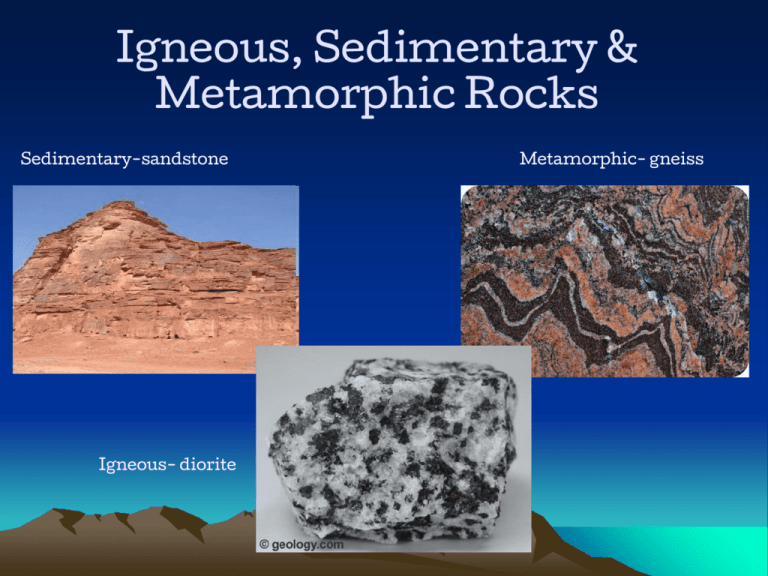
Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks Sedimentary-sandstone Igneous- diorite Metamorphic- gneiss 1. What is a Rock? • Naturally Occurring (not man made) • Solid • Mixture of minerals other organic matter 2. What makes a rock different from a mineral? Rock Both Mineral Made of one or more minerals Solid Made of one type of element Random crystal or no crystal structure Naturally Occurring Orderly crystal structure ←Granite= Quartz+ Feldspar+ Muscovite Igneous Rocks 3. Magma & Lava form different types of igneous rock • Igneous rock is classified by where rock forms Intrusive vs. Extrusive forms when magma/lava forms when magma cools inside the earth surface exits & cools on earth’s surface Intrusive Vs. Extrusive Diorite Granite Basalt Pegmatite Gabbro Rhyolite Andesite Scoria 4. Igneous Rocks: Crystal size & Cooling Time Location of Rock Crystal Size Intrusive (in earth) Extrusive (earth surface) Large crystals Small crystals Longer cooling time Shorter cooling time Picture Cooling time Sedimentary Rock 5. Some rocks form from rock particles •Sediment= materials that settles out of water or air – Materials can be: • tiny pieces of rock • broken minerals • pieces of plants and animal remains 6. How do sedimentary rocks form? • Sediments pile on top of each other on land or in water • As sediments pile, they become compacted and cement together Sedimentation Process Sedimentary rock layers Rock layers www.eos.ubc.ca/courses/eosc320/eosc320.htm 7. Some rocks form from plants or shells • Coal- created from plant remains (dead wood, bark, leaves, stems, and roots) – The coal we use today started forming millions of year ago in swamps • Limestone- created from the shells and skeletons of ocean organisms Can you see the plant remains? http://www.geology.pitt.edu/PAgeo/coal.html Limestone formation Metamorphic Rocks 8. Metamorphic Rocks • Heat and pressure change rocks – The original rock is called the parent rock – The new rock formed is called the metamorphic rock – Heat and pressure change the structure of the parent rock and their minerals recrystallize 9. Examples of Metamorphic Rocks Parent Rock= Shale Metamorphic Rock = Slate Increase Temp. & Pressure Examples of Metamorphic Rocks Parent Rock = Limestone Metamorphic Rock = Marble Increase Temp. & Pressure Examples of Metamorphic Rocks Parent Rock = Mica Metamorphic Rock = Phyllite Increase Temp. & Pressure 10. When a rock forms does it stay that way forever? NO!!!!!! • Rocks are always changing by processes like: – Weathering – Erosion – Compaction – Heat -Melting -Cooling -Cementation -Pressure Composition of Igneous Rocks •Igneous rocks are mainly composed of silicate minerals (quartz, feldspar,etc.) •Rocks with high silicate levels-are typically light in color •ex: granite, rhyolite •Rocks with low silicate levels- dark in color •ex: gabbro and basalt Igneous rocks make long-lasting landforms 1. Intrusive rock formations-as magma pushes up toward Earth’s surface, it makes channels and other formations underground. 2. Extrusive rock formations• builds plateaus when erupting from long crack • gently sloping volcanoes (Hawaiian islands) • cone-shaped volcanoes (1). contains greater amount of silica (2). erupts explosively (3). Mount St. Helens is an example •Rock cycle-the set of natural processes that form, change, break down, and reform rocks Our world is built of rocks Rocks have many purposes 1. used to build houses and skyscrapers 2. great source of metals 3. used to carve statues and other works of art 11. Rock Cycle Rock Cycle animation








