Unit 3 exam review answers
advertisement
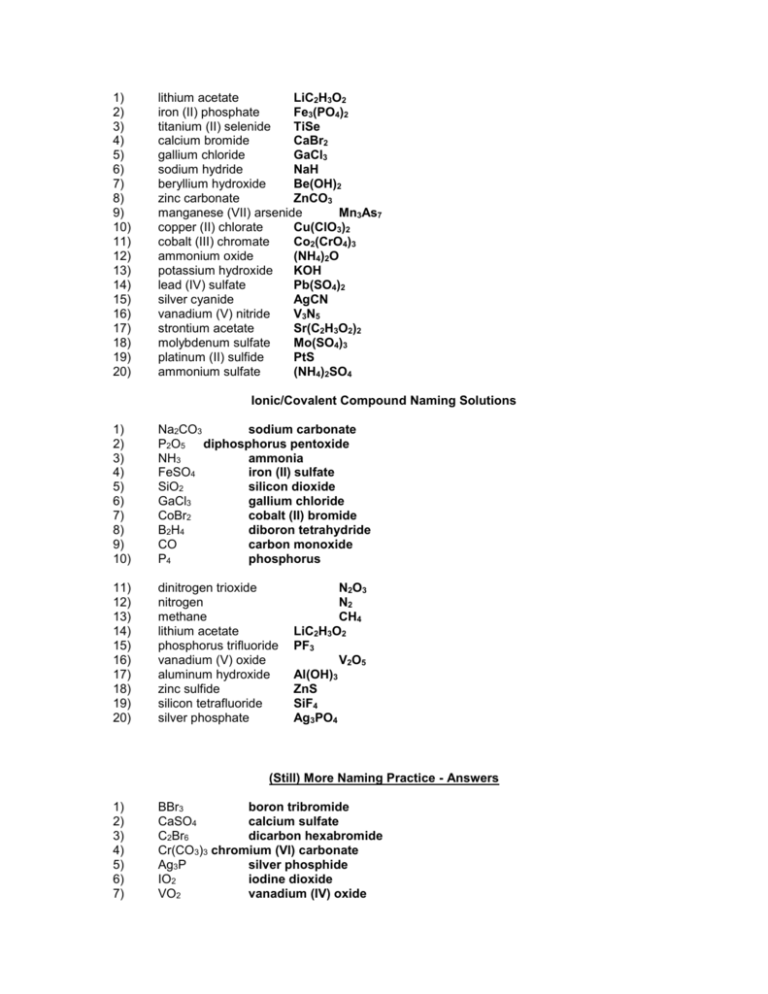
1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) 18) 19) 20) lithium acetate LiC2H3O2 iron (II) phosphate Fe3(PO4)2 titanium (II) selenide TiSe calcium bromide CaBr2 gallium chloride GaCl3 sodium hydride NaH beryllium hydroxide Be(OH)2 zinc carbonate ZnCO3 manganese (VII) arsenide Mn3As7 copper (II) chlorate Cu(ClO3)2 cobalt (III) chromate Co2(CrO4)3 ammonium oxide (NH4)2O potassium hydroxide KOH lead (IV) sulfate Pb(SO4)2 silver cyanide AgCN vanadium (V) nitride V3N5 strontium acetate Sr(C2H3O2)2 molybdenum sulfate Mo(SO4)3 platinum (II) sulfide PtS ammonium sulfate (NH4)2SO4 Ionic/Covalent Compound Naming Solutions 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) Na2CO3 sodium carbonate P2O5 diphosphorus pentoxide NH3 ammonia FeSO4 iron (II) sulfate SiO2 silicon dioxide GaCl3 gallium chloride CoBr2 cobalt (II) bromide B2H4 diboron tetrahydride CO carbon monoxide P4 phosphorus 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) 18) 19) 20) dinitrogen trioxide nitrogen methane lithium acetate phosphorus trifluoride vanadium (V) oxide aluminum hydroxide zinc sulfide silicon tetrafluoride silver phosphate N2O3 N2 CH4 LiC2H3O2 PF3 V2O5 Al(OH)3 ZnS SiF4 Ag3PO4 (Still) More Naming Practice - Answers 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) BBr3 boron tribromide CaSO4 calcium sulfate C2Br6 dicarbon hexabromide Cr(CO3)3 chromium (VI) carbonate Ag3P silver phosphide IO2 iodine dioxide VO2 vanadium (IV) oxide 8) 9) 10) PbS CH4 N2O3 lead (II) sulfide methane dinitrogen trioxide Write the formulas of the following chemical compounds: 11) tetraphosphorus triselenide P4Se3 12) potassium acetate KC2H3O2 13) iron (II) phosphide Fe3P2 14) disilicon hexabromide Si2Br6 15) titanium (IV) nitrate Ti(NO3)4 16) diselenium diiodide Se2I2 17) copper (I) phosphate Cu3PO4 18) gallium oxide 19) tetrasulfur dinitride S4N2 20) phosphorus P4 Ga2O3 Answers – Naming Chemical Compounds 1) NaBr sodium bromide 2) Ca(C2H3O2)2 calcium acetate 3) P2O5 4) Ti(SO4)2 titanium(IV) sulfate 5) FePO4 iron(III) phosphate 6) K3N potassium nitride 7) SO2 8) CuOH 9) Zn(NO2)2 10) V2S3 diphosphorus pentoxide sulfur dioxide copper(I) hydroxide zinc nitrite vanadium(III) sulfide Write the formulas for the following chemical compounds: 11) silicon dioxide SiO2 12) nickel (III) sulfide Ni2S3 13) manganese (II) phosphate Mn3(PO4)2 14) silver acetate AgC2H3O2 15) diboron tetrabromide B2Br4 16) magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 17) potassium carbonate 18) ammonium oxide (NH4)2O 19) tin (IV) selenide SnSe2 20) carbon tetrachloride CCl4 MgSO4.7H2O K2CO3 Naming Acids Name the following acids. 1. HIO3 iodic acid 2. HI hydroiodic acid 3. H2SO4 sulfuric acid 4. H2SO3 sulfurous acid 5. H2S hydrosulfuric acid Convert the following names of acids to formulas. 6. iodous acid HIO2 7. sulfurous acid H2SO3 8. sulfuric acid H2SO4 9. perchloric acid HClO4 10. phosphoric acid H3PO4 Metallic Bonding 1) What are the two types of alloy, and how do they differ from one another? Interstitial alloys are alloys in which one element takes up the spaces between the atoms of the other metal. Substitutional alloys are alloys in which the atoms of one element in the lattice are replaced by atoms of other elements. 2) How is bonding in metals different than bonding in either ionic or covalent compounds? In metals, the bonding electrons are delocalized among all of the atoms. As a result, the most common analogy for discussing metallic bonding is the “electron sea theory” in which the nuclei are islands of positive charge that are floating in a big ocean of electrons that hold them all together. Precipitate Reactions 1. LiCl ( ) + AgNO3 ( ) AgCl ( ) + LiNO3 ( ) 2. Na2S ( ) + CaCl2 ( ) 2NaCl ( ) + CaS ( ) 3. ZnCl2 ( ) + 2KOH ( ) Zn(OH)2 ( ) + 2KCl ( ) 4. Na2CO3 ( ) + Co(NO3)2 ( ) 2NaNO3 ( ) + CoCO3 ( ) Compare and contrast ionic and covalent compounds. Ionic Compounds 1. 2. 3. 4. Crystalline solids (made of ions) High melting and boiling points Conduct electricity when melted Many soluble in water but not in nonpolar liquid Covalent Compounds 1. 2. 3. 4. Gases, liquids, or solids (made of molecules) Low melting and boiling points Poor electrical conductors in all phases Many soluble in nonpolar liquids but not in water VSEPR For the following molecules, find the following. Draw the Lewis structure Determine the ABE formula State the electron pair geometry and molecular geometry Find formal charges 1. Water (dihydrogen monoxide) 2. Nitrogen triiodide 3. Carbon disulfide 4. Silicon tetrafluoride 5. Arsenic tribromide 6. Dihydrogen monosulfide Polarity For the following molecules: Draw the Lewis Structure Determine the molecular geometry Determine if the bonds are polar/nonpolar/ionic. Determine if the overall molecule is polar. 7. Oxygen gas 8. Selenium dibromide 9. Iodine pentachloride 10. Sulfur tetrafluoride 11. Xenon trichloride 12. Hydrochloric acid