Muscular Objectives
advertisement

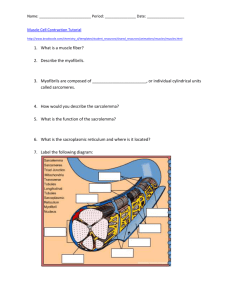
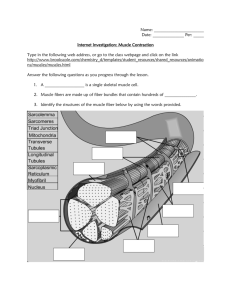
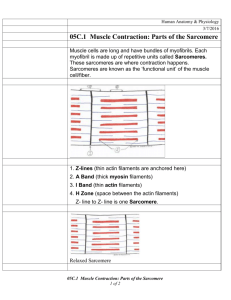
Thursday, November 12, 2015 • Put muscular worksheet in the blue basket • Get a textbook • Get a highlighter • Get out paper & something to write with FYI… •A muscle cell is also called a muscle fiber Read pgs. 182-185 • on your paper answer the following 1. Describe the similarities and differences in the structure and function of the 3 types of muscle tissue, and indicate where they are found in the body. 2. Define muscular system. •Organ system consisting of skeletal muscles and their connective tissue attachments 3. Define and explain the role of the following: endomysium, perimysium, epimysium, tendon, and aponeurosis. Endomysium • Connective tissue sheath that encloses each muscle fiber perimysium • Coarse fibrous membrane that encloses several sheathed muscle fibers / surrounds a bundle of fibers called a fascicle Epimysium • Tough, outer covering that bind together many fascicles; covers the entire muscles and blends into the tendons or aponeuroses; covered with fascia Both connect muscles indirectly to bones, cartilages, or connective tissue coverings Tendons • Cordlike • Provide durability & conserve space Aponeuroses • sheetlike A skeletal muscle is composed of a variety of tissues Muscle Bone Fascicles Tendon Muscle fibers (cells) Fascia (covering muscle) Myofibrils Epimysium Perimysium Thick and thin filaments Endomysium Fascicle Axon of motor neuron Blood vessel Myofibril Nucleus Sarcoplasmic reticulum Filaments Muscle fiber Sarcolemma Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4. Describe the microscopic structure of skeletal muscle and explain the role of actinand myosin-containing myofilaments • Sarcolemma—specialized plasma membrane • Myofibrils—long organelles inside muscle cell • Sarcoplasmic reticulum—specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum • Myofibrils are aligned to give distinct bands –I band = light band • Contains only thin filaments –A band = dark band • Contains the entire length of the thick filaments • Sarcomere—contractile unit of a muscle fiber • Organization of the sarcomere –Myofilaments •Thick filaments = myosin filaments •Thin filaments = actin filaments • Thick filaments = myosin filaments –Composed of the protein myosin –Has ATPase enzymes –Myosin filaments have heads (extensions, or cross bridges) –Myosin and actin overlap somewhat • Thin filaments = actin filaments –Composed of the protein actin –Anchored to the Z disc • At rest, there is a bare zone that lacks actin filaments called the H zone • Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) – Stores and releases calcium – Surrounds the myofibril Extra Credit • • • • Due Wednesday, November 18, 3015 Make a model of skeletal muscle Use Figure 6.1 as a guide Must label – – – – – – Muscle fiber (cell) Fascicle Perimysium Endomysium Epimysium fascia Homework •watch 5 videos on the Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction