CORE Case 2 Workshop
advertisement

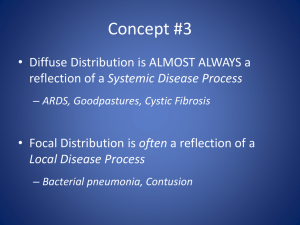
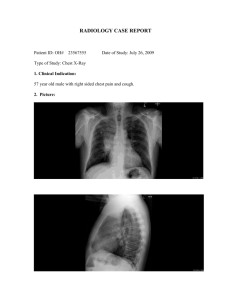
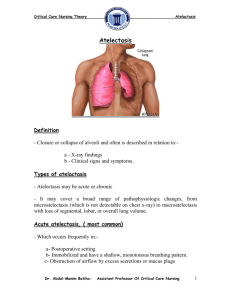
Petra Lewis MD Professor of Radiology and OBGYN Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Learning objectives Understand who should get a pre-op CXR Know what features affect how we manage SPNs Know some of the ways that we can manage SPNs in patients Understand the radiographic signs of atelectasis Be able to work out when atelectasis is present and what lobe is involved Apply an algorithm to distinguishing the different causes for an opacified hemithorax Recognize the features of a pneumothorax on different views Recognize tension on a radiograph and how to treat it What questions/difficulties did you have arising from the case Who should get a pre-op CXR? 37 year old man with no cardiorespiratory symptoms currently but a history of asthma pre-op ACL repair 70 year old asymptomatic woman pre-op hip replacement 45 year old diabetic man with no cardiorespiratory symptoms currently preop renal transplant Who should get a pre-op CXR? Acute cardiopulmonary findings by history or physical Chronic cardiopulmonary disease in the elderly (>age 70), previous chest radiograph within 6 months NOTE available. Possibly: Chronic cardiopulmonary disease in the elderly (>age 70), previous chest radiograph within 6 months available. Solitary Pulmonary Nodules What factors might affect whether we see a solitary pulmonary nodule? Where might we miss a nodule? What factors affect how we manage a lung nodule? Patient factors Radiographic factors How can we manage an SPN seen on a CXR? Assess Follow up Fleischner Criteria . McMahon et al. 2005 Radiology, 237, 395-400 Atelectasis What are the characteristics of atelectasis? What are the causes of atelectasis What are the signs of volume loss? RUL atelectasis RUL atelectasis RUL atelectasis Pig Bronchus Day 1 Day 2 LUL atelectasis Total lung atelectasis Total lung atelectasis DDx of unilateral hemithorax opacification Causes Pneumothorax What are the signs of a pneumothorax What can we do to see pneumothoraces better? So you find a pneumothorax… What is your next question ALWAYS? What are the signs of tension? Clinical Radiographic You think your patient has a tension pneumothorax? What will you do? www.brooksidepress.org Note, this should be a clinical diagnosis! Don’t wait for the CXR http://handbook.muh.ie Appendix Learning Objectives Know the current recommendations for preoperative chest radiographs in people who are healthy and in those with underlying chest and cardiac diseases Understand some of the challenges in detecting small nodules on chest radiographs. Have a concept of the different appearances of pulmonary nodules and their prognostic significance Understand the current status of low dose CT imaging for lung cancer screening. Understand some of the management issues related to pulmonary nodules (including the Fleischner Society recommendations). Have a basic understanding of the use of FDG PET imaging in the management of nodules and lung malignancies. Have reviewed the methods available for nodule biopsy Will understand indications for needle biopsy, how the procedure is done, and the possible complications. Be able to recognize a pneumothorax and understand the meaning and consequences of a tension pneumothorax. Know the options for treating a pneumothorax. Understand the purpose of TNM tumor staging and implications for long term survival Recognize the common appearances of lobar atelectasis on chest radiographs. Recognize the common appearances of linear and subsegmental atelectasis on chest radiographs. Know the different etiologies that may cause complete opacification of a hemithorax Know the expected postoperative appearance of the chest after pneumonectomy.