What are Cells?
advertisement

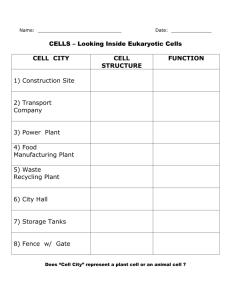
Structures and Processes of Living Things Key Concepts Cell functions, growth, and development Energy transfer through photosynthesis Types of reproduction http://leavingbio.net/CELL%20DIVERSITY.htm Click on link below: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/scale/ Key Idea #11 All living organisms are composed of cells – from one cell to many cells. Characteristics of Living Things Grow Move Reproduce Get energy Use energy Get rid of waste Adapt to changes Cells are Living Organisms Cells grow and die. use energy, nutrients, air, and water. produce wastes. reproduce. react to what's around them. All living organisms are made of one or many cells. Cells are the simplest unit of life. are the building blocks of life. are produced from other cells. FYI: Types of Cells FYI: Prokaryotic Cell does not have a nucleus FYI: Eukaryotic Cell has a nucleus (human cheek cells) (amoeba) (onion skin cells) FYI: According to scientific evidence: Organisms include all living things can be unicellular (one-celled) – example: protozoa (protists), bacteria (monera) can be multicellular (many-celled) – example: plants, fungi, animals Paramecia (protozoa): United Streaming Video: 3:49 min Paramecium (unicellular organism) Amoeba (Protist) United Streaming Video 1:00 min Amoeba (unicellular organism) shs.westport.k12.ct.us http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://blogs.southflorida.com/citylink_dansweeney/amoeba_proteus_X_100.jpg&imgrefurl=http://blogs.southflorida.com/citylink_dansweeney/2006/11/& usg=__HgYg6J6NLzcpCfZRExsCNSK0DY=&h=333&w=458&sz=12&hl=en&start=6&zoom=1&tbnid=G6JlMEfIv1OHCM:&tbnh=93&tbnw=128&ei=Fsc8TdCIDMrSgQfWvrSeCA&prev=/i mages%3Fq%3Damoeba%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DN%26biw%3D1003%26bih%3D567%26tbs%3Disch:1&um=1&itbs=1 Elodea Leaf cells (multicellular organism) Nucleus http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://4.bp.blogspot.com/_vdkkIjcBvLk/TQaowgCRv0I/AAAAAAAAADY/3pnXIeg6QHg/s1600/Elodea_Leaf_Cells_400x.jpg&imgrefurl=http://mrripplinger.blogspot.com/&usg=__7AHMiRTq6YRXUCyeqMPMjxTeB20=&h=307&w=490&sz=30&hl=en&start=0& zoom=1&tbnid=aN1EEr_Ootkw2M:&tbnh=78&tbnw=124&ei=-Mg8TZaqJ8jngQe_i_24CA&prev=/images%3Fq%3Delodea%2Bleaf%2Bcell%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26biw%3D1003%26bih%3D567%26tbs%3Disch:1&um=1&itbs=1&iact=rc&dur=297&oei=Mg8TZaqJ8jngQe_i_24CA&esq=1&page=1&ndsp=15&ved=1t:429,r:0,s:0&tx=74&ty=47 Multicelled Organisms in Pond Water (Video: 2 min) The Parts of a Microscope Procedure for Setting up a Slide Using a Compound Microscope Lab Supplies Packet Microscope Probe Tweezers Scissors Cutout newspaper articles Onion – See me Slide Cover slip Lens paper Beaker of water Dropper Paper Towel Prepared slides – See me e-Lab Turn nose piece to scanner lens Place the ruler on the stand and look through the eyepiece. – Record how many millimeters you can see _______ – What is the total power of magnification? – (power of eye piece X power of scanner lens) ______ Turn the nose piece to low power objective lens – Record how many millimeters you can see _______ – What is the total power of magnification? – (power of eye piece X power of scanner lens) ______ Lab Directions: Finish e-lab. – Leave the “e” slide on the microscope until you have checked your answers. After I have checked your answers to 1-11, clean your slide and cover slip. Next, read the directions for preparing the onion cell slide on the handout on the clipboard. Bring me a slide and a cover slip to get your onion cells sample. Animals and Plants are Multicelled Organisms Skeletal Muscle cells (animal) the muscle attached to the skeleton White Blood Cells (animal) Nucleus Onion cells (plant) Nucleus Cross-section of a Leaf Cell Structure Lab (*prepared slides) Packet pages 10-12, Honors 12-14 Onion Cells Leaf Cells (not elodea) Cheek Cells* Paramecium* Parts of an Animal Cell United Streaming Video: 4 min Parts of a Plant Cell United Streaming Video: 2 min Comparing Animal and Plant Cells Onion Skin Cell Red Blood Cells Elodea Leaf Cell Human Cheek Cell Nerve Cell White Blood Cells Similarities and differences between animal and plant cells Similarities: both cells have a cell membrane both are made up of organelles (ribosomes, golgi bodies etc….) both cells have a nucleus both combine to make tissues both have cytoplasm many are microscopic Differences: plant cells have a cell wall plant cells have chloroplasts where they make their own food plant cells have one large vacuole animal cells have small vacuoles plant cells have a rectangular shape animal cells have an irregular shape most plant cells are green Tour of a Cell http://www.nsf.gov/news/overviews/biol ogy/interactive.jsp Creepy Crawlies http://www.telegraph.co.uk/science/pictu re-galleries/7924099/Creepy-crawliesAmazing-Scanning-ElectronMicroscope-pictures-of-insects-andspiders.html Cells Alive! http://www.cellsalive.com/ Think of a City How does it operate? Who protects the city? Who runs the city? How does the city manage its trash? How does the city get food? How does the city get its power? How do you know when you are in the city limits? A plant cell can be compared to a city. Each part of the cell has its own function. The parts of the cell can be compared to the parts of a city based on their similar function. Cell Part A. Nucleus City Analogy Purpose city hall control center Cell Part A. Nucleus B. Cell Membrane City Analogy Purpose city hall control center city limits surrounds & border Cell Part A. Nucleus B. Cell Membrane C. Cytoplasm City Analogy Purpose city hall control center city limits surrounds & border lawns and atmosphere inner space Cell Part A. Nucleus B. Cell Membrane C. Cytoplasm D. Chloroplasts City Analogy Purpose city hall control center city limits surrounds & border lawns and atmosphere inner space Gardens/farms produces food Cell Part A. Nucleus B. Cell Membrane C. Cytoplasm D. Chloroplasts E. Vacuole City Analogy Purpose city hall control center city limits surrounds & border lawns and atmosphere inner space Gardens/farms produces food water tower stores water Cell Part A. Nucleus B. Cell Membrane C. Cytoplasm D. Chloroplasts E. Vacuole F. Ribosomes City Analogy Purpose city hall control center city limits surrounds & border lawns and atmosphere inner space Gardens/farms produces food water tower stores water factory & workers makes products Cell Part City Analogy Purpose city hall control center city limits surrounds & border lawns and atmosphere inner space Gardens/farms produces food water tower stores water F. Ribosomes factory & workers makes products G. Endoplasmic Reticulum roads or highways transportation system A. Nucleus B. Cell Membrane C. Cytoplasm D. Chloroplasts E. Vacuole Cell Part City Analogy Purpose city hall control center city limits surrounds & border lawns and atmosphere inner space Gardens/farms produces food water tower stores water F. Ribosomes factory & workers makes products G. Endoplasmic Reticulum roads or highways transportation system H. Golgi Bodies post office or UPS packs & carries A. Nucleus B. Cell Membrane C. Cytoplasm D. Chloroplasts E. Vacuole Cell Part City Analogy Purpose city hall control center city limits surrounds & border lawns and atmosphere inner space Gardens/farms produces food water tower stores water F. Ribosomes factory & workers makes products G. Endoplasmic Reticulum roads or highways transportation system H. Golgi Bodies post office or UPS packs & carries I. Mitochondria power plant produces energy A. Nucleus B. Cell Membrane C. Cytoplasm D. Chloroplasts E. Vacuole Cell Part City Analogy Purpose city hall control center city limits surrounds & border Controls what enters and leaves the cell lawns and atmosphere inner space gardens/farms produces food water tower stores water F. Ribosomes factory & workers makes products G. Endoplasmic Reticulum roads or highways transportation system H. Golgi Bodies post office or UPS packs & carries I. Mitochondria power plant produces energy police routes, borders, on and off ramps surrounds, supports and protects A. Nucleus B. Cell Membrane C. Cytoplasm D. Chloroplasts E. Vacuole J. Cell Wall