Wake.Acct-Eval.IS Overview.2015-02-27
advertisement
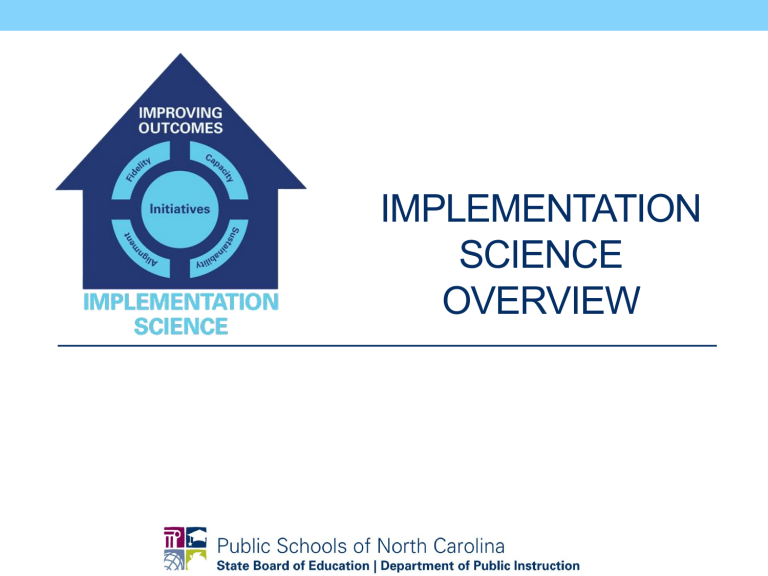
IMPLEMENTATION SCIENCE OVERVIEW CONTEXT & RATIONALE Activity Successful Implementation Unsuccessful Implementation Implementation Gap Implementation is defined as a specified set of activities designed to put into practice an activity or program of known dimensions. RESEARCH PRACTICE GAP IMPLEMENTATION Why Focus on Implementation? “Students cannot benefit from interventions they do not experience.” Business as Usual: Impact Do not Result in Implementation as Intended (used alone) • Diffusion/ Dissemination of information • Training • Passing laws/ mandates/ regulations • Providing funding/ incentives • Organization change/ reorganization • 5 to 10% return on investment NECESSARY BUT NOT SUFFICIENT OUTCOMES % of Participants who Demonstrate Knowledge, Demonstrate New Skills in a Training Setting, and Use new Skills in the Classroom Knowledge Skill Demonstration Use in the Classroom Theory and Discussion 10% 5% 0% ..+Demonstration in Training 30% 20% 0% …+ Practice & Feedback in Training 60% 60% 5% …+ Coaching in Classroom 95% 95% 95% TRAINING COMPONENTS —Joyce and Showers, 2002 Formula for Success WHAT: Effective Interventions Implementation Math HOW: Effective Implementation WHY: Positive Outcomes for Students WHERE: Supportive Contexts Planning for Change • Point of entry is District, not school • Use short-term infusion of resources • Establish long-term, district-based capacity for quality • Must focus on the program/practice/initiative/“IT” and the framework for installation IMPLEMENTATION FRAMEWORKS Active Implementation Frameworks Stages Drivers Usable Interventions Cycles Teams Usable Interventions Usable Interventions Performance Assessment Operational Definitions Essential Functions Clear Description Reflection Usable Interventions How will knowledge of Usable Interventions inform your future practice? Stages Implementation Stages Exploration • • • • Assess needs Examine intervention components Consider Implementation Drivers Assess Fit Installation • • • • Acquire Resources Prepare Organization Prepare Implementation Drivers Prepare Staff Initial Full Implementation Implementation • • • • 2-4 Years Adjust Implementation Drivers Manage Change Deploy Data Systems Initiate Improvement Cycles • • • Monitor & Manage Implementation Drivers Achieve Fidelity & Outcome Benchmarks Further Improve Fidelity & Outcomes Reflection • How will knowledge of Stages Stages inform your future practice? Drivers Implementation Drivers Performance Assessment (Fidelity) Coaching Systems Intervention Training Facilitative Administration Decision Support Data System Selection Leadership © Fixsen & Blase, 2008 Adaptive Technical Implementation Drivers • Help to develop, improve, and sustain educators’ competence and confidence to implement effective educational practices and supports. • Help ensure sustainability and improvement at the organization and systems level • Help guide leaders to use the right leadership strategies for the situation Drivers How: Why: Positive Outcomes for Students What: Effective Educational Practices Staff capacity to support children/families with the selected practices Institutional capacity to support teachers & staff in implementing practices with fidelity Core Implementation Components Leadership Capacity to provide direction and vision © Fixsen & Blase, 2008 Competency Drivers • Build competency and confidence • Develop, improve and sustain competent & confident use of innovations Implementation Drivers: Competency Performance Assessment (Fidelity) Coaching Training Selection © Fixsen & Blase, 2008 Organization Drivers • • Change Organizations and Systems • Create and sustain hospitable organizational and system environments for effective services • Develop functional data systems that can be used to inform decisionmaking Implementation Drivers: Organization Performance Assessment (Fidelity) Coaching Training Selection Systems Intervention Facilitative Administration Decision Support Data System © Fixsen & Blase, 2008 Leadership Drivers • Purpose • Identifying “wicked” problems and applying effective strategies to address those problems Leadership Drivers Implementation Drivers: Leadership Performance Assessment (Fidelity) Coaching Systems Intervention Training Facilitative Administration Decision Support Data System Selection Leadership © Fixsen & Blase, 2008 Adaptive Technical Reflection • How will knowledge of Drivers Drivers inform your future practice? Cycles Improvement Cycles • New approaches need New Ways of Work • Transparent, protocol-driven feedback loops and processes • Aligned policies, funding, guidance to support new ways of work • There are no administrative decisions, they are all education quality decisions. Cycles Improvement Cycles: Usability Testing Act Plan Act Plan Act Plan Study Do Study Do Study Do Reflection • How will knowledge of Cycles Cycles inform your future practice? Teams Linked Team Structures “We tend to focus on snapshots of isolated parts of the system and wonder why our deepest problems never seem to get solved.” —Senge, 1990 State-based Implementation Team Regionally-based Implementation Team District-based Implementation Team School-based Implementation Team Decisionmakers: Data, Curriculum, Funding, Personnel Implementation Teams IMPLEMENTATION INTERVENTION Impl. Team Effective NO Impl. Team 80%, 3 Yrs 14%, 17 Yrs Making it Happen Letting it Happen Helping it Happen Fixsen, Blase, Timbers, & Wolf, 2001 Balas & Boren, 2000 Green & Seifert, 2005 Implementation Teams Focus on: • Increasing “buy-in” and readiness, • Installing and sustaining the implementation infrastructure, • Assessing and reporting on fidelity and outcomes, • Building linkages with external systems, and • Problem-solving and promoting sustainability. Implementation Teams Core Competencies: • Knowledge and understanding of the selected program or innovation including the linkage of components to outcomes. • Knowledge of implementation science and best practices for implementation, and • Applied experience in using data for program improvement. Practice-Policy Communication Cycle Feedback Practice Informs Policy Policy Enables Practices Plan Study - Act External Implementation Support Policy Do Practice FORM SUPPORTS FUNCTION Policy Structure Procedure Practice Reflection • How will knowledge of Teams Team Structure inform your future practice? TOOLS & RESOURCES Getting Started: Tools & Resources • Hexagon Tool • Initiative Inventory • Practice Profile • District Capacity Assessment • The Active Implementation Hub • Quick Start Video Practice Profiles • http://implementation.fpg.unc.edu/modules-and-lessons • Lesson 3: Practice Profiles • Provide clear definitions and descriptions of developmental variations of an implementation • Examples • http://mtss.ncdpi.wikispaces.net/Practice+Profiles • http://ncimplementationscience.ncdpi.wikispaces.net/LEA+SelfAssessment DCA