Chp. 4 Review - St. Paul School
advertisement

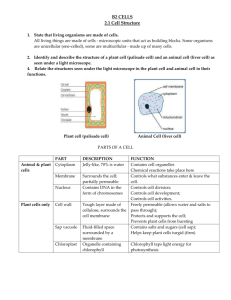
Chapter 4 Review Vocabulary A plant cell differs from an animal cell because it has a _______ outside of the cell membrane. Cell Wall Vocabulary The basic unit of structure and function for all living things is the _________. Cell Vocabulary The chlorophyll in a ____ gives a plant its green color? Chloroplast Vocabulary Cell activities, including division, are controlled by information in the cell’s ________. Nucleus Vocabulary A set of statements called the _______ describe the basic concepts about cells. Cell theory Vocabulary The group of tissues that works together to perform a special function is called an ________. Organ Vocabulary The living material in the cell, excluding the nucleus, is called ________. Cytoplasm Vocabulary In plants, sun energy is used to make food by the compound __________. Chlorophyll Vocabulary Specialized cells organized to perform a certain function are called __________. Tissues Vocabulary The thin outer covering, or the _________, controls what enters and exits cells. Cell membrane Vocabulary The tiny, special parts of the cell that carry out life processes are called ________. Organelles Check Your Knowledge Explain the statement “some cells are specialized” Different types of cells perform specific functions for an organism. Check Your Knowledge What is one purpose of the cell membrane? The cell membrane protects the inside of the cell, gives it shape, and helps control materials entering and leaving. Check Your Knowledge Where in a cell is the cellulose located? Cellulose is located in the cell wall. Check Your Knowledge List the statements in the cell theory. All living things are made up of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. All cells come only from other living cells. Check Your Knowledge List two organelles and their functions. Mitochondria-energy source. Ribosomes- proteins makers. Vacuoles- food and water storage. Golgi Bodies- package materials. Lysosomes- break down materials. Endoplasmic Reticulum- transports materials. Chloroplasts- energy source in plant cells. Cell wall- protects plant cells. Cell membrane- see previous slide. Check Your Knowledge How did the term “cell” originate? Cell is the Latin word for “little room”. Complete the Sentence The unit of structure for living things is __________. Cell Finish the Sentence Digestive chemicals in ________ break down food, wastes, and old cell parts. Lysosomes Finish the Sentence The _______ protects cells, and controls movement of materials in and out. Cell membrane Finish the Sentence The cell theory states cells come only from __________. Living cells Finish the Sentence To grow skin cells in a laboratory, scientists must provide the cells with the same _____ as as a normal skin cell. Environment Finish the Sentence The first person to observe living cells was probably ______. van Leeuwenhoek Finish the Sentence The cell powerhouses are the _________. Mitochondria Finish the Sentence Your heart is an example of an _______. Organ Finish the Sentence The cell’s information center is the _________. Nucleus Check Your Understanding Where is DNA found in a cell? The nucleus Check Your Understanding What organs make up the circulatory system? Heart, blood, and a network of blood vessels. Check Your Understanding What was an important event that led to the development of the cell theory? Robert Hooke made microscopes that had two lenses in a metal tube. Check Your Understanding What is the process of growing cells in the laboratory called? Culturing Check Your Understanding What is a disadvantage of using TEM microscopes to view living cells? TEM electron beams produce a vacuum. Check Your Understanding What electronic device can help regulate a person’s heart beat if it is too slow or uneven? Pacemaker Check Your Understanding What are the three types of muscle in the human body? Smooth, muscle, and cardiac Check Your Knowledge What is homeostasis? Homeostasis- ability of a cell to maintain a stable internal environment.