Adolescence and emerging adulthood

Adolescent Development
Psychology 242
Professor Jean Rhodes
Adolescence in a Changing
Population
• There are about 40 million 10-19 year olds in the U.S.
– 14% of population
• Average age of parents is about 35
• 27% of all children under 18 live with one parent (mostly mothers)
– 29% Hispanic
– 53% African American
• 16% of children under 18 live below poverty
Fig. 1.2
Actual and Projected Number of U.S.
Adolescents Aged 10-19, 2000-2100
Today’s Adolescents
Fig. 1.3
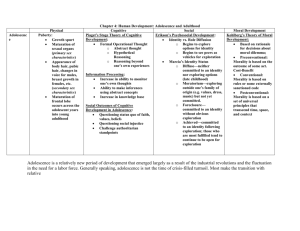
Developmental Changes are a Result of Biological,
Cognitive, and Socioemotional Processes
Development Processes
Development Processes
Biological,
Cognitive, and
Socioemotional
Processes
Biological processes
Physical changes within an individual’s body.
Development Processes
Biological,
Cognitive, and
Socioemotional
Processes
Cognitive processes
Changes in thinking and intelligence.
Development Processes
Biological,
Cognitive, and
Socioemotional
Processes Socioemotional processes
Changes in relationships, emotions, personality, and social contexts.
Adolescence 242
• Assignments:
• Natural observation or flim clip (20%)
• Midterm and Final examinations (35% midterm,
40% final).: Multiple-choice, short answer, and short essay exam take will include questions about topics from the class. To do well, you will want to have studied information from class presentations and discussions, from readings, and from your observations.
• Attendance, reading, participation (5%)
Periods of Development
• Childhood
– Prenatal Period
– Infancy
– Early Childhood
– Middle and Late Childhood
Periods of Development
• Adolescence
– Early Adolescence
– Late Adolescence
Periods of Development
• Adulthood
– Early Adulthood
– Middle Adulthood
– Late Adulthood
Adolescence & Early
Adulthood
• Early adolescence
– 11-15
• Late adolescence
– 18-19
• Early adulthood
– 19-30
Historical Perspective
• The 20th Century
– G. Stanley Hall’s Storm-and-Stress View
– Margaret Mead’s Sociocultural View
Myth of Storm and Stress
• Most youth do not experience a stormy adolescence
• Those who do, often exhibit problems throughout childhood
• Adolescence is generally a time of continued positive relations with parents, and most adopt their parents’ values
Theories of Adolescence: G
Stanley Hall
• Recapitulation Theory:
– life-span changes mirror evolutionary changes of humans from ape-like to civilized.
– First person to present a scientific theroy of developoment that thought of adolescence as a distinct portion of the life span
• A period of transition from being “beastlike” to being
“humanlike”
– Based on a misunderstanding of Darwinian theory
Theory
• An interrelated, coherent set of ideas that helps to explain and make predictions
Psychoanalytic theories
• Freud
Personality Structure
Id Ego Superego
Psychoanalytic
Freud
– Defense Mechanisms
• Unconscious methods the ego uses to distort reality and protect itself from anxiety
• Examples: Repression and Regression
Freud
Psychoanalytic
Fig. 2.1
Psychoanalytic
Revisions of Freud’s Theories
– Less emphasis on sexual motivations
– More emphasis on social aspirations
Fig. 2.3
Psychoanalytic
(Continued…)
(Continued from previous slide)
Psychoanalytic
Fig. 2.4
Cognitive
Piaget
Cognitive
Vygotsky
– Cognitive skills are mediated by words, language, and forms of discourse
– Cognitive skills have their origins in social relations
Cognitive
Information Processing Theory
– How information is:
• Perceived
• Encoded
• Represented
• Stored
• Retrieved
Behavioral
Skinner
– The scientific study of observable behavior responses and their environmental determinants
– Behavior is learned and often changes according to environmental experience
Fig. 2.5
Social Cognitive
Bandura’s Social Cognitive Theory
Ecological, Contextual
Bronfenbrenner
– Microsystem
– Mesosystem
– Exosystem
– Macrosystem
• Levels
Bronfenbrenner
Eclectic Theoretical
Orientation
Eclectic Theoretical Orientation
– Not following any one theoretical approach, but rather selecting from each theory whatever is considered the best in it