Chapter 1: Vocabulary and Notes
advertisement

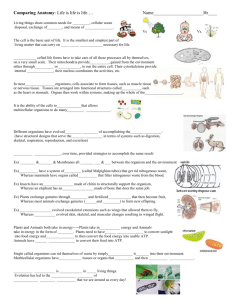
the basic unit that makes up living things A function that a living thing performs to stay alive and reproduce a part of an organism that performs a specific function Any living thing that can carry out life processes on its own A group of organs that work together to carry out life processes To make more living things of one’s own kind A group of similar cells that work together Plant Cell Cell wall Chloroplasts Animal Cell Mitochondria Vacuoles Cytoplasm Nuclei Cell membrane Chromosomes 1. Plants take in ________ __________ and give off ____________. Animals take in _______________ and give off __________ _______________. 2. __________ and __________ _________ have many parts in common, but animal cells do not have _________ _________ or _______________. 3. The _____________ store food, nutrients, and wastes in a cell. Time to test yourself! Can you label this diagram of a plant cell? 4. __________ and some green plants are single celled, ___________ organisms. They make their ________ ____________. 5. _________ __________ organisms trap ____________ from the sunlight in the _________________ where they make food. 6. _________ organisms do not have a heart or brain. 7. ___________ are single celled algae that live in water. They are _________ organisms with 1 cell. 8. ___________ are __________ organisms with many cells. 9. Complex organisms have many ____________ kinds of cells. In complex organisms: ________ make up tissues. Tissues make up ___________. ________ make up organ systems. 10.An example of a complex organism with many cells is a flower. Complex Simple No distinct organs Some made of single cells Carry out life processes Some made of many similar cells Made of cells Many different kinds of cells Different kinds of tissues Have organ systems What do all living things have in common? Made of cells Carry out life processes Take in nutrients Reproduce Grow and develop Give off wastes Release energy React to surroundings Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems a green material in plants that traps energy from sunlight and gives leaves their green color the part of a plant that uses sunlight and air to help the plant make food the process plants use to make food the part of a plant that takes in water (moisture) and nutrients from the ground An undeveloped plant sealed in a protective coating the part of the plant that carries food, water, and nutrients to and from the roots and leaves 1. A plant has 3 main parts: a) ________ b) ________ c) ________ 2. In most plants, food is made in the ___________. 3. Plants provide us with _________ to breathe. If we had no plants, we wouldn’t have enough oxygen. 4. 3 types of leaves: a) __________ leaves- thick leaves that help the plant store water. (dry areas) b) _______leaves- help plants trap energy from sunlight. (moist areas) c) ____________ leaves- grow in dry and cold climates 5. 2 types of roots: 1. ____root- one large, main root Examples: _____________ and ______________ 2. _________ roots- roots that branch out in a netlike pattern to gather water from a wide area Fibrous roots taproot 6. Some plants have different stems. 3 types of stems are: 1. ______ stems- covered in a layer of bark and can survive in warm and cold climates Example: _____________ 2. _______ stems- can only survive in warm weather and are held up by water Example: _____________ 3. ______ stems- store water and can survive long periods without rain Example: _____________ Thick stem Soft stem Woody stem 7. Plants use __________ to reproduce. 2 groups of plants are: 1. _____________ plants- produce seeds in __________ __________. Example: pine trees 2. _ ___________ plants- produce seeds inside _________, and __________ is formed only by flowers. Example: peach trees 8. Most leaf cells have special parts called chloroplasts that contain _______________. 9. In the chloroplasts during photosynthesis, a plant takes in ______________, ____________ ____________, and ___________. The plant produces __________ and ______________.