Health communication outline
advertisement

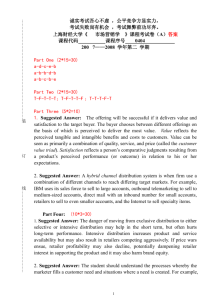
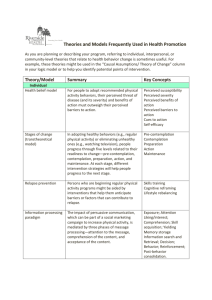
Chapter 9 Health Communication Chapter Summary Health communication is the examination of the relationship between communication and health-related issues. This chapter discusses these relationships by exploring: the place of theory in health communication, patient–provider interactions, the comprehensive model of information seeking, the theory of planned behavior, and the health belief model. Health Communication Defined and the Place of Theory Health communication is an interdisciplinary field of communication that deals with the influence of communication on health and related issues. A major consideration about this line of research for many researchers is that unl,ess it has a practical influence on prompting healthy practices, health communication theory is not of value. Also, it should be reality-based, axiological, and approachable. Patient–Provider Interactions Patient–provider interaction is a shared theme of study that deals with the interpersonal communication between health-care providers and patients. Three major areas in this field are patient and provider skills/competence, interaction outcomes, and disclosure in the interactions. Effective communication between providers and patients is one of the main objectives in this interpersonal approach, because without such an effective relationship, the health-care process will face serious problems. The significance of this relationship has resulted in the establishment Understanding Communication Theory, by Stephen Croucher © Taylor & Francis 2015 of more and more health communication programs in universities and similar communication courses. Comprehensive Model of Information Seeking (CMIS) CMIS is an information-seeking model aimed at informing and educating the public to be more active, informative, and communicative patients. The bases of the model are in the excessive passion to seek and find information about illness via online and other resources. This information may cause an increase or decrease of related anxiety. A variety of models such as the health information acquisition model, the risk information seeking and processing model, information adequacy and uncertainty reduction, and motivated information management have been proposed. Relating to antecedents that affect the information-seeking process, the theoretical perspective of CMIS has been introduced to explore how source characteristics may affect information-seeking behaviors. Generally according to CMIS, the way people seek information is influenced by perceived usefulness of sources. This model assumes people as active information seekers consciously select a variety of sources to satisfy their information needs. This model also defined four different health related factors and two information-career related factors. Theory of Planned Behavior and the Health Belief Model This body of research deals with the way in which people perceive and behave regarding health issues. The theory of planned behavior (TPB) is a revised form of the theory of reasoned action (TRA) that focuses on the attitudes toward health as the effective factor in the expectations of behaviors. TPB added the element of behavioral control to TRA. The main factors of intent to Understanding Communication Theory, by Stephen Croucher © Taylor & Francis 2015 perform an action in TPB are attitude toward behavior, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control. The health belief model (HBM) investigates how perceived benefits and barriers, and perceived seriousness and susceptibility, can affect preventative health behaviors. This model draws on five factors: perceived susceptibility, perceived seriousness, perceived benefits, perceived barriers, and cues to action. Different areas of research have used TPB and HBM to explain the behaviors of their subjects. Communication studies have also used these theories in numerous communication fields. These lines of research have immense practical implications. Understanding Communication Theory, by Stephen Croucher © Taylor & Francis 2015