Sunken Lesson
advertisement

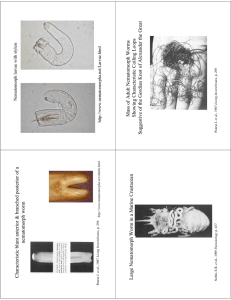
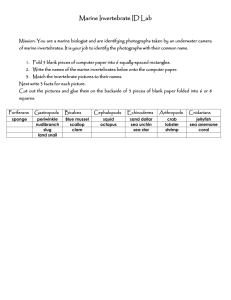
Sunken Lesson Classifying Animals Grade 5 Materials from Quia.Com Site of Joseph Marley http://yksd.com/index.html How Animals are Classified Key Concepts • “Biologists classify organisms based on similarities such as appearance, cell structure, hereditary material, and means of getting food and reproducing. • The seven levels of classification are kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Key Concepts • Each level of classification groups organisms that are more similar to each other. • The scientific name of an organism is its genus then its species such as: Tyto alba. (barn owl) Key Vocabulary • Classify - group things based on the features they share. • Phylum - subdivision of a kingdom (plural is phyla). • Genus - A group of living things that includes separate species. Vocabulary • Species - a group of organisms that can breed with each other to produce offspring like themselves. • Scientific name - the name given to each species, consisting of its genus and its species. Vertebrates Key Concepts • All vertebrates have an internal skeleton made of bone or cartilage, a backbone, and a skull. • A shark is unlike most fish because its skeleton is made of cartilage and most fish have skeletons made of bone. Key Concepts • Many animals go through a metamorphosis; A frog starts out as a tadpole, which grows legs, loses its gills and tail, and develops into an adult frog. Key Concepts • Mammals have two features other vertebrates do not have; mammals have mammary glands to feed their young and mammals have hair to hold in body heat. Key Vocabulayr • Vertebrate - An animal with a backbone. • Cartilage - a soft material found in vertebrate skeletons. • Vertebra - one of the bones or blocks of cartilage that make up a backbone. Vocabulary • Swim bladder - A gas-filled organ that allows a bony fish to move up and down in water. • Amphibian - a vertebrate that lives at first in water and then on land . • Metamorphosis - a major change in form that occurs as some animals develop into adults. An example would be a frog. • reptile - an egg-laying vertebrate that breathes with lungs. Vocabulary • Cold-blooded - having a body temperature that changes with temperature of surroundings. • Warm-blooded - having a body temperature that stays the same. • Mammary gland - a milk-producing structure on the chest or abdomen of a mammal. Invertebrates Key Concepts • Invertebrates have many methods of feeding for instance a sponge strains its food particles out of the water that moves through their bodies. • Body plans are different in invertebrates; radial symmetry is like spokes on a wheel and bilateral symmetry is a body plan that has identical right and left sides. Key Concepts • There are three main types of worms; flatworms (tapeworms), roundworms (hookworms), and segmented worms (leeches, earthworms). • Many invertebrates molt as they grow, for example, arthropod's external skeleton does not grow, so they must shed (molt) their skeleton to grow in size. Key Concepts • Invertebrates have many different ways of movement, for example, Echinoderms attach their tube feet to surfaces and pull themselves along. Key Vocabulary • Invertebrate - an animal that does not have a backbone. • Cnidarian - an invertebrate animal that includes jellyfish, corals, and hydras. • Radial symmetry - an arrangement of body parts that resembles the arrangement of spokes on a wheel. Vocabulary • Tentacle - an arm like body part in invertebrates that is used for capturing prey. • Flatworm - a simple worm that is flat and thin. • Bilateral symmetry - a body plan that consists of left and right halves that are the same. Vocabulary • Roundworm - a worm with a smooth, round body and pointed ends. • Segmented worm - a worm whose body is divided into sections, such as earthworms or leeches. • Mollusk - an invertebrate divided into three parts. Vocabulary • Arthropod - a member of the largest group of invertebrates, which includes insects. • Molting - the process by which an arthropod sheds its external skeleton. • Crustacean - a class of arthropods that includes crabs, lobsters, crayfish, and sow bugs. Vocabulary • Arachnid - a class of arthropods that includes spiders, scorpions, mites, and ticks. • Complete metamorphosis - changes in form during development in which earlier stages do not look like the adult, example is a butterfly. • Incomplete metamorphosis - changes in form during development in which earlier stages look like the adult. Vocabulary • Pupa - a stage in the development of some insects that leads to the adult stage. • Tube foot - a small structure used by echinoderms for movement.”