Chapter 3 Biochemistry
advertisement

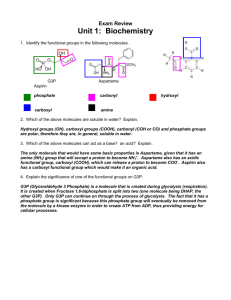
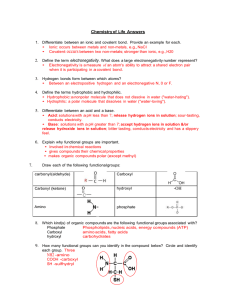
Chapter 3 Biochemistry Pg. 50 Section 1: Carbon Compounds Organic Compounds • Contain carbon • Come from living things How can you tell whether a compound is organic or not? By the presence of the element, carbon. H2SO4 ? C6H12O6 ? A carbon atom has 4 electrons in its outermost energy level… What does this mean? It means that carbon will form four covalent bonds with atoms of other elements. A carbon atom Unlike other elements; however, • Carbon will also bond with other carbon atoms A molecule of ethane Carbon atoms bond together in various arrangements… • Straight chains • Branched chains • Rings Each line in a structural model represents a single bond where 1 pair of electrons is shared • How many pairs of electrons are shared in a double bond? • Where is the double bond ? Functional Groups • A cluster of atoms that influence the molecules they compose • There are 4 functional groups: 1. hydroxyl 2. carboxyl 3. amino 4. phosphate 1. Hydroxyl ( -OH) * can make the molecule it is attached to polar • Polar molecules are soluble in water • An alcohol is an example of an organic compound that has a hydroxyl group An alcohol called ethanol Is alcohol soluble in water? (Does it dissolve in water?) • Yes! Because it is a polar compound like water. “LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE” 2. Carboxyl Carboxylic acid 3. Amino • The amino group is found in all amino acids which make up proteins 4. Phosphate • Ex. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) • There are 3 phosphate groups in ATP. • ATP is a molecule that stores energy AND supplies that energy directly to cells • Energy is released from ATP when the bonds between phosphate groups are broken. For Review: • What is the name of each functional group? A. Hydroxyl B. Carboxyl C. Amino