Lesson 1 Homework Assignment - Functional Groups - kyoussef-mci
advertisement

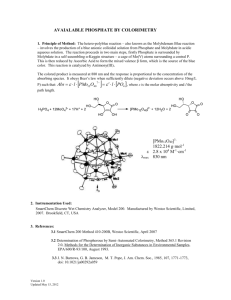
Exam Review Unit 1: Biochemistry 1. Identify the functional groups in the following molecules. G3P Aspartame Aspirin phosphate carbonyl carboxyl amine hydroxyl 2. Which of the above molecules are soluble in water? Explain. Hydroxyl groups (OH), carboxyl groups (COOH), carbonyl (COH or CO) and phosphate groups are polar, therefore they are, in general, soluble in water. 3. Which of the above molecules can act as a base? an acid? Explain. The only molecule that would have some basic properties is Aspartame, given that it has an amine (NH2) group that will accept a proton to become NH3+. Aspartame also has an acidic functional group, carboxyl (COOH), which can release a proton to become COO-. Aspirin also has a carboxyl functional group which would make it an organic acid. 4. Explain the significance of one of the functional groups on G3P. G3P (Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate) is a molecule that is created during glycolysis (respiration). It is created when Fructose 1,6-biphosphate is split into two (one molecule being DHAP, the other G3P). Only G3P can continue on through the process of glycolysis. The fact that it has a phosphate group is significant because this phosphate group will eventually be removed from the molecule by a kinase enzyme in order to create ATP from ADP, thus providing energy for cellular processes.