Ch1- Study Guide

Chapter 1 – Hierarchical Network Design
Study Guide
After completion of this chapter, you should be able to:
Describe how a hierarchical network model is used to design networks.
Explain the structured engineering principles for network design: Hierarchy, Modularity, Resiliency, Flexibility.
Describe the three layers of a hierarchical network and how they are used in network design.
Identify the benefits of a hierarchical design.
Describe the Cisco Enterprise Architecture Model.
Describe the three new business network architectures: borderless network architecture, collaboration network architecture, and the data center or virtualization network architecture.
1.
Why is it important to determine the size of a network before determining a design?
Network size will help to determine the complexity of a network.
2.
Briefly describe the following network design principles: a.
Hierarchy – It breaks the complex problem of network design into smaller and more manageable areas.
b.
Modularity – By separating the various functions that exist on a network into modules, the network is easier to design.
c.
Resiliency – The network must remain available for use under both normal and abnormal conditions.
d.
Flexibility – The ability to modify portions of the network, add new services, or increase capacity without going through a major upgrade.
3.
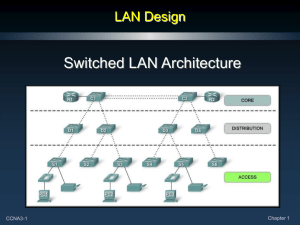
List functions of the Hierarchical Network layers:
Access
Layer 2 switching
High availability
Port security
QoS classification and marking and trust boundaries
Address Resolution
Protocol (ARP) inspection
Virtual Access Control
Lists (VACLs)
Spanning tree
Power over Ethernet
(PoE) and auxiliary VLANs for VoIP
Distribution
Aggregation of LAN or WAN links
Policy-based security in the form of access control lists (ACLs) and filtering
Routing services between LANs and
VLANs and between routing domains
(e.g., EIGRP to OSPF)
Redundancy and load balancing
A boundary for route aggregation and summarization configured on interfaces toward the core layer
Broadcast domain control, because routers or multilayer switches do not forward broadcasts. The device acts as the demarcation point between broadcast domains
4.
What is the purpose of a “collapsed core” design?
Core
Providing high-speed switching (i.e., fast transport)
Providing reliability and fault tolerance
Scaling by using faster, and not more, equipment
Avoiding CPU-intensive packet manipulation caused by security, inspection, quality of service (QoS) classification, or other processes
To reduce network cost, while maintaining most of the benefits of the three-tier hierarchical model
5.
Complete Activity 1.1.2.6 – Identify Hierarchical Network Characteristics
6.
What are some advantages to using the modular approach in network design?
It enables flexibility and facilitates implementation and troubleshooting, failure isolation, and security control
7.
Describe the basic network modules: a.
Access-distribution – fundamental component of a campus design b.
Services – a generic block used to identify services (e.g. LWAPP, unified comm, policy gateways…) c.
Data Center – responsible for managing and maintaining data systems (server farm) d.
Enterprise Edge – Internet edge and WAN edge, offer connectivity to voice, video and data outside the enterprise
8.
Complete Activity 1.2.1.3 – Identify modules in a Network Design
9.
What submodules make up the Enterprise Campus and what is there function?
Building Access, Building Distribution, Campus Core, and Data Center
Multilayer design provides high availability, protection against attacks through integrated security, and highcapacity data center module can provide internal server resources to users.
10.
What submodules make up the Enterprise Edge?
E-commerce networks and servers, DMZ, Remote Access and VPN, and WAN
11. What is the function of the Service Provider Edge?
Spans across large geographic areas in a cost effective manner
Converges voice, video, and data services over a single IP communications network
Supports QoS and service level agreements
Supports security using VPNs (IPsec / MPLS) over Layer 2 and Layer 3 WANs
12.
Determine which category the following connections fall into, choose either “Single” ISP or “Mulitple” ISP. a.
Single-homed: Single b.
Multihomed: Multiple c.
Dual-homed: Single d.
Dual-multihomed: Multiple
13.
Explain the three Remote modules: a.
Enterprise Branch – Allows employees to work at non-campus locations while extending head office applications and services to these areas.
b.
Enterprise Teleworker – provides connectivity for workers who operate out of different geographical locations such as home or while traveling. Teleworkers can use VPN services to connect securely while using local ISP services.
c.
Enterprise Data Center – provide backup, load balancing, and an added layer of security by providing disaster recovery and business continuance services for the enterprise.
14.
Complete Activity 1.2.2.6 – Identify Modules of the Cisco Enterprise Architecture
15.
What are some of the top trends that are creating new challenges for IT departments?
BYOD, Online collaboration, Video communication, Cloud computing
16.
Match the following network architectures with their functions:
__ B ___ Cisco Borderless
A) A comprehensive set of virtualization technologies and services that bring the network, computing, storage, and virtualization platforms together.
__ C ___ Collaboration
__ A ___ Data Center/Virtualization
B) Allows users to connect securely and reliably in a BYOD environment. It is based on wired/wireless, routing, switching, security, and application optimization devices working together.
C) Provides devices/services that allow for unified communication, conferencing, scheduling, etc… Allowing people to come together to socialize, work together, cooperate/contribute to production, and to innovate.
17.
What is the function of Cisco AnyConnect?
It enables the device to establish a secure, persistent, policy-based connection for seamless user experience.
18.
Complete Activity 1.3.2.5 – Identify Evolving Network Architecture Terminology