Nervous System Worksheet: Reflexes, Sensory Responses, CNS
advertisement

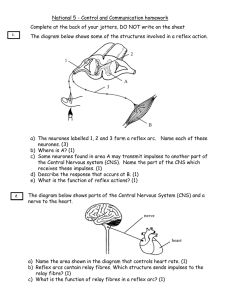
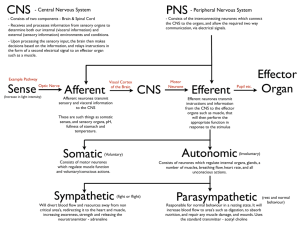
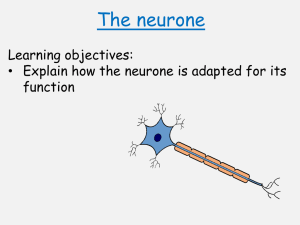
Name:……………………………………………………. Date: …………………… The Nervous System Worksheet This worksheet accompanies Nerves and Reflexes and The Nervous System.ppt 1. Answer the following questions about reflexes. a) Fill in the missing words in the table below. terms stimulus descriptions A change in the internal or external ………………… of an organism. They are fast, automatic, protective, biological control ……………… systems that link a stimulus to a response. b) Reflexes help animals survive. Name one reflex action that helps in survival. ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… c) Give two examples of reflex actions you have experienced. ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… d) Is it possible for humans to override reflex actions? Think about what happens if you pick up a boiling hot mug of tea. Explain your answer. ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… e) Why are reflex actions so quick? Give one benefit of this. ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… © Boardworks Ltd 2011 1 Name:……………………………………………………. Date: …………………… 2. Answer the following questions about sensory responses. a) Receptors enable us to detect certain types of stimuli. Receptors are found in sense organs. What receptors are you using to read this question? ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… b) Effectors are the organs that carry out the responses. Give two examples of effectors in the human body. ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… c) Fill in the missing words in the table below. terms description Chemicals that are produced in glands and that travel in the blood. They create slow, long-lasting responses. Insulin and …………………… oestrogen are two examples of this. neurones Specialised cells that transmit information throughout the body in the form of nerve impulses. An example of this is a ………………… neurone. Contains a network of specialized cells called neurones and uses electrical impulses to ensure a quick response to any …………………… internal or external stimuli. d) In the CNS, impulses are passed from sensory neurones to motor neurons via relay neurons. Fill in the gaps in the following text using the words in the box below. i) ………………… neurones transmit messages from sense receptors like the eye or ………………. to the brain or spinal cord. ii) Relay neurones relay messages from one side of the ………………… to the other. They also connect sensory neurones to motor neurones. iii) Motor neurones transmit messages from the brain and spinal cord to the ………………… such as muscles or glands. CNS nose © Boardworks Ltd 2011 effectors sensory 2 CPS hair receptors Name:……………………………………………………. Date: …………………… 3. Answer the following questions about the CNS. a) In humans and other vertebrates, the CNS is made up of the spinal cord and brain. What does CNS stand for? ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… b) The peripheral nervous system connects the CNS to the rest of the body via neurones that run to and from the CNS. Name this neurone and label its parts using the words in the box below. ………………........... ………………........... ………………......... ………………........... axon cell body dendrites myelin sheath c) Suggest one reason why some axons are surrounded by a myelin sheath. ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… d) What do neurones transmit when they are stimulated by nerve impulses? ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… e) Nerves are made up of many nerve fibres. What are nerve fibres made up of? ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… © Boardworks Ltd 2011 3 Name:……………………………………………………. Date: …………………… 4. Answer the following questions about stimuli and responses. a) Explain what happens in terms of stimulus and response when a lion spies a gazelle in a bush 10 metres in front of him. Use the following terms in your answer: stimulus, receptor, response, effector, electrical impulse, brain, motor neurone, eye, muscle. ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… ………………………………………………………………………………………….…………… b) Draw a labelled diagram to show a reflex arc for the knee-jerk reflex when a doctor taps your knee. Use the key words in your diagram: stimulus, receptor, neurones, nerve impulse, effector, muscle, CNS, brain, spinal cord. © Boardworks Ltd 2011 4