13.1.1 Nerves - PrelimBio

Communication
Topic 13: Nerves
Biology in Focus, HSC Course
Glenda Childrawi, Margaret Robson and Stephanie Hollis
DOT Point(s)
identify that a nerve is a bundle of neuronal fibres
perform a first-hand investigation using stained prepared slides and/ or electron micrographs to gather information about the structure of neurones and nerves
Introduction
In this section we are going to study how signals from the eye and ear are transmitted and processed by the brain. We’ll start by looking at neurones.
webspace.ship.edu
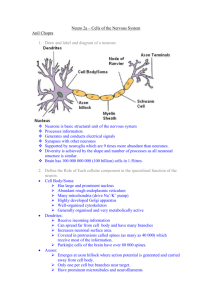
Neurones
The units which make up the nervous system are the nerve cells or neurones (also called neurons). There are three types:
1.
Sensory neurones: transmit impulses from sense organs to other neurones in the central nervous system (CNS)
2.
3.
Motor neurones: transmit impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands
Connector neurones: connect sensory neurones with motor neurones, usually in the brain and spinal cord.
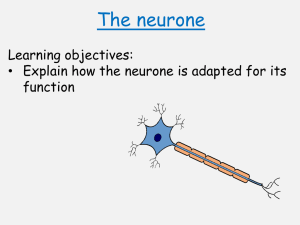
Neurones
No two neurones are exactly alike.
Each neurone is considered to have three parts:
1.
Cell body: this contains the nucleus and forms the grey matter of the CNS.
2.
3.
Dentrites: fine branching extensions which conduct nerve impulses towards the cell body.
Axon: a single, long extension which conducts impulses away from the cell body. This forms the white matter of the CNS.
www.bbc.co.uk
Neurones
Dendrites and axons are collectively referred to as neuronal fibres.
They consist of fluid-filled tubes, the myelin sheath.
The myelin sheath is gradually built up as concentric layers which are produced and supported by special cells
(schwann cells) on the outside. anatomyphysiology2009-10.wikispaces.com
Neurones
The cell body of a neurone is usually in the brain or the spinal cord, while the axon or the dendrites usually extend, as part of a nerve, towards a sensory organ of an effector organ. Nerves can often stretch over a long distance, for example from the spine to the hand.
www.webmd.com
Neurones
Nerve fibres are able to transmit messages rapidly along their entire length and pass them to a successive neurone, over small gaps called synapses.
www.alz.org
Neurones
The myelin sheath has small gaps called the nodes of Ranvier between the Schwann cells. The ion channels that function in the action potential are concentrated in the node regions of the axons. Also, extracellular fluid is in contact with the neuronal membrane only at these nodes. bioweb.wku.edu
Neurones
The action potential actually ‘jumps’ from node to node, skipping the insulated regions of the membrane between the nodes. The greater the insulation through the myelin sheath, the faster transmission of the nerve impulse. www.tokresource.org
Structure of Nerves
The cell bodies of neurones are usually situated in the grey matter of the brain or the spinal cord. Some occur outside the
CNS in clusters called ganglia. Ganglia co-ordinate impulses. best-diving.org
Structure of Nerves
The nervous system is made up of millions of neurones. The sensory motor fibres of the neurones are gathered into bundles called nerves. The bundle is held together by a connective tissue sheath.
best-diving.org
Activity
-Students to complete PRAC/DOT Point 7.3 Structures of neurones and nerves