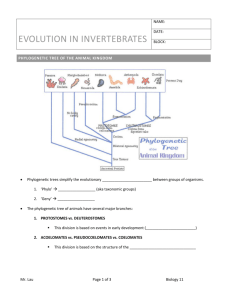
Domain Eukarya – Kingdom Animalia
advertisement

Domain Eukarya – Kingdom Animalia Origins: Colonial flagellated Protista, from the protozoa group Little to no evidence Characteristics: Multicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms Use ingestion:* takes in food through a mouth No cell walls, has intercellular junctions Carbohydrates stored as glycogen Have muscles & nervous tissue Life cycle o Mainly sexual & diploid o Eggs and sperm are the only haploid cells o Egg & Sperm fuse, form a zygote o Blastula:* hollow ball of cells o Gastrula:* invaginated ball of germ layers o Some animals have larval stage & undergo metamorphosis to form adult (can be used to distinguish the animal groups) Larva:* immature stage, looks different from adult Metamorphosis:* change in body form, adult form Distinguishing Characteristics: Body Plans o Radial Symmetry:* Mirror image; body radiate from center Has a top & bottom but no left & right Passive organisms, all sides equal o Bilateral Symmetry:* Left/right mirror image Dorsal (top/back) & ventral (bottom/belly) Anterior (head) & posterior (tail) Cephalization: evolving a head Germ Layers: embryonic tissue layers o Ectoderm:* outer layer Forms the skin (outer covering) and nerves o Mesoderm:* middle layer Forms the muscles, bone & blood o Endoderm:* inner layer Forms the digestive tract and associated organs Organization of Tissue o No tissues: sea sponges o Diploblasty: 2 tissue layers Have an endoderm and ectoderm layers Jellyfish, sea anemones o Triploblasty: 3 tissue layers All higher and intermediate organisms Two groups distinguished by development ▫ Blastopore: hole that forms in the Archenteron ▫ Archenteron: primitive gut , develops into the digestive tract Protostomes:* ▫ Blastopore opening becomes the mouth ▫ Spiral cleavage that is determinate (cell fate is determined as they are formed) ▫ Coelom forms from the mesoderm Deuterostomes:* ▫ Blastopore opening becomes the anus ▫ Radial cleavage that is indeterminate ▫ Coelom forms from invaginations in the gut Types of Body cavity o Body Cavity:* fluid filled space between the digestive tract and body wall o Acoelomates: 3 layers, no body cavities Flatworms o Pseudocoelomates (pseudocoelom):* 3 layers; body cavity not surrounded by mesoderm All are protostomes Round worms o Coelomates (coelom):* 3 layers; body cavity lined by mesoderm Fluid filled cavity, allows organs to grow and move independently of the body wall Annelids & most bilateral animals, including vertebrates Skeletons o Hydrostatic:* fluid, filled cavity forms a rigid structure against which muscles can contract o Exoskeleton:* external, protects the animal, provides points for muscle attachment o Endoskeleton:* internal, protect internal organs Major Groupings Protozoa: Protista that led to kingdom (possibly) No true tissues: Phylum Porifera (sponges) o Pores o Asymmetrical o Sessile as adults o Diffusion for circulation & excretion o No nerves or muscles True tissues: 2 Tissues. Phylum Cnidaria (jellyfish, hydra) o 1 opening o Radial symmetry o 2 forms: polyp and medusa o Gastrovascular Cavity: digestion, excretion & circulation o Diffusion for circulation & excretion o Basic contractile and nerve network True tissues: 3 tissues, bilateral symmetry o Acoelomates Phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms) ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Diffusion for circ Simple circ system 2 openings Pseudocoelomates Rotifera (cilia around mouth) Nematoda (round worms) Both have ▫ ▫ ▫ o Flame cells for excrete 1 open Nemertina (ribbonworms) ▫ ▫ o Muscle, ganglia Ceolomic fluid as circ Muscle 2 open Coelomates: PROTOSTOMES, 2 openings Mollusca (snail, clam, octopus) Foot, mantle, gills, CaCO3 shells No segments Open circ system (fluid bathes organs, does not stay in vessels) Annelida (earthworms) No joints Closed circ with vessel pumps Metanephria for excretion Diffusion for gas exchange Arthropoda - Insecta (6), arachnida (8), crustacean (10 or more legs) Jointed limbs, chitin exoskeleton Tracheal system for gas exchange Malphigian tubules for excrete Open circ with heart Coelomates – deuterostomes (a throwback) Echinodermata (starfish) Radial symmetry Spiny skin Water vascular system with tube feet for feeding, circ, diffusion Larva is bilateral Coelomates – deuterostomes – Chordata - bilateral, closed cir with heart, segmented Chordata characteristics Notochord Dorsal, hollow nerve chord Pharyngeal slits Postanal muscular tail Urochordata and cephalochordate Possible paedogeneis to get chordates as Larval stage gained sexual organs Agnatha (jawless fish), Chondrichthes (cartilage fish) Gills, toothlike scales Internal fertilization Eggs/live birth 2 chamber heart Osteichthyes (bone fish) Gills, flat scales Internal fert Eggs 2 chamber heart Amphibian Skin body covering skin, lungs, gills for gas exchange External fert Eggs/live Reptilian Scale body covering Lungs Internal fert amniote egg Has Membranes http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/vertebrates/tetrapods/amniota.html amnion - filled with amniotic fluid, provides stable fluid environment. allantois- providing for gas diffusion and removal of wastes. yolk sac - Food chorion – most exterior o o