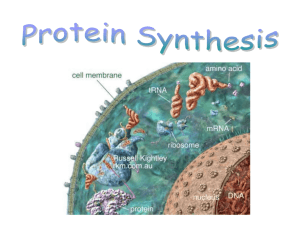
RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Define Gene – What does a gene
advertisement

RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Define Gene – What does a gene ultimately code for? _____________________________________ RNA review o 3 main differences compared to DNA ________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ o 3 types of RNA ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ Protein Synthesis o Occurs in two main steps: ______________________________________ ______________________________________ o Transcription occurs in the _____________________________________ o Translation occurs in the _______________________________________ Transcription o Occurs in 3 main steps: o Initiation – The enzyme ___________________________________ recognizes a specific sequence of DNA called a __________________________ region. Promotors – RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands by breaking the _______________ bonds. o Elongation – RNA polymerase uses the DNA strand as a ______________________ and pairs free-floating RNA nucleotides together to form the backbone of the _________________________ strand. o Termination – mRNA strand is continuously built until RNA polymerase reaches a specific sequence of DNA known as the __________________________________ sequence. Then, mRNA separates from the DNA and transcription is complete. Transcription vs. Replication o Transcription results in : o Replication results in: The Genetic Code o What is the overall purpose of the genetic code in DNA? __________________________________________ Proteins o Long chains of _________________ ____________________ that are joined together by ___________________________ bonds. o There are _______________ different amino acids. o The _________________________ and ___________________________ of proteins are determined by the sequence of amino acids. Codon o The genetic code is read in groups of __________ letters at a time o ____________ codons are possible Codons either code for an amino acid or they give instructions. Translation o Takes place on __________________, either in the cytoplasm or attached to the E.R. o The ribosome will _____________________ the message on the mRNA strand to produce a protein (polypeptide). o Occurs in 3 main steps: o Initiation: mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels through the cytoplasm to the ribosome. mRNA attaches to the ribosome. _______________= the start codon = codes for __________________ tRNA anticodon will temporarily bind to the complementary codon on the mRNA molecule o Elongation: The ribosome has two __________________ sites, allowing two tRNA molecules to line up side by side. The ribosome forms a __________________ __________________ between the first and second amino acids on the tRNA molecules. At the same time, the ribosome ___________________ the bond that held the first tRNA molecule to its amino acid and releases the tRNA from the ribsome. The __________________ floats away, allowing the ribosome to move down the mRNA molecule and bind another tRNA. The ribosome continues to move along the __________________, attaching new tRNA molecules and adding more _______________________ _______________________ to the __________________________________________ chain. o Termination: This process continues until the ribosome reaches one of the three possible __________________ codons on the mRNA. Then, the ____________________________ detaches from the mRNA. The result is a ______________________ that then travels to the _____________________ apparatus to be modified for use in the cell.