Translation and Transcription
advertisement

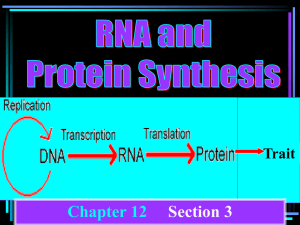
Transcription and Translation Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University 1. DNA Transcription (Nucleus) Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: mRNA Chelsea Bio 212(1) Coffman/Howell/Addis 2/19/12 ? (?) ? 2. During Transcription the RNA Polymerase recognizes a specific base sequence called the _______ and will bind with it. This unit can identify the start of a gene, which strand is to be copied and which way it will be copied, which is __ to __, meaning the new strand is made __ to __. The Polymerase also unwinds the DNA. Once these steps occur, the RNA Polymerase assembles the bases that are complementary to the DNA strand being copied. The one difference is that the RNA strand has a ________ base instead of the ________ base we see in DNA. A __________ code will tell the Polymerase to stop and transcription will cease and ______ is produced. 3. After the mRNA is made, the strand must be further modified. A cap is added to the 5’ end and a ___________ is added to the 3’ end. Also, part of the gene contains regions that do not translate to ________. These regions are called ________ and must be removed by splicing. The rest, called exons, can then be removed from the nucleus so translation can occur. 4. The mRNA protein moves into the cytosol so it can interact with __________. The two subunits of ribosome and an initiator tRNA assembles onto the mRNA. Translation can begin when a start codon or _____ is present. The mRNA moves through the subunits from the ___ to the ___ end. The tRNA functions to recognize the sequences and determine which ______ ______ are needed. The amino acid groups are joined together from the ____ to ____ terminus. Translation will end when the ribosome comes upon a _____ codon. 5. The way the ribosome subunits know which amino acids to use is based on aminoacyl RNA synthetase. The enzyme binds ____ and the ______ ______. After both are bonded, the ATP becomes ______. Then a specific tRNA with a codon that matches that of the amino acid will bind. AMP is then released and the tRNA and the amino acid create a bond. Now called a ______ tRNA. Once this occurs the ribosome can add the amino acid to the growing peptide chain. 6. During this process, the tRNA moves to three positions, known as APE. What does this stand for? What happens during each process and in what order? Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu