Postgastrectomy Diet

Postgastrectomy Diet
報告者:臺北醫學大學 • 市立萬芳醫院 張靜怡 營養師
報告日期:民國 90 年 8月10日
* Purpose
Ⅰ
. Provide adequate calories and nutrients
to support tissue healing
Ⅱ
. Prevent weight loss
Ⅲ
. Prevent dumping syndrome after gastric surgery
* Use
Ⅰ . Vagotomy 、 pyloroplasty
Ⅱ . Hemigastrectomy ( Billroth Ⅰ & Ⅱ anastomosis )
Ⅲ
.Total gastrectomy
Ⅳ . Esophagogastrectomy
Ⅴ . Whipple’s procedure
Ⅵ . Gastroenterostomy
Ⅶ . Gastrojejunostomy
Ⅷ . Roux-en-Y procedure
* Modification
Ⅰ . Limits beverages and liquids at meals
Ⅱ . Limits the intake of simple carbohydrates
Ⅲ
. High in protein and moderate in fat
Ⅳ . Small , frequent feeding
The diet generally progress after surgery
↓ NPO for 3 ~ 5 days
↓ Ice chips or sip water
( warm water better than ice chips or cold water )
↓ Clear liquid diet
( e.g. broth , bouillon , diluted unsweetened fruits juices )
↓ Bland diet
Related physiology
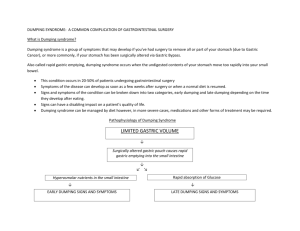
Ⅰ . Dumping Syndrome
Ⅱ . Lactose Intolerance
Ⅲ
. Hypoglycemia
Ⅳ . Steatorrhea
Ⅴ .Vitamins and Minerals deficiency
Dumping Syndrome
* Define:
1.occur in response to the presence of digested food in the
duodenum or the jejunum .
2. following some types of gastric surgery , food is
“dumped” into the jejunum 10 to 15 minutes after
ingestion .
* Cause:
poor function of pyloric sphincter regulate release
( bypass or excise)
* Symptoms:
abdominal fullness , nausea , dizzy , faint , cold sweat,
crampy abdominal pain followed by diarrhea , weak ,
increased pulse rate
Lactose Intolerance
* Cause:
1. Complication of dumping syndrome
2. Lactase deficiency
* Diagnose:
1. Lactose tolerance test
2. Breath hydrogen test
* Diet note:
1. Avoid malnutrition of calcium & vitamin D
( osteomalacia)
2. Milk intolerance is caused by lactose intolerance
lactose-free commercial formula with high and
protein densities and low osmolalities
Hypoglycemia
* Hypoglycemia may occur 1 to 2 hours following meals .
* Use : total gastrectomy or vagotomy
* Cause : rapid digestion and absorption of food (CHO)
blood glucose ↑
insulin production ↑
hypoglycemia
Symptoms : weakness , nausea , perspiration , anxiety ,
tremors
Steatorrhea
* Use : Billroth Ⅱ anastomosis
* Cause : pancreatic insufficiency & defective digestion
dietary food
bypass
duodenal mucosa secret seretin & pancreozymin ↓
〤
pancreatic enzymes & bicarbonate
〤
fat absorption
* Diet note : medium-chain triglycerides(MCT) provide calories
* Deficiency : iron , vitamin B
12
, folic acid
* Cause :
1. Dietary intake ↓
2. Blood loss
3. Loss of factors that facilitate vitamin & mineral absorption
( intrinsic factor , HCl )
* Complication : anemia
* Treatment : IV injection
Vitamins and Minerals deficiency ( Ⅱ )
impaired food bypass bleeding from
absorption the duodenum recurrent ulcers
( 50 % )
rapid stomach emptying
prevent food from mixing with HCl
Fe 3+ 〤 Fe 2+ Fe deficiency
Vitamins and Minerals deficiency ( Ⅲ )
Total gastrectomy
bacterial overgrowth in
the proximal small bowel or afferent loop
gastric mucosa ↓
intrinsic factor ↓ bind vitamin B
12
vitamin B
12 absorption ↓
Pernicious anemia
Dumping Syndrome
General guidelines
Alimentary Hypoglycemia
Dumping Syndrome(
Ⅰ
)
* Liquids :
1. Avoid taking liquids with meals.
2. Take 30 to 60 minutes after meals .
3. Limited to 0.5 - to 1-cup serving .
4. At least 6 cups of fluids
( replace losses resulting from diarrhea)
5. Carbonated beverages and milk are not recommended in
the initial stages of the diet .
* Small , frequent feeding ( depend on patient’s tolerance)
* Diet : low in simple carbohydrates , high in complex
carbohydrates & protein moderate in fat
Energy : 35 ~ 45 kcal /kg. BW/ day
Protein : 1.5 ~ 2.0 g/ kg. BW/ day
* All food & drink should be moderate in temperature.
( cold drinks tend to cause increased gastric motility)
* Lie down 20 to 30 minutes after meals or even up to an hour
( retard transit to the small bowel )
* Introduce small amounts of milk to determine tolerance.
If milk intolerance
( ∵ lactase deficiency → lactose free formula)
* Steatorrhea → MCT oil support
* Pectin , a dietary fiber found in fruits & vegetables , may be helpful for treating dumping syndrome .
∵ 1. delay gastric emptying
2. slows carbohydrates absorption
3. reduce the glycemic response
Alimentary Hypoglycemia
* Avoid concentrated sweets
( candy, sugar, cola drinks, cookies, cake, and ice cream
unless made with sugar substitutes )
* Have concentrated form of sugar available only for treatment of hypoglycemia .
* Eat small meals six times each day .