SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION - rosedalegrade12biology
advertisement

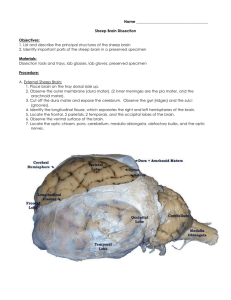
Name:___________________________ Partner(s): _______________________ SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION: PRE-LAB DUE: _______________________________ (Pre-Lab must be submitted to start the lab) Part 1: Planes and Axis of the Brain 1. Label the diagram to the right with the dorsal-ventral axis and the anterior-posterior axis. 2. Name the view of the brain shown in the diagrams below: Part 2: Techniques 1. In the box A, use stippling to show dark shading. In box B, use stippling to show light shading. BOX A BOX B 2. a) What is the “macro” setting on cameras? b) Why would it be beneficial to use when capturing your images in this lab? 1 Part 3: Terminology In the table below, describe the structures and anatomical location in reference to at least two other structures. Indicate which view (see part 1) would be best to observe the structure. Use the following videos to help: http://tinyurl.com/sheepbrain1 http://tinyurl.com/sheepbrain2 http://tinyurl.com/sheepbrain3 Structure Description Location Best View Lateral Ventricle Cerebral aqueduct Choroid Plexus Grey and White Matter Longitudinal Fissure Central Fissure Dura Mater 2 Name:___________________________ Partner(s): _______________________ SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION Objective: To carefully examine the structures of the mammalian brain. Materials: - safety goggles - dissecting tray - dissection tools - gloves - sheep brain - pins - camera - pencil - group name tag - ruler - paper towels Procedure: 1. In pairs, collect all materials and setup work space at the laboratory benches. 2. Clearly with dark bold letters, write the names of all group members on the name tag. This must be placed in all the photos to identify the group. 3. Examine the sheep brain and sketch a labelled diagram of the lateral side of the brain. Indicate the following structures in your sketch: cerebellum, cerebrum, brain stem, medulla oblongata and pons. Observation 1: Sketch of sheep brain 3 4. Closely examine the cerebrum. The raised areas or ridges are called gyri and the depressed areas are called fissures or sulci (singular: sulcus). Locate the longitudinal and central fissures. a. Describe the location of the longitudinal fissure with reference to at least 3 other brain structures. Use at least 1 term from the pre-lab terminology. b. Describe the location of the central fissure with reference to at least 3 other brain structures. Use at least 1 term from the pre-lab terminology. 5. Place the brain with the dorsal side on the dissecting tray. a. Using a scalpel, carefully remove the pituitary gland by cutting the infundibulum and the surrounding dura mater from the sheep brain. b. Measure the diameter of the pituitary gland using a ruler. Record the diameter below in the space provided. Pituitary gland diameter: _________________________ 4 6. With the aid of the diagram, examine the ventral side of the sheep brain. a. Identify the structures listed in table 1. Indicate each structure with the assigned coloured pin. Take a picture with the group name tag in frame. Remove the pins for later use. TABLE 1 Structure Coloured Pin Optic chiasma Red Olfactory bulb or tract Infundibulum White Medulla oblongata Yellow Pons Blue Green b. Describe the location of the optic chiasma with reference to at least 3 other brain structures. Use at least 2 terms from the pre-lab terminology. 7. Gently move the cerebral hemispheres apart to expose the corpus callosum. Using a scalpel, carefully dissect along the sagittal plane fully through the corpus callosum, cerebellum and brainstem. 5 8. With the aid of the diagram, examine the sagittal view of the sheep brain. a. Identify the structures listed in table 2. Indicate each structure with the assigned coloured pin. Take a picture with group name tag in frame. Remove the pins for later use. TABLE 2 Structure Coloured Pin Corpus callosum Red Pineal body White Intermediate mass Green Hypothalamus Yellow Cerebellum Blue b. Describe the location of the hypothalamus with reference to at least 3 other brain structures. Use at least 3 terms from the vocabulary list. c. Sketch a labelled diagram of a sagittal view of the cerebellum depicting by stippling any colour differences. Observation 2: Sketch of the sheep’s cerebellum 6 9. Using the scalpel, cut an approximately 5mm thick, 5 cm by 5 cm section through the forebrain. Carefully examine the cerebrum section. A dorsal view of the sheep brain 10. Examine the cerebrum section and cerebellum sagittal section. a. Sketch a labelled diagram of the cerebrum section depicting by stippling any colour differences. Observation 3: Sketch of the sheep’s cerebrum b. Describe the observed colour differences in the brain sections. Comment on the cerebrum and cerebellum referring to the sketches. 7 11. There are four ventricles in the brain. The ventricles are cavities in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid. Identify the structures listed in table 3. Indicate each structure with the assigned coloured pin. Take a picture with the group name tag in frame. Remove the pins for later use. TABLE 3 Structure Coloured Pin Lateral ventricle Red Third ventricle Green Forth ventricle Yellow Cerebral aqueduct Blue 12. Insert a probe into one of the lateral ventricles and gently scrap along the edges of the ventricle. Use the probe and withdraw a piece of the choroid plexus. Describe the choroid plexus. 13. Describe the flow of cerebral spinal fluid from the lateral ventricles to the forth ventricles. 14. Clean up your work station. Rinse all tools used and return them clean and ready to use. Dispose of specimens in the appropriate waste bins. 8 Name:___________________________ Partner(s): _______________________ SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION- POST-LAB Questions: 1. Compare the cerebrum of humans and sheep. What are some differences and similarities between the two? 2. What is the function of the pons? 3. What is the function of the medulla oblongata? 4. What does the “X” shape of the optic chiasma indicate how visual information is processed in the brain? 5. How does grey and white matter relate to the structure of the neuron? 9