AP US History – Unit 1 Review Packet
advertisement

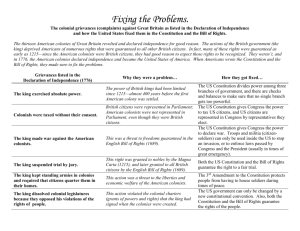
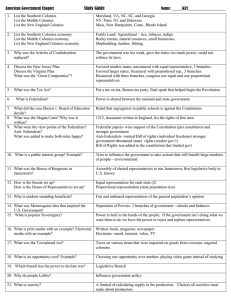
AP US History – Unit 1 Review Sheet Objective 1 1. Immigrants to the colonies who signed on to work for a set number of years in exchange for their passage: 2. Colonies founded by one person or family: 3. A colony ruled by a royal governor: 4. The first document of majority rule in the New World: 5. The first written Constitution in the New World: 6. The first example of guaranteed religious freedom in the New World: 7. A nasty little affair in Virginia that symbolized the conflict between the Back Country and the Tidewater regions: 8. The first colony wide religious movement: 9. The first attempt to unite the colonies in a plan of defense: 10. The British policy of ignoring the Navigation Acts because it was good for the economy to do so: 11. His case helped establish freedom of the press: 12. The City Upon the Hill refers to which city and colony: 13. Two who founded Rhode Island: 14. Led the Great Awakening: Objective 2 1. The first successful organization of the colonies to protest British actions: 2. The Stamp Act and Quartering Act were this type of tax: 3. The Townshend Acts and Tea Act were this type of tax: 4. The first British attempt to tax the colonies: 5. The second attempt, an internal tax, that really angered the colonists: 6. Lowered the price of the good but angered the colonists: 7. Passed in response to the Boston Tea Party: 8. Met in 1774 and voted to send a petition to the King to urge him to repeal the Intolerable Acts, and also voted to set up committees so the colonies could communicate with each other: 9. Met from spring 1775 until the summer of 1776. Passed the Declaration of Independence, created an Army and put GW in charge: 10. Persuaded many colonists to support revolution: 11. Part of the Intolerable Acts that extended the Catholic province of Quebec into the Ohio Valley: Objective 3 1. The term used by historian John Fiske to describe the 1780s: 2. Created a system for admitting new states: 3. Created a system for surveying and dividing up the land in the west for sale to settlers: 4. A farmers’ revolt that lasted for a year and symbolized the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation: 5. Gave freedom of religion and outlawed slavery in the Old Northwest: 6. Set aside land for schools and churches in the ‘west’: Objective 4 1. Supported the ratification of the new Constitution: 2. Opposed the ratification of the new Constitution: 3. The system of dividing power between states and the federal government: 4. The agreement that settled the issue of how states would be represented in Congress: 5. Settled the issue of how citizens would be counted for representation in the House: 6. Demanded by AntiFederalists, before they would ratify the Constitution, to protect individual liberties: 7. Allows the Federal government to expand its power and make any laws necessary and proper: 8. The Supreme Courts power to declare laws unconstitutional: 9. Provides for an indirect election of the President: 10. The small state plan for Congress: 11. The large state plan for Congress: 12. The series of essays written by Madison, Hamilton, and Jay to persuade people to support the new Constitution: