Tigris- Euphrates Valley - Sumer
advertisement
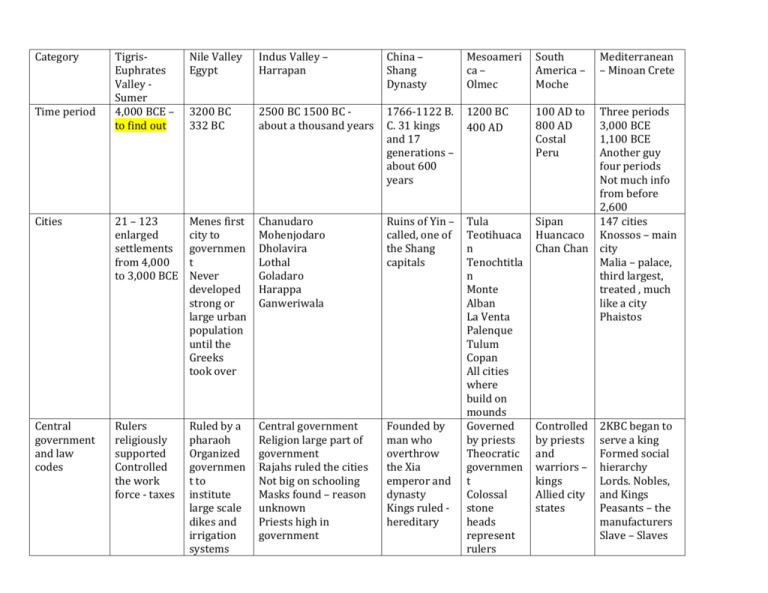
Category TigrisEuphrates Valley Sumer 4,000 BCE – to find out Nile Valley Egypt Indus Valley – Harrapan China – Shang Dynasty Mesoameri ca – Olmec South America – Moche 3200 BC 332 BC 2500 BC 1500 BC about a thousand years 1766-1122 B. C. 31 kings and 17 generations – about 600 years 1200 BC 400 AD 100 AD to 800 AD Costal Peru Cities 21 – 123 enlarged settlements from 4,000 to 3,000 BCE Menes first city to governmen t Never developed strong or large urban population until the Greeks took over Chanudaro Mohenjodaro Dholavira Lothal Goladaro Harappa Ganweriwala Ruins of Yin – called, one of the Shang capitals Central government and law codes Rulers religiously supported Controlled the work force - taxes Ruled by a pharaoh Organized governmen t to institute large scale dikes and irrigation systems Central government Religion large part of government Rajahs ruled the cities Not big on schooling Masks found – reason unknown Priests high in government Founded by man who overthrow the Xia emperor and dynasty Kings ruled hereditary Tula Teotihuaca n Tenochtitla n Monte Alban La Venta Palenque Tulum Copan All cities where build on mounds Governed by priests Theocratic governmen t Colossal stone heads represent rulers Time period Mediterranean – Minoan Crete Three periods 3,000 BCE 1,100 BCE Another guy four periods Not much info from before 2,600 Sipan 147 cities Huancaco Knossos – main Chan Chan city Malia – palace, third largest, treated , much like a city Phaistos Controlled by priests and warriors – kings Allied city states 2KBC began to serve a king Formed social hierarchy Lords. Nobles, and Kings Peasants – the manufacturers Slave – Slaves Writing and record keeping Called cuneiform – marks made on wedges, used wordpictures on clay tablets, they where good farmers and so they used tablets to keep records Two kingdoms known as lower and upper Egypt Believed it was important to record informatio n Written scripts called hieroglyphi cs able to preserve the history and ideas of ancient Egypt wrote on tombs walls and on papyrus scrolls First civilization to use language Wrote on buildings and monuments Characters are hieroglyphs Ideograms Symbolic graphs Language never decode Sentences comprise of 5-26 characters The Chinese believed that recording history was very important. They kept accurate records and even devised a system to tell if someone had counterfeited a historical document, based on writing styles Full writing system that had been developed earlier. Complex symbols where, complex meaning complex Written records Limited No writing evidence of or record writing keeping from Olmecs Debate where symbols are actually writing May have been first Mesoameri cans to develop writing Pictographs 2100-1700 BC Linear A script middle Minoan Linear B script 1450 Specialized jobs Potters, farmers, merchants – traders, smiths, jewelers Bakers Beer makers Farmers Builders Cattle herders Stone cutters Painters Mathematic ians priests Not much info Merchants Farmers Landowners Craftsmen Etc. Social classes Ruling class , financed and controlled long distance trade , merchants where the rulers agents – they sometimes acted on their own Pharaohs Priests Scribes Military Civil population System of who had the most power of the ninjas like people Highest: nobles, priests, highest officers Middle: merchants, farmers, landowners, and craftsmen Lowest: slaves Priests and slaves higher than nobles – a bit Slaves not picked by race, could free themselves after 3 years of service confirm the existence of the Shang dynasty society based on agriculture and supported by hunting and breeding animals priests farmers artists traders and merchants potters all things found in specialized societies historians 11 royal tombs found in Yin King of military nobility Territorial rulers appointed based on support in military campaigns Priests, kept Farmers Buildings The buildings where to large to be built by one person State officials Healers Architects Engineers Religious officials Oligarchs and kings Farmers Constructi on workers soldiers Soldiers Farmers Philosophers Priests Soldiers played the biggest role in Greece Farmers where a large part of the Minoan economy The elite and the common Common sometimes burned crops and the like to retaliate Fishers where the lowest Firmest a little higher – in different parts of the land Supreme king Further social structure Nobles Peasants Slaves Slaves almost no power Peasants where the manufacturers of the society Nobles included the king and other wealthy people Hierarchy powerful political and religious leaders and wealthy landowners - controll ed power rights prestige and backed with religious ideas elite officials, managers, high ranking military -saw that rulers wishes where carried out Small pop with special skills or wealth from manu. or trade Bottom was peasants and records and in charge of religion Hereditary slavery Warriors very special because of the amount of violence and the wars that they got into Had slaves Peasants at bottom of social scale based on occupatio n Gender roles laborers, few possessions, rights, or life options Slavery became widespread 2,800 slaves where POW Women where inferior to men Shared social standing of husbands and fathers Occasionally held high offices Priestesses – good position Women had about 75% of options as men 2,000 BCE women became inferior to a high level and became confined to the house Men where rulers Women bore and raised children Responsibl e for familiar domestic relationshi ps Women took care of daily needs Men interpreted women as serving them Men taught their boys their own trades and related to society at large Human figurines ad seals More female figurines than males Not much info Three types of figurines Men till, women weave Although men worked outside the home and women inside, both were portrayed as productive members of society. – both online quotes The women were awarded to their husbands at a bride price of how much it cost to raise them – seems like they were Women cared for children Both farmed Males hunted in addition to farming Women wove and cooked Sometime s being paid Many female deities Women smaller variety of jobs to complete Not subordina te to men Had their own world Both patriarcha l and matriarch al at once Men and women almost equal Men slightly more power Men valued for contributions Woman valued for weaving and pottery considered inferior to men Most frequently the women’s positions were servitudes Younger girls forbidden to leave rooms at age ten in the higher classes Women where subjugated and looked upon as objects for mans pleasure Chinese believed that sexual activity was the most natural thing in the world The Shang believed that their was a connection between sex, health, living long, and Complex technologies Wheels, boats, weapons, larger building projects Irrigation ditches The water wheel A Shaduf to put water in their irrigation canals Constructio n of pyramids and temples Mummifica tion High agriculture technology Uniform weights and measures Made instruments Copper bronze lead and tin Idea of density Used gold testing Plumbing and sanitation immortality Confucians and Buddhist heavily attacked these notions about sex Copper and Tin allows Better bronze working than that in the Middle East Chariots Metal working – large cup, weapons, using foundations to make larger structures bronze, jade, ceramic, and other types of artifacts have been found, the workmanship in the bronze in shows that they could work metal and had higher technologies Calendars – very accurate Not many domesticat ed animals – mainly plants True zero Used Mayan numerals Had irrigation system for their crops One of the first civilization s to build pyramids Metallurg y Fishhooks Earrings Chisels Spear points Shovels tweezers Plumbing and sanitation systems in every house Lead pipes, until realized it was poisoning the water Had boats and trade many items with Egypt Asia minor and Syria Discovered mars and various comets with astronomy Complex astrological tools millet, wheat, rice, mulberry, and hempindustrial grade marijuana’s fibers-George Washington did the same created a calendar based on moon cycles with big and small months use mathematics and understood decimals – used numbers up to 30,000 created mirrors that allowed people to Art Organized religion view their entire face Black-top Ceramic pictures Bronze was ware Beads, pendants, more White cross bangles, button seals, commonly line ware painted pottery used for art Copper Some human figurines than instead of – some with animal weapons stone use body parts Bronze to make casting and tools and poetry where weaponry advanced in Silver gold Shang culture lapis Many musical Faience instruments where used where ornamental invented in ly the time of Grinding the Shang palettes for dynasty paint Pottery was another common form of art in the Shang dynasty Many gods Goddess centered The Shang Believed in religion worshipped a after life Polytheistic supreme god Deities Some gods represented they called combined by animals “Shang Ti” or to form Mother goddess cattle “Lord on new deities god High.” It was Believe Some male gods a supreme physical Started in two villages god ruled body had to Baluchistan over lesser be Afghanistan – in these gods of the Naturist art Monument al Art depicted jaguars and monkeys Stone sculptures carved with perfect proportion s Represent s ceremony mythology daily life Mostly used clay Pottery for burial practices and drinking Mainly clay and pottery Pottery Architecture Painting Sculpting Metal working The art tells of a joyous society in touch with their environment In awe of logical order of the natural world Humans from hole in the ground Plumed serpents, jaguars – worshippe d Warfare between Murderou s deity known as decapitato r Appears in pictures of human sacrifice Leaders drank Orients itself around animals Numerous deities Worshipped trees, rocks, and springs Evil figures represented as human demons with the limbs persevered to go to afterlife Large pyramids used to bury pyramids regions sun, the moon, the wind, the rain, and other natural forces and places. Shang-Ti also regulated human affairs as well as ruling over the material universe. The Shang also believed that when their ancestors died, they went to heaven, but continued to show an interest in their descendants and family. The obligations within the family included the ancestors. If a family failed its duties to its cults Worshippe d ancestors and may have had something to do with megaliths human blood formed by gruesome ritual – spiced with and coagulant herb Kings – high – priests lower level of lions or other carnivores ancestors, it could bring all sorts of disasters and hardships on a family. Sacrifices were made to all gods and ancestors, but we do not know how frequent these sacrifices were, or how they were carried out. Shang sacrifices sometimes involved humans. The king preformed oracle bone divinations, especially towards the end of the life heated bones of animal sacrifices up to 40 animals like pigs and sheep sacrificed for 1 person many sacrifices for dead kings and sometimes queens http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/ - an online encyclopedia that was recommended to me by other students here at DA Shang Dynasty. (2008, April 2). New World Encyclopedia. Retrieved 17:29, November 6, 2008 from http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Shang_Dynasty?oldid=683093. http://library.thinkquest.org/12255/library/dynasty/shang.html - found by google http://www.warriortours.com/intro/history/shang/ - found by google http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/shzh/hd_shzh.htm http://www.wsu.edu:8080/~dee/ANCCHINA/SHANG.HTM http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Shang_Dynasty http://www.uni-tuebingen.de/uni/ans/eastm/back/cs12/cs12-5-bray.pdf