1. What structures are in our mouth for physical digestion?
advertisement

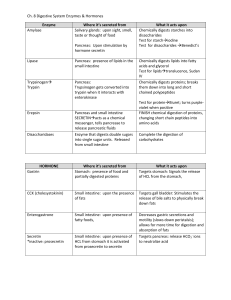
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Physical and Chemical Digestion in the Mouth (pages 408 - 409) 1. What structures are in our mouth for physical digestion? _____________ 2. State the role of a) incisors: __________________________________ b) canines: __________________________________ c) premolars: _______________________________ d) molars: __________________________________ 3. Why do herbivores have more molars than carnivores? ________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 4. What enzyme does saliva have? ________________ 5. Describe the chemical digestion that this enzyme is involved in. ________________________________________________________________________ 6. What else does saliva contain? _______________ why? ______________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 7. Once swallowed, food travels from the mouth to the stomach by way of a long tube called the ___________________________ 8. The bolus of food stretches the walls of the esophagus, activating smooth involuntary muscles that set up waves of contractions called ________________________. The Structure of the Stomach (pages 409 - 410) 9. a) Which nutrient is partly digested in the stomach? _______________ b) Which nutrients are not digested here? _________________________ 10. What controls the movement of food into and out of the stomach? ____________________ 11. The semi-liquid mixture of food and gastric juice is called ____________ 12. Nerves detect when food is present and release which hormone? ______________________________ 13. This hormone stimulates the release of gastric juice which is made up of mucus, acid and digestive enzymes. What is the purpose of the mucus? ____________________________________________________________ 14. What is the range of pH of the acid in gastric juice? _______________ 15. The acid converts the inactive enzyme pepsinogen to its active form pepsin. What is the role of pepsin? ________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ The Structure of the Small Intestine (pages 412 - 413) 16. How long is our small intestine? ______ how wide? _______________ 17. Name the three parts of the small intestine; ____________________, _____________________ and ________________. 18. a) In which part does most of the digestion occur? _________________ b) In which part does most of the absorption occur? ________________ 19. Describe how villi and microvilli increase the surface area of the small intestine for the absorption of nutrients. 20. Within each villus, a) where do digested fats get transported? ___________________________ b) where do all other nutrients enter the bloodstream? _________________ The Role of the Pancreas in Digestion (page 414 – 416) 21. When chime enters the duodenum from the stomach, the hormone cholecystokinin (CCK) is secreted. a) What does CCK signal the pancreas to do? ___________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ b) What does CCK signal the stomach to do? _____________________________________________________________ 22. Secretin is another hormone that stimulates the release of bicarbonate ions from the pancreas. What is their role? _____________________________________________________________ 23. Copy Figure 6 on page 415 below which summarizes the breakdown of proteins into amino acids. 24. The pancreas also secretes lipases. What group of nutrients do lipases break down? ___________. The Liver and Gall Bladder (page 416) 25. What is the digestive function of the liver? __________________________________________________________ 26. What does bile do? Why is this step important? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 27. What is the function of the gall bladder? _____________________________________________________________ The Structure and Function of the Large Intestine (page 418 – 419) 28. The large intestine is only 1.5 m long but is quite large in diameter. How large is it in diameter? ________ 29. What substances are absorbed by the large intestine back into the body? _____________________________________________________________ 30. What is the role of bacteria in the large intestine? _____________________________________________________________ Egestion 31. Why is fibre important in our diet? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 32. Nerves in the walls of the large intestine detect the movement of feces into the rectum. Feces are then eliminated through the anus. How are the anal sphincters controlled? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________