4×6 Module 12 drug cards
advertisement
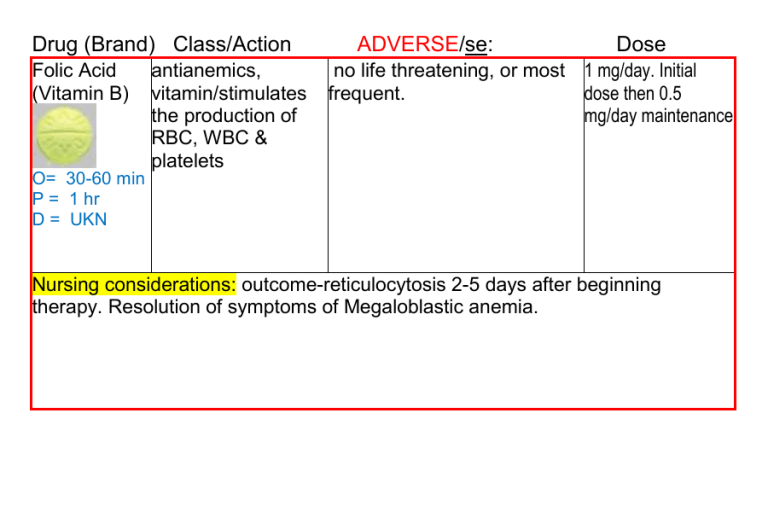
Drug (Brand) Class/Action Folic Acid (Vitamin B) antianemics, vitamin/stimulates the production of RBC, WBC & platelets ADVERSE/se: Dose no life threatening, or most 1 mg/day. Initial frequent. dose then 0.5 mg/day maintenance O= 30-60 min P = 1 hr D = UKN Nursing considerations: outcome-reticulocytosis 2-5 days after beginning therapy. Resolution of symptoms of Megaloblastic anemia. Drug (Brand) Class/Action ADVERSE/se: Dose hydroxyurea antineoplastics/interferes anorexia, N&V, PO 60-80 mg/kg as a single dose q 3 (Hydrea) with DNA synthesis diarrhea, leukopenia days or 20-30 (cellcyle S specific) Therapeutic effect: death mg/kg/day as a single dose. of rapidly replicating cells, O= 7 days particularly malignant 2 mg/day (sickle P = 10 days ones. ↓d frequency of cell) D = 21 days painful crises and ↓d need for transfusions in sickle cell anemia. Nursing considerations: assess for signs of infection/anemia/bleeding. Avoid IM injections/Monitor I/O. Labs: CBC. Hold Hydroxyura if Neurtrophils < 2,000 cells/mm3, platelet is <80,000, hgl < 9g/dl. Monitor BUN, creatinine, uric acid and liver function tests. LEUKEMIA: encourage fluid intake of 2000-3000 ml/day. Drug (Brand) Class/Action Ibuprophen (Motrin, Advil ) O P D anti-pyretic 0.5-2.5 hr 2-4 hr 6-8 hr analgesic 30 min 1-2 hr 4-6 hr inflammation 7 days 1-2 wk UKN ADVERSE/se: antipyretic, GI BLEEDING, antirheumatics, HEPATITIS, nonoppioid EXPOLIATIVE analgesics, DERMATITIS, TOX NSAID/inhibits EPIDERMAL prostaglandin NECROLYSIS, synthesis. Therp. ALLERGIC REACTION, eff: ↓d pain and ANAPHYLAXIS, N&V, inflammation. constipation, dyspepsia, Reduction of headache. fever Dose PO 400-800 mg 3-4 times daily (3600 max) take w/full glass water. remain upright 15-30 min. Nursing considerations: Patients who have asthma, aspirin-induced allergy, and nasal polyps are at ↑d risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions. Assess for rhinitis, asthma, and urticaria. Drug (Brand) Class/Action Enoxaparin (Lovenox) O= UKN P = 3-5hr D = 12 hr ADVERSE/se: BLEEDING, anemia, anticoagulant/pr thrombocytopenia (can occur up evention of to several weeks after thrombus discontinuation of therapy). formation Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. may develop on 8th day. may ↓ platelet count to 5,000/mm3 Dose VTE prophylaxis in patients undergoing knee replacement surgery-SQ-30 mg q 12 hr starting 12-24 hr po stop for 7-10 days Nursing considerations: No lab est or antidote. Davis Drug says Protamine Sulfate is antidote. Long term use can contribute to osteoporosis. Drug (Brand) Class/Action Heparin O= 20-60 min P = 2 hr D = 8-12 hr anticoagulant/ PROPHYLAXIS, prevents new clots. ADVERSE/se: Dose BLEEDING, anemia, Small 30-40 ml 3-4 x day thrombocytopenia (can occur is Prophylactic up to several weeks after Medium 40-80 mL is for discontinuation of therapy). High Risk prophylactic Therapeutic – MG/KG IV SQ Protamine sulfate Heparin-induced Antidote is the antidote thrombocytopenia. may Protamin STOPS DIC4 Hr Shelf Life develop on 8th day. may Sulfate Production of reduce platelet count to Platelets 5,000/mm3 HIT or HAT Nursing considerations: Administer deep into SQ tissue. Alternate sites abdominal wall above the iliac crest. 45° or 90° angle into a skin fold, hold skin fold throughout injection. Do not aspirate or massage. Rotate sites frequently. Do not administer IM because of danger of hematoma formation Assess for signs of bleeding and hemorrhage (bleeding gums; nosebleed; unusual bruising; black, tarry stools; hematuria; fall in hematocrit or blood pressure; guaiac-positive stools). Notify physician if these occur. aPTT, platelet count every 2-3 days throughout therapy Drug (Brand) Class/Action ADVERSE/se: Dose colony-stimulating medullary bone pain IV, SQ 5 mcg/kg/day factors/stimulates avoid use for 24 hrs immature Neurtrophils before and after to divide and chemotherapy. differentiate. ↓d incidence of infection in chemo pt. improve progenitor cells for BMT Nursing considerations: monitor HR, BP, RR, bone pain. LAB CBC. After bone filgrastim (Neupogen) O= P= D= marrow transplant, the daily dose is titrated by the neutrophil response. When the ANC is >1000/mm3 for 3 consecutive days, the dose should be ↓d by 5 mcg/kg/day. If the ANC remains >1000/mm 3 for 3 or more consecutive days, filgrastim is discontinued. If the ANC ↓s to <1000/mm3, filgrastim should be resumed at 5 mcg/kg/day. Drug (Brand) Class/Action ADVERSE/se: Dose SQ IV: 50-100 epoetin antianemics/stimula SEIZURES, hypertension units/kg 3 times (Epogen) tes erythropoiesis weekly initially, IV RBC then adjust dose O= 7-10 based on days hematocrit. P = 2 month D = 2 wk Nursing considerations: May ↑ the requirement for heparin anticoagulation during hemodialysis. Monitor BP, anemia, dialysis shunts. Labs: May cause ↑ in WBCs and platelets. May ↓ bleeding times. Serum ferritin, transferrin, and iron levels should also be monitored to assess need for concurrent iron therapy. Transferrin saturation should be at least 20% and ferritin should be at least 100 ng/ml. Institute seizure precautions in patients who experience greater than a 4-point ↑ in hematocrit in a 2-wk period or exhibit any change in neurologic status. Risk of seizures is greatest during the first 90 days of therapy Drug (Brand) Class/Action Warfarin (Coumadin) ADVERSE/se: Dose PO IV (Adults): 2.5-10 anticoagulant/ BLEEDING Prevention of the antidote is vitamin K mg/day for 2-4 days; thromboembolic (phytonadione, then adjust daily dose by events. Helps inhibit AquaMEPHYTON). results of prothrombin When taken with other time or international blood clots. O= 36-72 hr Prophylaxis take meds, they go first normalized ratio (INR). P = 5-7 days home drug. hard to and warfarin Initiate therapy with D = 2-5 days PT control accumulates in blood. lower doses in geriatric > 13 or INR > 3.0 LONG Term or debilitated patients. means you are taking too long to form a clot Nursing considerations: Before administering, evaluate recent INR or PT results and have second practitioner independently check original order. Assess patient for signs of bleeding and hemorrhage (bleeding gums; nosebleed; unusual bruising; tarry, black stools; hematuria; fall in hematocrit or blood pressure; guaiac-positive stools, urine, or nasogastric aspirate). Withholding 1 or more doses of medication is usually sufficient if INR is excessively elevated or if minor bleeding occurs. If overdose occurs the antidote is vitamin K (phytonadione, AquaMEPHYTON). no Grapefruit juice Drug (Brand) Class/Action predniSONE (Sterapred) antiasthmatic, corticosteroids ADVERSE/se: PEPTIC ULCERATION, THROMBOEMBOLISM, osteoporosis, muscle wasting, N&V, hypertension, ↓d wound healing, ecchymoses, fragility , hirsutism, Petechiae, adrenal suppression, anorexia, depression, euphoria, cushingoid appearance. Dose most uses PO 5-60 mg/day w/meals, Capsules should be swallowed who≤ do not crush, break, or chew. O= UKN P = UKN D = 1.25-1.5 days Nursing considerations: monitor I/O, wt, edema, rales/Dyspnea, cerebral edema, Lab: lytes, glucose, May cause hyperglycemia, especially in persons with diabetes. May cause hypokalemia. Patients on prolonged therapy should routinely have CBC, serum electrolytes, and serum and urine glucose evaluated. May ↓ WBCs. May cause hyperglycemia, especially in persons with diabetes. May ↓ serum potassium and calcium and ↑ serum sodium concentrations. Guaiac-test stools. Promptly report presence of guaiac-positive stools. May ↑ serum cholesterol and lipid values. May ↓ uptake of thyroid 123I or 131I. Drug (Brand) Class/Action ADVERSE/se: dexamethasone antiasthmatic, PEPTIC ULCERATION, (Decadron) corticosteroid/su THROMBOEMBOLISM, osteoporosis, muscle wasting, ppress N&V, hypertension, ↓d wound inflammation Dose PO,IM,IV mg/daily dependent upon therapy Capsules should healing, ecchymoses, fragility , be swallowed hirsutism, Petechiae, adrenal O= UKN who≤ do not suppression, anorexia, crush, break, or P = 1-3 hr depression, euphoria, chew. D = 2.75 days cushingoid appearance. Nursing considerations: monitor I/O, wt, edema, rales/Dyspnea, cerebral edema, Lab: lytes, glucose, May cause hyperglycemia, especially in persons with diabetes. May cause hypokalemia. Patients on prolonged therapy should routinely have CBC, serum electrolytes, and serum and urine glucose evaluated. May ↓ WBCs. May cause hyperglycemia, especially in persons with diabetes. May ↓ serum potassium and calcium and ↑ serum sodium concentrations. Guaiac-test stools. Promptly report presence of guaiac-positive stools. May ↑ serum cholesterol and lipid values. May ↓ uptake of thyroid 123I or 131I. Drug (Brand) Class/Action ADVERSE/se: Dose Renal Allograft azathioprine immuneSERUM SICKNESS, Rejection Prevention (muran ) suppressant/antagoi leucopenia, anemia, PO IV 3-5 mg/kg/day zes purine thrombocytopenia, initially; maint. dose 1metabolism –inhibit pancytopenia, chills, 3 mg/kg/day. DNA/RNA fever, anorexia, RA PO: 1 mg/kg/day PO synthesis. hepatotoxicity, N&V for 6-8 wk, ↑ by 0.5 O= 6-8 wk mg/kg/day q 4 wk until P = 12 wk response D = UKN Nursing considerations: assess for infection, I/O, wt, ↓ urine output- toxicity. Leukocyte count of < 3000 or platelet count of <100,000/mm 3 may necessitate a reduction in dosage or temporary discontinuation. ↑ Drug (Brand) Class/Action ADVERSE/se: Dose cyclophopha antineoplastics, PULMONARY PO 1-5 mg/kg/day High Alert: Fatalities have mide immuneFIBROSIS, occurred with chemotherapeutic (Cytoxan) suppressants/ MYOCARDIAL interferes with FIBROSIS, agents. Before administering, clarify all ambiguous orders; DNA HEMORRHAGIC double check single, daily, and CYSTITIS, O= 7 days LEUKOPENIA, N&V, course-of-therapy dose limits; P = 7-15 days anorexia, Hematuria, have second practitioner D = 21 days independently double check alopecia, thrombocytopenia original order, calculations and infusion pump settings. Nursing considerations: Monitor blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate, and temperature frequently during administration. Report significant changes. Monitor I/O. To ↓ the risk of hemorrhagic cystitis, fluid intake should be at least 3000 ml/day for adults and 1000-2000 ml/day for children. May be administered with mesna. Monitor for bone marrow depression. Assess for bleeding (bleeding gums, bruising, petechiae, guaiac stools, urine, and emesis) and avoid IM injections and taking rectal temperatures if platelet count is low. Apply pressure to venipuncture sites for 10 min. Drug (Brand) Class/Action ADVERSE/se: Dose Assess for signs of infection during neutropenia. Anemia may occur. Monitor for ↑ fatigue, dyspnea, and orthostatic hypotension. Assess nausea, vomiting, and appetite. Weigh weekly. Antiemetics may be given 30 min before administration of medication to minimize GI effects. Anorexia and weight loss can be minimized by feeding frequent light meals. Encourage patient to drink 2000-3000 ml/day to promote excretion of uric acid. Alkalinization of the urine may be used to help prevent uric acid nephropathy. Assess cardiac and respiratory status for dyspnea, rales/crackles, weight gain, edema. Pulmonary toxicity may occur after prolonged therapy. Cardiotoxicity may occur early in therapy and is characterized by symptoms of CHF. Lab Test Considerations: Monitor CBC with differential and platelet count before and periodically during therapy. The nadir of leukopenia occurs in 7-12 days (recovery in 17-21 days). Leukocytes should be maintained at 2500-4000/mm3. May also cause thrombocytopenia (nadir 10-15 days), and rarely causes anemia. Monitor BUN, creatinine, and uric acid before and frequently during therapy to detect nephrotoxicity. Monitor ALT, AST, LDH, and serum bilirubin before and frequently during therapy to detect hepatotoxicity. Urinalysis should be evaluated before initiating therapy and frequently during therapy to detect hematuria or change in specific gravity indicative of SIADH. cyclophophamide (Cytoxan) continued. Drug (Brand) Class/Action ADVERSE/se: Dose Arginine amino acid supplementation/antisickling properties enhancing the (L-Arginine) availability of nitric oxide (vasodilator) resulting in decreased pulmonary artery pressure. Arginine is synergistic with hydroxyurea and can be useful as combination therapy for managing pulmonary hypertension. Nursing considerations: used in patient w/sickle cell disease