4.7 Bonding Practice Questions bonding_practice_qs
advertisement

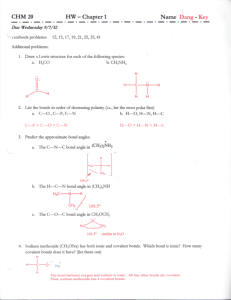
Name________________________________________________ Date ______________ Per __________ Bonding Practice 1. What is an ionic bond and how do they form? Provide an example of an ionic substance. 2. What ions are formed by each of the following atoms and why do they have those charges? a. Sodium b. Calcium c. Aluminum d. Phosphorus e. Oxygen f. Bromine 3. What is a covalent bond and how do they form? Provide an example of a covalent substance. 4. Draw the Lewis structures for a. Chlorine gas b. Ammonia c. Ammonium ion d. Methane (CH4) 5. When C2H4 , C2H2 and C2H6 are arranged in order of increasing C–C bond length, what is the correct order? Explain. 6. What is unique about transition elements’ ability to form ions? 7. What type of bond occurs between lithium and fluorine? How do you know? 8. What is the formula for: a. Sodium hydroxide b. Calcium carbonate c. Potassium phosphate d. Sodium sulfate 9. Explain, relative to its structure, how the chlorine and sodium ions of sodium chloride combine to form a grain of salt. 10. Draw the Lewis structures, give the bond angles, identify the shape, determine the polarity of, and tell the type of intermolecular force each of the following compounds or ions form: a. SO2 b. H2S c. H3O+ d. C2H6 e. PO4-3 11. Which substance from the question above has the highest polarity? Lowest? 12. Rank from highest to lowest between: H2, N2, O2… a. Number of bonds b. Bond strength c. Bond length 13. Explain the different molecular structures that can be formed by silicon. 14. Describe the differences in structure for: graphite, diamond and fullerenes. 15. Rank the boiling points of the following substances, from highest to lowest: HF, CH 4, CH3Cl 16. Why is copper wire used as a common electrical conductor? (Refer to its sub-atomic makeup) 17. Rank the types of bonds and intermolecular forces from strongest to weakest. 18. What is the difference between accuracy and precision? Name________________________________________________ Date ______________ Per __________ Bonding Practice 1. What is an ionic bond and how do they form? Provide an example of an ionic substance. 2. What ions are formed by each of the following atoms and why do they have those charges? a. Sodium b. Calcium c. Aluminum d. Phosphorus e. Oxygen f. Bromine 3. What is a covalent bond and how do they form? Provide an example of a covalent substance. 4. Draw the Lewis structures for a. Chlorine gas b. Ammonia c. Ammonium ion d. Methane (CH4) 5. When C2H4 , C2H2 and C2H6 are arranged in order of increasing C–C bond length, what is the correct order? Explain. 6. What is unique about transition elements’ ability to form ions? 7. What type of bond occurs between lithium and fluorine? How do you know? 8. What is the formula for: a. Sodium hydroxide b. Calcium carbonate c. Potassium phosphate d. Sodium sulfate 9. Explain, relative to its structure, how the chlorine and sodium ions of sodium chloride combine to form a grain of salt. 10. Draw the Lewis structures, give the bond angles, identify the shape, determine the polarity of, and tell the type of intermolecular force each of the following compounds or ions form: a. SO2 b. H2S c. H3O+ d. C2H6 e. PO4-3 11. Which substance from the question above has the highest polarity? Lowest? 12. Rank from highest to lowest between: H2, N2, O2… a. Number of bonds b. Bond strength c. Bond length 13. Explain the different molecular structures that can be formed by silicon. 14. Describe the differences in structure for: graphite, diamond and fullerenes. 15. Rank the boiling points of the following substances, from highest to lowest: HF, CH 4, CH3Cl 16. Why is copper wire used as a common electrical conductor? (Refer to its sub-atomic makeup) 17. Rank the types of bonds and intermolecular forces from strongest to weakest. 18. What is the difference between accuracy and precision?