The Nursing Process
advertisement

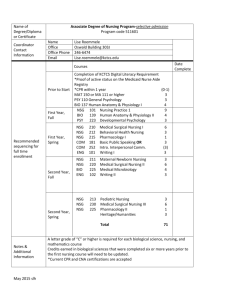
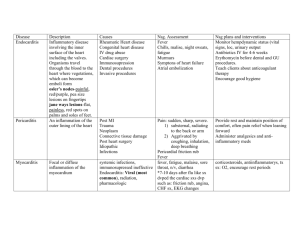
The Nursing Process I. Historical Development: ANA defines nursing as “the diagnosis and treatment of human responses to actual or potential health problems”. 1960’s: 1955: 1950 & early 60’s: 1970’s 1973 1973 1982 Nsg educators began to ID and describe what nurses did to help students understand the intellectual process of nsg. Nsg process first used as a term by Lydia Hall 1959 Dorothy Johnson 1961 Ida Orlando 1963 Ernestine Wiedenbach 1967 Lois Knowles – 5 D’s Discover, Delve, Decide, Do, discriminate 1967 WICHE (Western Interstate Commission of Higher Education) & Catholic University: Assessment, Planning, Intervention, Evaluation Conferences on Nursing Diagnoses began North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) Developed the first list of approved nsg dx. Holds national conferences every 2 years to revise the list. ANA used the nsg process as a guide to develop “Standards of Nursing Practice”. The 5 Step Process began. NCLEX (professional state board licensing exam) included the nsg process as one of the concepts for competent nsg practice. II. Definition: Systematic problem-solving method for providing individualized care for individuals, families, and communities in all states of health and illness. Purpose is to develop a holistic plan of individualized care to help the client meet goals. III. Steps: Assessment, Nsg dx, Planning, Implementation, Evaluation Purpose: The written plan of care provides for continuity between nurses as they change shifts and on different days. Changes in the plan must be passed on from shift to shift. A. Assessment: Subjective: Objective: Physical Exam: Inspection, Palpation, Percussion, and Auscultation B. Nursing Diagnosis The statement of actual or potential (Risk for) problems that can be resolved, diminished, or in some way changed by nursing intervention. ANA defines nsg diagnosis: “A clinical judgment about individual, family, or community responses to actual or potential health problems or to life processes”. 1. 2. Nursing dx has three parts: Problem Statement: From NANDA list. Etiology: Related to…. This cannot be the medical diagnosis. It must be something that you can work to improve. Ideally this can be resolved through independent nsg interventions. Signs & Symptoms: Assessment findings that validate the presence of the problem. Types of Nsg Dx Actual: Response that the client is currently experiencing as a result of the health problems or life processes. Risk for: Recognition of risk factors that could contribute to an actual problem. Possible: When the nurse thinks that a client may have a certain dx, but more data is needed for confirmation. Collaborative: Nonnursing dx that result as a complication of the altered health state. These problems require nsg and medical interventions for dx and tx. 3. Prioritization: B. Planning Development of goals. Note that the goal statement is composed of three parts: an introduction (that states the overall goal), time frame for completion, measurable outcome criteria. The outcomes need to be: very specific, measurable, appro. & realistic, Developed with the client &/or family. C. Interventions Use action verbs: No passive words: walk, assist, and demonstrate encourage, try, etc. 1. Specifications: Need to be appro for the client’s health status, his age, developmental level. Include a mix of independent, interdependent, and dependent nsg actions. Very specific re: time, action, frequency, quantity, method. Note that ea should be written such that another nurse would implement it exactly as you would. 2. Types of Interventions: Independent: May be complete without a MD order. Based on the nurse’s independent judgement. Interdependent: Need MD order to institute requires nsg action to carry out. May require nurse’s independent judgement as to when to carry out. Dependent: Need MD order to institute and carry out. 3. Categorize the interventions: Develop interventions appro to Assessment, Treat, Teach. Write down a header and list all appro interventions for ea. 4. Address ea outcome criteria of the goal statements: Implementation: Carry out the nsg care plan. Cont. assessment of the client to ensure that his status has not changed. D. Evaluation: