NURSING PROCESS
advertisement

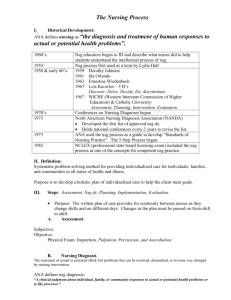
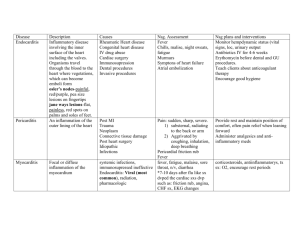
NURSING PROCESS PRE TEST 1. Identify all steps of the nsg process 2. Identify the step of the Nsg process where goals are identified. 3. Identify the step of the Nsg. Process where expected outcomes are identified. 4. What does NANDA stand for? 5. Identify 1 benefit of the Nsg Process for the Pt. NSG PROCESS DEFINITION 1. Systematic, rational method of planning & providing NSG care 2. Goal is to: identify a Pt.’s healthcare status, actual or potential health problems 3. To establish plans to meet the identified needs 4. To deliver specific NSG interventions to address those needs (Con’t) NSG process is an organized, systematic method of giving goaloriented, humanistic care that’s both effective and efficient BENEFITS (5) 1. Improves quality of care Pts. Receive 2. Promotes efficient use of time & resources 3. Serves as framework for nurses’ accountability 4. Enhances collaboration 5. Assists NSG to define its unique role in healthcare system STEPS OF NSG PROCESS 1. Assessment 2. Diagnosis =A =Delicious 3. Planning =P 4. Implementation =I 5. Evaluation/Reassessment =E NSG PROCESS & THE LVN COMPETENCIES NLN (1989) defines role of LPN/LVN: “Primary role of LPN/LVN is to provide nsg. Care for clients in structured health care settings who are experiencing common, well defined health problems.” 2 Roles are designated for LPN/LVN: – Care Provider – Member of the Discipline of Nsg. COMPETENCIES IN CARE PROVIDER ROLE LPN/LVN 1. Assessment: assesses basic needs of Pts.=collecting data & identifying deviations from normal. Documents these data & communicates findings. PLANNING Contributes to development of Nsg care plans, prioritizes Pt. care needs & assists in revising such care plans. Uses established Nsg. Diagnoses in this planning process for Pts. With common, well-defined health problems IMPLEMENTATION Provides care using effective communication, collaborating with other health team members and instructing Pts. Regarding health maintenance. Uses accepted standards of practice & records & reports implementation activities EVALUATION Seeks guidance & continues collaboration with others in modifying Nsg. Approaches and revising Nsg. Care plans In Member of Discipline Role LVN COMPETENCIES 1. Identifies personal strengths, weaknesses & potential, using educational opportunities 2. Adheres to Nsg’s code of ethics 3. Functions as a healthcare consumer advocate NCLEX-PN TEST PLAN (1989) LVN ROLE IN NSG PROCESS Acts in a more dependent role when participating in planning and evaluation phases and in a more independent role when participating in data collecting & implementing phases Assists with collection of data about Pt., contributes to plan of care, performs basic therapeutic & preventive Nsg measures, assists in evaluating outcomes & nsg orders ADN & NSG. PROCESS COMPETENCIES NLN (1990) identified 3 roles of AND: 1. Provider of Care 2. Manager of care 3. Member within the Discipline of Nsg. ADN in Care Provider Role ASSESSMENT 1. In addition to competencies at LVN level, ADN conducts a more extensive data collection process, using a variety of resources 2. Contributes this information to a data base & is able to identify changes in Pt.’s health status DIAGNOSIS The ADN has educational preparation to analyze & interpret data, identifying actual or potential healthcare needs & selecting Nsg Diagnoses PLANNING 1. In addition to competencies at LVN level, A.D.N. establishes Pt.-centered goals, develops client-specific care plans 2. Develops individualized teaching plans in collaboration with other healthcare workers IMPLEMENTATION 1. In addition to LVN competencies, A.D.N. initiates Nsg. Interventions, implementing care plans according to priorities of goals & making adjustments as client conditions change. 2. Also fosters a health-supportive environment, promoting rehab potential (con’t) 3. Provides environment with physical & psychological safety 4. Uses communication techniques that assist clients with coping & problem solving. 4. Individualized, client- centered care management & teaching plans are implemented, providing continuity of care & referrals prn EVALUATION Evaluates client’s progress toward goals & the effects of interventions, revising care plans as needed A.D.N. post 6 months of practice competencies Clinical competence, effective communication, decision making, ability to develop, implement evaluate individualized plans of care, promoting participation by client and others NCLEX-RN TEST PLAN & ROLE IN NSG PROCESS 1. Establishes a data base 2. Identifies health care needs/problems, formulating Nursing Diagnoses 3. Sets goals & strategies to meet Pt. needs, involving Pt. & others & collaborating with other health team members 4. Implements & manages Delivery of Pt. care; counsels & teaches Pt (con’t) 5. Evaluates outcomes, Pt. ability with self-care, & impact of teaching on health team members 6. Communicates findings, analysis, responses ASSESSMENT 1. Data collection 2. Data organization 3. Data validation 4. Communication/documentation of data TYPES OF DATA 1. 2. 3. 4. Objective Subjective Primary Secondary How nurses collect data 1. 2. 3. 4. Observation Examination Interview Consultation ORGANIZATION OF DATA 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Biological data Psychological data Social data Cultural data Communication DATA VALIDATION Complete, factual, accurate? 1. Cues: subjective & objective 2. Inferences = nurse’s interpretation of the cues 3. Premature closure= making inferences based on insufficient data COMMUNICATING & DOCUMENTING DATA 1. Assessment flow sheets 2. Narrative assessment documentation sheets 3. Report DIAGNOSING DEFINITION Nsg Diagnosis is a clinical judgement about individual, family or community responses to actual & potential health problems/life processes… provide the basis for selection of NSRG interventions to achieve outcomes for which the nurse is accountable TYPES OF NURSING DIAGNOSES 1. 2. 3. 4. Actual Risk for Possible Wellness North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) Established a classification system of diagnostic labels or problem statements PARTS OF THE NURSING DIAGNOSIS 1. P = Problem 2. E= Etiology 3. S= Signs & symptoms or manifestations PLANNING 1. Prioritize 2. Develop goals/expected outcomes or outcome criteria 3. Develop Nsg. Orders or prescriptions NURSING INTERVENTIONS 1. Implement or put into use these in order to assist the client in achieving the stated goal 2. Interventions will prevent, reduce, eliminate the client’s health problems TYPES OF NSG INTERVENTIONS 1. Independent 2. Dependent 3. collaborative COMPONENTS OF NSG ORDERS 1. Date written 2. Specific as to: who will do what, when, where, how long or how often 3. Signature/title at end of orders 4. Each order must be accompanied by the scientific rationale ( and its source) that addresses why a particular Nsg. Order addresses the Nsg. Diagnosis and goal EVALUATION & REASSESSMENT 1. Goal met 2. Goal partially met 3. Goal not met 4. Goal in progress Reassessment= the entire plan of care (data, ND, goal/EO, Nsg orders) must be reassessed USING NURSING CARE PLAN PUBLICATIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. Carpenito Text & handbook Kozier deWitt Gulanik USING NURSING CARE PLAN GRADING CRITERIA NURSING DIAGNOSIS & RESPIRATORY NURSING DIAGNOSIS & CARDIOVASCULAR NURSING DIAGNOSIS & UROLOGICAL NURSING DIAGNOSIS & Psychosocial Health DEVELOPMENTAL FACTORS & NURSING PROCESS SOCIOCULTURAL FACTORS & NSG PROCESS PEDIATRICS & NURSING PROCESS