Notes on the Periodic Table
advertisement

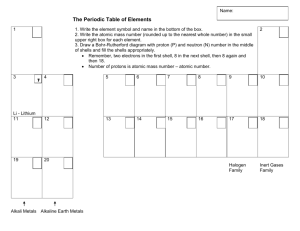
11/20/15 The Periodic Table – organizes elements into Groups and Periods. 1) Periods: (7) a set of elements that runs left to right a. They are arranged to increase by atomic number i. The atomic number is the number of protons and (in a stable atom,) the number of electrons in an atom. 2) Groups: (8 or 18) groups are arranged according to the number of electrons in the outer shell of the atom. Alkali Metals: Group 1 - Lose one electron (one electron in the outer shell) - Very reactive - Do not exist freely in nature - Have the characteristics of all metals: o Are malleable – bendable o Are ductile – can be strung into wire. o Are good conductors of heat and electricity. Alkaline Earth Metals Group 2 - Two electrons in the outer shell - Lose two electrons - Very reactive - Typical metals Transition Metals - 38 elements - Have properties/characteristics of metals - Iron, cobalt, and nickel produce a magnetic field. Other Metals - 7 elements in this group - They are ductile and malleable - They are solids, have a relatively high density, and opaque (not see-through) Group – Metalloids - Possess properties of metals and non-metals. - Carry an electric charge under special conditions - Semi-conductors: silicon and germanium Group – Non-Metals - Characteristics: - 1) don’t reflect light - 2) not conductors - 3) very brittle - 4) not ductile or malleable. Group 7 – Halogens - Salt forming elements - Compounds from these are called salts - 7 electrons in the outer shell - They exist as solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature. Group 8 – Noble gases - Inert or stable - 8 electrons in the outer shell (valence electrons) Group – Rare Earth Elements - 30 elements - Trans-uranium – man-made or synthetic.