Name - Long Branch Public Schools
advertisement
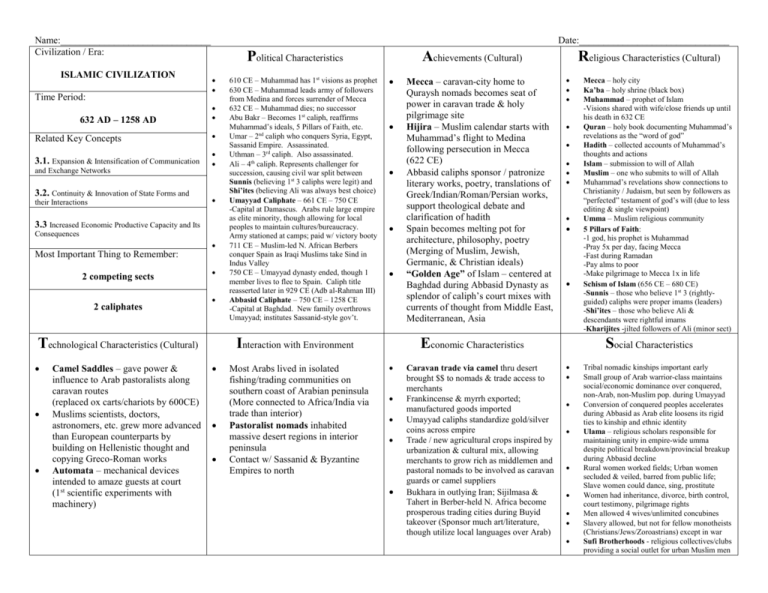
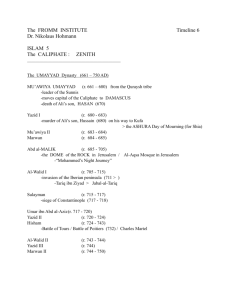
Name:_______________________________ Civilization / Era: ISLAMIC CIVILIZATION Time Period: 632 AD – 1258 AD Date:_______________________________ Political Characteristics Related Key Concepts 3.1. Expansion & Intensification of Communication and Exchange Networks 3.2. Continuity & Innovation of State Forms and their Interactions 3.3 Increased Economic Productive Capacity and Its Consequences Most Important Thing to Remember: 2 competing sects 2 caliphates Technological Characteristics (Cultural) Camel Saddles – gave power & influence to Arab pastoralists along caravan routes (replaced ox carts/chariots by 600CE) Muslims scientists, doctors, astronomers, etc. grew more advanced than European counterparts by building on Hellenistic thought and copying Greco-Roman works Automata – mechanical devices intended to amaze guests at court (1st scientific experiments with machinery) 610 CE – Muhammad has 1st visions as prophet 630 CE – Muhammad leads army of followers from Medina and forces surrender of Mecca 632 CE – Muhammad dies; no successor Abu Bakr – Becomes 1st caliph, reaffirms Muhammad’s ideals, 5 Pillars of Faith, etc. Umar – 2nd caliph who conquers Syria, Egypt, Sassanid Empire. Assassinated. Uthman – 3rd caliph. Also assassinated. Ali – 4th caliph. Represents challenger for succession, causing civil war split between Sunnis (believing 1st 3 caliphs were legit) and Shi’ites (believing Ali was always best choice) Umayyad Caliphate – 661 CE – 750 CE -Capital at Damascus. Arabs rule large empire as elite minority, though allowing for local peoples to maintain cultures/bureaucracy. Army stationed at camps; paid w/ victory booty 711 CE – Muslim-led N. African Berbers conquer Spain as Iraqi Muslims take Sind in Indus Valley 750 CE – Umayyad dynasty ended, though 1 member lives to flee to Spain. Caliph title reasserted later in 929 CE (Adb al-Rahman III) Abbasid Caliphate – 750 CE – 1258 CE -Capital at Baghdad. New family overthrows Umayyad; institutes Sassanid-style gov’t. Achievements (Cultural) Interaction with Environment Most Arabs lived in isolated fishing/trading communities on southern coast of Arabian peninsula (More connected to Africa/India via trade than interior) Pastoralist nomads inhabited massive desert regions in interior peninsula Contact w/ Sassanid & Byzantine Empires to north Mecca – caravan-city home to Quraysh nomads becomes seat of power in caravan trade & holy pilgrimage site Hijira – Muslim calendar starts with Muhammad’s flight to Medina following persecution in Mecca (622 CE) Abbasid caliphs sponsor / patronize literary works, poetry, translations of Greek/Indian/Roman/Persian works, support theological debate and clarification of hadith Spain becomes melting pot for architecture, philosophy, poetry (Merging of Muslim, Jewish, Germanic, & Christian ideals) “Golden Age” of Islam – centered at Baghdad during Abbasid Dynasty as splendor of caliph’s court mixes with currents of thought from Middle East, Mediterranean, Asia Religious Characteristics (Cultural) Economic Characteristics Caravan trade via camel thru desert brought $$ to nomads & trade access to merchants Frankincense & myrrh exported; manufactured goods imported Umayyad caliphs standardize gold/silver coins across empire Trade / new agricultural crops inspired by urbanization & cultural mix, allowing merchants to grow rich as middlemen and pastoral nomads to be involved as caravan guards or camel suppliers Bukhara in outlying Iran; Sijilmasa & Tahert in Berber-held N. Africa become prosperous trading cities during Buyid takeover (Sponsor much art/literature, though utilize local languages over Arab) Mecca – holy city Ka’ba – holy shrine (black box) Muhammad – prophet of Islam -Visions shared with wife/close friends up until his death in 632 CE Quran – holy book documenting Muhammad’s revelations as the “word of god” Hadith – collected accounts of Muhammad’s thoughts and actions Islam – submission to will of Allah Muslim – one who submits to will of Allah Muhammad’s revelations show connections to Christianity / Judaism, but seen by followers as “perfected” testament of god’s will (due to less editing & single viewpoint) Umma – Muslim religious community 5 Pillars of Faith: -1 god, his prophet is Muhammad -Pray 5x per day, facing Mecca -Fast during Ramadan -Pay alms to poor -Make pilgrimage to Mecca 1x in life Schism of Islam (656 CE – 680 CE) -Sunnis – those who believe 1st 3 (rightlyguided) caliphs were proper imams (leaders) -Shi’ites – those who believe Ali & descendants were rightful imams -Kharijites -jilted followers of Ali (minor sect) Social Characteristics Tribal nomadic kinships important early Small group of Arab warrior-class maintains social/economic dominance over conquered, non-Arab, non-Muslim pop. during Umayyad Conversion of conquered peoples accelerates during Abbasid as Arab elite loosens its rigid ties to kinship and ethnic identity Ulama – religious scholars responsible for maintaining unity in empire-wide umma despite political breakdown/provincial breakup during Abbasid decline Rural women worked fields; Urban women secluded & veiled, barred from public life; Slave women could dance, sing, prostitute Women had inheritance, divorce, birth control, court testimony, pilgrimage rights Men allowed 4 wives/unlimited concubines Slavery allowed, but not for fellow monotheists (Christians/Jews/Zoroastrians) except in war Sufi Brotherhoods - religious collectives/clubs providing a social outlet for urban Muslim men Name:_______________________________ Civilization / Era: ISLAMIC CIVILIZATION Date:_______________________________ Political Characteristics (cont.) Time Period: 632 AD – 1258 AD Related Key Concepts 3.1. Expansion & Intensification of Communication and Exchange Networks 3.2. Continuity & Innovation of State Forms and their Interactions 3.3 Increased Economic Productive Capacity and Its Consequences Most Important Thing to Remember: 2 competing sects 2 caliphates 850 – 1050 CE – Political fragmentation era (Provinces break away, tax base lost at Baghdad, slow travel/communication, taxes and administration inefficient for expansive empire) Turkic Mamluk slaves trained as standing army for caliphs; failure to pay them sees them depose caliphs and choose their own while draining funds to build new temporary capital at Samarra from 835 CE – 892 CE. Fatimid Dynasty - 909 CE – 969 CE -Capital at Cairo. Takes over all N. Africa, then Egypt. Prosperous sub-Saharan trade with Ghana for gold, spreads Islam there. 945 CE – Buyid Shi’ites – Takeover of caliphate; they maintain it as puppet regime. Al-Andalus 740 CE – 1492 CE – Umayyad controlled Spain. Becomes major melting pot. 1030’s CE – Seljuk Turks gain power, ruling at Baghdad. Win Battle of Manzikert vs. Byzantines (1071 CE) taking all of Anatolia. -Seljuks feud over claims to who is sultan (caliph), thus for years ignoring irrigation, city maintenance, etc. -Major pop. decline, cities shrink, drying up of Mesopotamia region The Crusades - 1099 CE – 1187 CE -Muslims lose Jerusalem to Christian knights, then regain it back under Saladin, who also ends Fatimid Dynasty by uniting Egypt & Syria Saladin’s descendants split land-holdings, but surrender power to Turkic Mamluk troops, who rule at Cairo and fight off Mongols until 1517 CE. 1258 CE - Mongol invasion from East leads to sacking of Baghdad and end of Abbasid Caliphate. Shari’a – Post-Quran Islamic law that contains 6 Sunni & 4 Shi’ite holy books that offer thousands of anecdotes on ritual, customs, beliefs all purported to be Muhammad’s views (Widely consistent from Morocco to India)