Ag Decision Maker Activity
advertisement
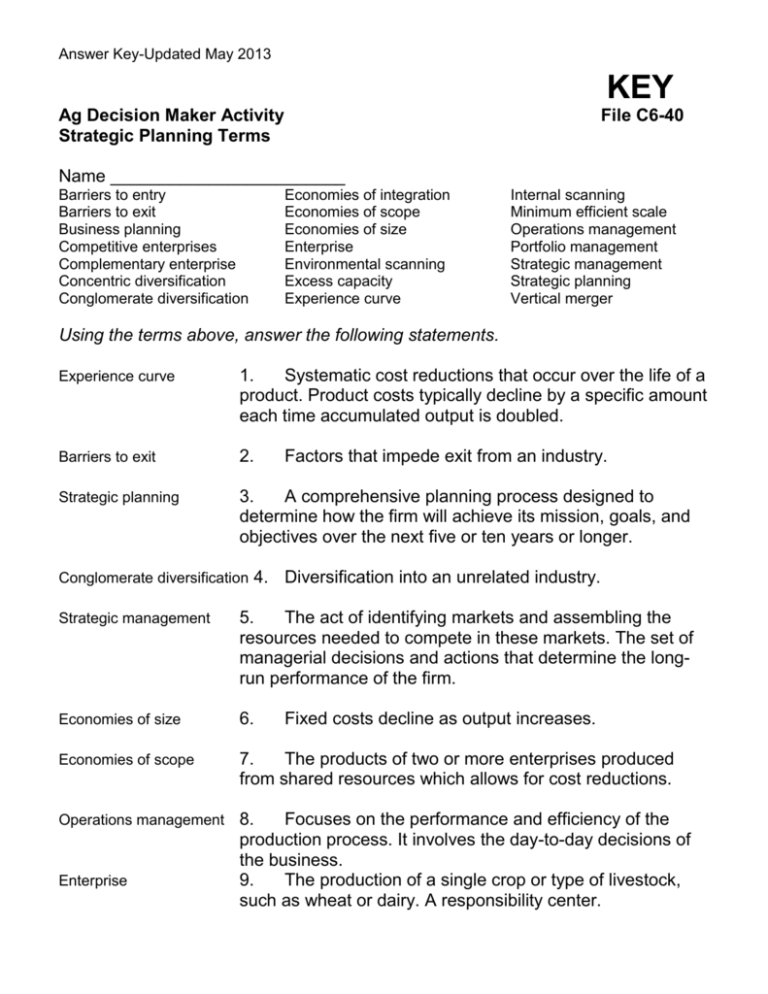
Answer Key-Updated May 2013 KEY Ag Decision Maker Activity Strategic Planning Terms File C6-40 Name ________________________ Barriers to entry Barriers to exit Business planning Competitive enterprises Complementary enterprise Concentric diversification Conglomerate diversification Economies of integration Economies of scope Economies of size Enterprise Environmental scanning Excess capacity Experience curve Internal scanning Minimum efficient scale Operations management Portfolio management Strategic management Strategic planning Vertical merger Using the terms above, answer the following statements. Experience curve 1. Systematic cost reductions that occur over the life of a product. Product costs typically decline by a specific amount each time accumulated output is doubled. Barriers to exit 2. Strategic planning 3. A comprehensive planning process designed to determine how the firm will achieve its mission, goals, and objectives over the next five or ten years or longer. Conglomerate diversification 4. Factors that impede exit from an industry. Diversification into an unrelated industry. Strategic management 5. The act of identifying markets and assembling the resources needed to compete in these markets. The set of managerial decisions and actions that determine the longrun performance of the firm. Economies of size 6. Economies of scope 7. The products of two or more enterprises produced from shared resources which allows for cost reductions. Operations management 8. Focuses on the performance and efficiency of the production process. It involves the day-to-day decisions of the business. 9. The production of a single crop or type of livestock, such as wheat or dairy. A responsibility center. Enterprise Fixed costs decline as output increases. Answer Key-Updated May 2013 Ag Decision Maker Activity Continued... Strategic Planning Terms Competitive enterprises File C6-40 10. Enterprises for which the output level of one can be increased only by decreasing the output level of the other. Complementary enterprise 11. Enterprises for which increasing the output level of one also increased the output level of the other. Excess capacity 12. The ability to produce additional units of output without increasing fixed capacity. Barriers to entry 13. Internal scanning 14. Looking inside the business and identifying strengths and weaknesses of the firm. Environmental scanning 15. To monitor, evaluate and disseminate information from the external environment to key people within the firm. Concentric diversification 16. Factors that reduce entry into an industry. Diversification into a related industry. Vertical merger 17. Firms in different stages of the production and distribution chain are linked together. Business planning 18. A plan that determines how a strategic plan will be implemented. It specifies how, when, and where a strategic plan will be put into action. Economies of integration 19. Cost savings generated from joint production, purchasing, marketing or control. Portfolio management 20. Management of a firm’s individual enterprises and resources across these enterprises. Minimum efficient scale 21. The smallest output for which unit costs are minimized. . . . and justice for all The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on the basis of race, color, national origin, gender, religion, age, disability, political beliefs, sexual orientation, and marital or family status. (Not all prohibited bases apply to all programs.) Many materials can be made available in alternative formats for ADA clients. To file a complaint of discrimination, write USDA, Office of Civil Rights, Room 326-W, Whitten Building, 14th and Independence Avenue, SW, Washington, DC 20250-9410 or call 202-720-5964. Issued in furtherance of Cooperative Extension work, Acts of May 8 and June 30, 1914, in cooperation with the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Cathann A. Kress, director, Cooperative Extension Service, Iowa State University of Science and Technology, Ames, Iowa.











