1.7 Growth and Evolution(2)
advertisement

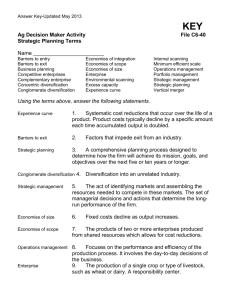
IB Business & Management Revision Workbook – ANSWERS 1.7 Growth and Evolution U nit 1 .7 Grow th a n d Ev olut io n Task 1 - Complete the missing words… retained organic acquiring inorganic external takeover joint venture cost average purchasing optimum Task 2 – Vocab Quiz Key Term Acquisition Conglomerate integration Franchises Horizontal Integration Inorganic growth Integration Merger Strategic alliance Task 3 – Economies and Diseconomies of Scale a. There are relatively higher barriers to entry in the pharmaceutical trade, e.g. licensing, patents and government restrictions. b. Traffic congestion, escalating rents, higher market wage rates... 1 IB Business & Management Revision Workbook – ANSWERS 1.7 Growth and Evolution Task 4 - True or false? True / False a. F b. T c. T d. T e. F f. T g. F h. F i. T Task 5 – Ansoff’s Matrix a. True b. True c. Diversification d. Product Development e. Diversification f. Market Penetration g. Product Development h. False New Existing New Diversification Product Development Existing Products Markets Market Development Market Penetration j. A saturated market suggests that sales may experience decline as a product reaches the end of its life cycle; There will be established market leaders in a saturated market and hence entry might be futile. 2 IB Business & Management Revision Workbook – ANSWERS 1.7 Growth and Evolution k. Diversification entails entering new markets with new products – both of which are unfamiliar to the organisation since they lack experience and/or know-how. Task 6 – Explain the difference between a. The franchisee is the buyer of a franchise whereas the franchisor is the seller. b. Management buy-in occurs when external investors buy a controlling interest in an organisation in order to take control; Management buy-out occurs when the internal (management) investors buy a controlling interest. c. Acquisitions (or takeovers) tend to be hostile and occur when the buyer has purchased a controlling interest (majority stake) in the target firm. Mergers occur when two (or more) firms agree to amalgamate as a new company. Task 7 – Economies and Diseconomies of Scale Multiple Choice 1. C. Enjoy economies of scale 2. A. The exercise of control by managers being weakened with a larger workforce 3. C. There is sufficient market demand for the product 4. A. Industry, location 5. B. Potential diseconomies of scale 6. B. Economies of scope 7. A. Internal diseconomies of scale 8. C. Specialised back-up services available in a particular region 9. C. Acquisition 10. D. Late deliveries due to congestion in busy locations 11. C. Decreasing returns to scale 12. B. Mergers and acquisitions 13. D. Ferrari (luxury car manufacturer) 14. D. To minimise internal communication problems 15. C. Generate lowering unit costs 3 IB Business & Management Revision Workbook – ANSWERS 1.7 Growth and Evolution Task 8 – External and Organic Growth Multiple Choice 1. D. Profits from the venture can be shared equally 2. B. Focused marketing 3. D. Lowest cost supplier with image for high quality 4. D. Market extension 5. B. Economies of scale that may be achieved 6. D. Better management control 7. B. A firm acquires or merges with another firm at the same stage of production 8. D. Opportunities 9. A. Organic growth 10. B. Right to trade using another firm’s products, name and image 11. B. Horizontal integration 12. C. Agree, external 13. B. Increased staff turnover 14. D. It is suitable for firms looking to grow rapidly 15. D. Choice of finance options 16. C. A joint venture 17. B. Diversification 18. B. Franchisors have little if any control over the way the franchise operates 19. A. Market Penetration 20. D. Corporate culture 21. D. Potential market dominance 22. C. Joint venture 23. D. Franchising is considered as a form of internal growth 24. C. Product development 25. A. Market penetration 26. B. Market development 27. C. They can grow through diversification 28. B. Cost leadership 29. A. Brand acquisition 30. C. Horizontal integration 4