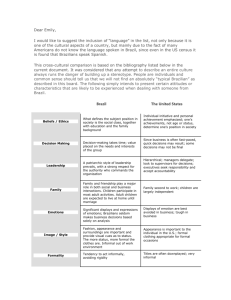
Author: Ambassador Guilherme Leite Ribeiro
advertisement

1 DID YOU KNOW THAT . . . Author: Ambassador Guilherme Leite Ribeiro Head of the Brazilian Financial Office of the Ministry of External Relations of Brazil, New York In November of 2001 AERONAUTICS INDUSTRY Santos Dumont, a Brazilian, invented the airplane. EMBRAER, the Brazilian Aeronautics company, sold 4.959 airplanes in 27 years. EMBRAER sells jets and turbo propellers to developed countries like USA, (Continental Express, American Eagle, etc.), France, Italy, Switzerland, Portugal, Spain, Luxembourg, Holland, Poland, China, and Sweden. AGRICULTURE AND CATTLE RAISING Brazil has the largest cultivable area in the world (22%). Brazil is first in the world in the production of coffee, oranges, and sugar cane; the second in the production of manioc, beef, and poultry, beans, and soy; the third in the production of refined sugar and corn; the fourth in grains and cocoa; the seventh in eggs and pork; the eighth, in cotton and rice. Also, Brazil is ranked the second exporter of poultry and fourth of pork . AREA Brazil is the fifth largest country in the world with an area of 8,547,403 square km and in Brazil’s territory can fit all the countries in Europe and Brazil’s territory is equal to 28 times the territory of Italy. CLIMATE Although Brazil is essentially a tropical country, from São Paulo towards the South, the annual average temperature is 66 F. In some southern states, it can snow. 2 COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY The number of computers in Brazil increased from 5.1 million in 1997 to 9.2 million in 2000. Brazil is ranked seventh in the world in the number of computers and Brazil is the largest world market of computer technology. ECONOMY Brazil is the eighth largest economy in the world with a Gross National Product (GNP) of US$ 840 billion. In 20 years we will be the fourth largest economy, at least as large, or larger than, France, Italy and England. Brazilian GNP grew an average of 4% every year from 1994 through 1997. In comparison with an annual increase of 0.22% from 1990 through 1993. In 2000 Brazilian GNP grew 4%. Brazilian GNP per capita, which decreased 1.25% per year from 1990 to 1993, increased 2,51% per year during the period from 1994 to 1997. According to the World Bank, Brazil, China, India, Indonesia and Russia will have the highest rate of development in the next 25 years. During the period from 1947 through 1988, Brazilian GNP increased 12.5 times, second only to Japan’s increase in GNP of 19 times. Brazilian GNP constitutes 38% of South American GNP. Among the 500 largest South American companies, 300 are Brazilian, 80 Mexican, 60 Argentinean and 30 Chilean. MERCOSUL composed of Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay, has a GNP of 1,141 billion of dollars, occupies 10% of the area of the Americas and it has a population of 212 million of inhabitants (26% of the continent’s total). Brazil is responsible for 30% of the coffee production in the world, 20% of the soy, 8.5% of chicken meat, 4.5% of manufactured shoes, 3.2% of steel and 2.9% of automobiles. Brazilian supermarkets in 1999 had gross receipts of US$ 35 billion with their 55.300 stores, hiring 670 thousand employees directly and 2 million indirectly and being responsible for the 85% of the country’s food supply. 3 Between 1990 and 1999, 4.9 million companies were created, of which 2.7 million (55.1%) are micro or small enterprises, representing a production of about 20% of the GNP, 60% of jobs and it is responsible for 30% of the gross amount of the industrial production of the country. EDUCATION The illiteracy index has been decreasing rapidly, from 17.0% in 1990 to 13.0% in 1998. Also in 2000, 91% of the children between the ages of 10 and 14 years old were attending school. Illiteracy among youngsters in the ages between 10 and 14 in urban regions is less than 5%. In 1992, 18.2 % of children between the ages of 7 to 14 years old were not in school and in 1999, only 4% were not in school. The percentage of the population over 10 years of age, who had completed high school, increased from 25.4% in 1992 to 29.8% in 1996. The enrollment in high school increased 57% between 1994 and 1999 and the number of students attending university courses increased 28% between 1994 and 1998. In 1998, there were more than 2.1 million students attending university, an increase of 28% from 1994. The number of students in university graduate courses increased from 43 thousand in 1994 to 53.9 thousand in 1999. During the period from 1994 to 1999, the number of professors who graduated every year increased from 2.7 thousand to 4.7 thousand and the number of scholarships granted increased from 5.867 to 8.009. The average period of time dedicated to study increased from 5.7 years in 1992 to 6.6 years in 1999. In the year 2000, the Government distributed 110 million school books helping 32.5 million students of elementary schools, continuing the “National Program of School Books”. The “TV School Program” was created with the objective to help and enable teachers in underdeveloped rural areas. It was responsible for the distribution of kits (with TV set, VCRs, tapes and satellite antennas) for all the elementary schools with over 100 students, targeting 1 million teachers and 28 million students. 4 The Informatics Education Program (PROINFO) has been responsible for the installation of 30 thousand computers and accessories in more than 2. 2276 elementary schools, benefiting about 200,000 students. ENERGY Itaipu is the largest hydroelectric plant in the world. Brazil is the tenth producer of electric energy in the world. ENVIRONMENT The Northern countries cannot teach the Southern countries how to take care of their forests. In Europe, for instance, only 2% of native forests are left. In Latin America 59% of native forest remain. The countries that are mainly responsible for global warming are USA, members of the European Union, and Russia which since 1950, totaled respectively, 186.1 billion tons, 127.8 billion tons and 68.4 billion tons of carbonic gas emitted. Brazil only had 6.6 billion tons of gas emissions in the same period, representing less than 4% of the North-American total. And these countries are always talking bad regarding Brazil… More than 1500 different species of fish live in the waters of the Amazon River. Thirty three percent of the world large-leafed tree forests are in the Amazon, with 3,500,000 hectares of virgin forests and 750 different varieties of trees. The Amazon retains about 30% of the genetic store of the planet and represents the most diversified and complex ecosystem known to mankind. HEALTH Brazil has 143 thousand community health representatives, who visit 82 million Brazilians every month, as part of the Family Health Program. The Brazilian program for AIDS with free distribution of the “drugs cocktail”, is considered by the World Health Organization, as one the best in the world. The Brazilian drug market generates sales equal to US$ 8 billion dollars annually. Annually, 20 million children are vaccinated free of charge against many diseases, among them poliomyelitis. 5 Between 1989 and 1998, the death index among children declined from 50.9 to 36.1 per thousand of born-alive infants, which corresponds to a decrease of 29.1% in nine years. The average life span of Brazilians increased from 66 years in 1992 to 68 in 1999. HISTORY During World War II, Brazil had sent 25,000 soldiers to Italy to fight nazi-fascism and of those 500 of them died on Italian soil defending democracy. In Pistóia, Italy there is a cemetery in the memory of these Brazilians. HOMELESS CHILDREN Despite what has been published by the international press, Brazil does not have 2, 5, 7 or 11 million of homeless children. According to a research made by IBASE, a non-governmental organization, in 1994 (last year of the research), there were less than one thousand homeless boys in Rio de Janeiro. About 2.7 million children in Brazil, between the ages of 7 and 14, are still out of school and the Government created an special program called “All Children in School”, which intends to take them to school until the end of this year. INDIANS In Brazil, there are 554 Indian territories with a total of 946.452 km2 (11.12% of the country’s area), corresponding to three times the size of Italy. From this total, 220 areas (436.400 km2) were already delimited, corresponding to 47.24%. In these areas 325.652 Indians of 227 different ethnic groups live, and they speak 170 different dialects. They live mainly in the Amazon, but are spread all over the country. In Roraima State in the extreme north of Brazil with an area of 224,000 square km (Italy has 301,308 square km), there are Indian reservations covering an area of 94.190 square km. Also in these territories live 9,910 Ianomami Indians, corresponding to one Indian for each 10 square km. The number of indigenous natives increases twice as fast as the regular population (3.2% compared to 1.4%). 6 INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTION Brazil has the tenth largest industrial complex in the world. Brazil is the world’s twelfth automaker and among others, Audi, Chrysler, Fiat, Ford, General Motors, Honda, Mercedes, Peugeot-Citroen, Renault, Scania, Toyota, Volkswagen and Volvo manufacture there. As far as manufactured products are concerned, Brazil is the second largest producer of ceramic tiles and refrigeration compressors; the fourth of beer; the fifth of gasoline and radios; the sixth of cigarettes and CDs; the seventh of refrigerators, textiles and clothing and the eighth in corrugated paper, chemicals and prepared foods. Seventy percent of Brazil’s exports are manufactured products. PETROBRAS, a national corporation, with all Brazilian technology, has the world record in oil extraction in deep water, at 1.700 meters. INVESTMENTS According to business specialists, there are series of factors, which explain why Brazil became one of the stars in the developing world in the recent years. The factors are economic stability, the size of the consumer market, the existence of a solid financial system, democracy, the fact that Brazil is one of the countries which is better positioned as far as the New Economy and it has the most competitive agriculture in the world. More Japanese capital has been invested in Brazil than in any other South American country. The Brazilian Program of Privatization is the largest in the world and its total is US$ 130 billion in telecommunications, energy, sanitation, banking, gas distribution, and also that the steel, petrochemicals and fertilizers industry have already been privatized. In the last decade, the total volume of foreign direct investment in Brazil increased 3,000%. In the year 2000, the total volume of foreign direct investment reached US$ 27 billion dollars. According to research carried out in February 2001 by A.T. Kearney, the North American consulting firm, which interviewed a thousand business people responsible 7 for 90% of the world’s direct investments, Brazil is in the third place with regard to the preference for mega investors, after the United States of America and China. LAND REFORM In six years, 400 thousand families were given pieces of land, with a total area equivalent to twice the size of Belgium. To implement land reform 13.2 million hectares were purchased of expropriated. That area is equal to three and a half times the territory of Switzerland or half Italy’s territory. LIFESTYLE AFTER THE REAL PLAN After the problem of hyper inflation was solved and the consequent recovery of purchase power, coupled with a major emphasis of Fernando Henrique Cardoso’s government with social issues, the average income of employed people increased 27% in the urban areas. During the period from 1998 to 2000, 13 million people went above the poverty line, reducing the percentage from 43.8% to 32.7%. The average poverty percentage decreased from 42% in July 1994 to 28% in the month of January 1996, in the six major cities in Brazil. The average monthly income of the population also changed from 364 Reais in 1992 to 472 Reais in 1999. Between 1992 and 1997, the number of families receiving tap water increased from 69.5% to 81% of the population. Between 1992 through 1997, the number of residences provided with garbage removal services increased from 64% to 74% of the population. From 1992 through 1999, the number of homes served with the sewage system increased from 50.3% to 59.4%. From 1994 through 1998, the consumption of construction materials in general grew 24%. On June 1994, a minimum wage would buy 12.4 sacks of cement and in May 1998, 20 sacks. The use of processed foods has also increased in the period of 1994 through 1997. For chicken, beef and pork meat, the growth was about 39.9%, 27.1% and 26.1%, 8 respectively. Also the yogurt consumption increased 85.9%; cheeses 51.8%; beer 56.8%; sodas 71.5%; and cookies 42.6%. The cost of the monthly basic food supply per family increased 25%, compared to an increase of 70% of the index which regulates the increase of prices from the time the Real was established until now. The unemployment rates in Brazil were lower than ones in Europe (Italy: 12%) and were around 4.8% in December 2000. MARKET The present number of consumers in Brazil estimated at 43 million will increase to 65 million in the year 2005, which then will make Brazil the fifth largest consumer market in the world. Brazil is third worldwide in the franchising market, only surpassed by USA and Canada. Also, the total numbers of units grew 96% between 1995 and 1999, reaching 46,534 units, with a total of 226.334 direct jobs. The Brazilian middle class is composed of 35 million families, according to IBGE: a) 8% larger than the population of Germany and greater than the sum of the population of Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, Hungary, Ireland, Iceland, Luxembourg, Norway, Portugal, Sweden, Switzerland and the Czech Republic; b) greater than the sum of the population of France and Canada; c) equivalent to 1/3 of the population of the United States of America and 72% of the population of Japan. Brazil is the fifth country in the world in purchasing power with more that US$ 1 trillion in Purchasing Power Parity, after the united States of American, China, Japan and Germany. MINING Brazil is the second largest producer in the world of iron minerals; the fifth of manganese; the sixth of aluminum; the seventh of gold, and the eighth of pewter. Brazil has the sixth largest supply of iron in the world. POPULATION Brazil is fifth in the world in population, with 165 million inhabitants. Brazil has 40% of the population of Latin America. 9 The Brazilian population is young, as 63% is younger than 29 years of age. Ethnically, the Brazilian population is 55% white, 40% mulatto, 5% black, 0.5% Asian and 0.1% native and that our tendency is to become a mulatto country. Twelve Brazilian cities have more than 1,000,000 inhabitants. They are: São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Salvador, Belo Horizonte, Fortaleza, Brasília, Curitiba, Recife, Belém, Nova Iguaçu, Porto Alegre and Manaus. There are 23 million Italians and Italian descendants in Brazil and São Paulo has 5 million of them. Therefore, Sao Paulo has more Italians than Rome. 16% of Brazilians live in poverty and it is estimated that by 2005, it will decrease by 10%. PUBLIC OPINION According to a research done at the end of last year, 58% of Brazilians are confident about their country’s future, 22% are undecided and only 20% are pessimistic. SLUMS The Mayor of Rio de Janeiro is developing a project called “Project Slum-Borough”, which intends to urbanize all the slums in the city. TELECOMMUNICATIONS In 1994, Brazil had less than one million cellular phones. In 1998, cellular phones in Brazil totaled 5.6 million, and today Brazil has 23.2 million. This means an increase of 310% since 1998. By 2005, Brazil will have 60 million cellular phones. In 1994, Brazil had 13 million regular telephones and, at the end of 2000, this number has risen to 38,3 million. Brazil is ranked ninth among the countries which utilize the Internet the most, with 10,9 million users, after USA, Japan, Germany, United Kingdom, China, Canada, South Korea, and Italy. Sixty percent of Latin American Internet sites are Brazilian. 10 TRANSPORTATION Brazil has the eighth largest fleet of vehicles in the world, behind only USA, Japan, Germany, Italy, France and Great Britain. Brazil has the seventh largest fleet of helicopters in the world, with 900 helicopters. OTHER In 1998, more than 2,500,000 Brazilians have sent their income taxes via Internet. During the last elections held in October 3, 2000, 144,969 electronic ballot boxes were used, 65% of voters used this system and 67,000 new ballot boxes showed the candidates’ photos. TV Globo is ranked the fourth TV station in the world. WORLD RANK First worldwide: Cattle; coffee, sugar cane, fruits and oranges; iron reserves; in Latin America, Internet user. Second worldwide: Producer of iron minerals, beans, manioc, soy and beef; ceramic tiles, refrigeration compressors and jeans; chicken producer and exporter of chicken; largest market for executive jets, helicopters, fax machines and painkillers; Third worldwide: Producer of refined sugar and corn; maker of regional flight aircraft; largest market for franchising, sodas and motorcycles; Fourth worldwide: Producer of grains, cocoa and beer; producer and exporter of pork meat; largest market of computer technology, of shopping centers, refrigerators and freezers and clothes washing machines; television network; Fifth worldwide: Country in size and population; producer of gasoline, radios and manganese; major consumer market; Sixth worldwide: Producer of milk, iron, pig iron, primary aluminum, cement and music records; largest market of musical CDs; iron mineral reserve. Seventh worldwide: Producer of gold, cellulose and eggs; of refrigerators, textiles and clothing; in number of computers and TV sets: largest fleet of helicopters and vehicles; 11 Eight worldwide: Producer of cotton, rice, steel and tin: of corrugated paper, chemicals and prepared foods; in number of credit cards; vehicle fleets; Ninth worldwide: Internet users; Tenth worldwide: Industry in general; energy producer; Twelfth worldwide: Automaker; lubricant producer; Fourteenth worldwide: Nickel producer; Seventeenth worldwide: Zinc producer; Eighteenth worldwide: Crude oil and copper producer. Sources: The major data above was taken out of “Perfil da Economia Brasileira – 2000”, edited by CBMM – Companhia Brasileira de Metalurgia e Mineração, “Brasil – Conjuntura Econômica”, from the Brazilian Ministry of External Affairs, e “Sete Anos de Real”, from the Office of the President of Brazil. Another resources: Anthropos Consulting (Dr. Luis Marins); the Brazilian magazines VEJA and EXAME, Brazilian newspapers (Jornal do Brasil e O Globo), Secretaria de Estado de Assistência Social do Ministério da Previdência Social (Brazilian Social Security Agency); Annual Statistics Report from the IBGE.