ICT Curriculum Map Year 1
advertisement

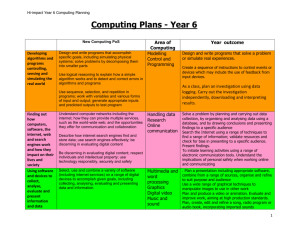
Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Computing Plans - Year 5 New Computing PoS Developing simple algorithms, controlling, sensing and simulating the real world Design and write programs that accomplish specific goals, including simulating physical systems; solve problems by decomposing them into smaller parts Area of Computing Modelling Control and Programming As a class, plan an investigation using data logging. Carry out the investigation independently, downloading and interpreting results. Use sequence, selection, and repetition in programs; work with variables and various forms of input and output; generate appropriate inputs and predicted outputs to test program Understand computer networks including the internet; how they can provide multiple services, such as the world-wide web; and the opportunities they offer for communication and collaboration. Using software and devices to collect, analyse, evaluate and present information and data Select, use and combine a variety of software (including internet services) on a range of digital devices to accomplish given goals, including collecting, analysing, evaluating and presenting data and information. Design and write programs that solve a problem or simulate real experiences. Create and refine a sequence of instructions to control events, using programmed procedures. Use logical reasoning to explain how a simple algorithm works and to detect and correct errors in algorithms and programs Finding out how computers, software, the internet, web and search engines work and how they impact on their lives and society Year outcome Handling data Research Online communication Search a large (pre-prepared) database to research information, using a range of search techniques Describe how internet search engines find and store data; use search engines effectively; be discerning in evaluating digital content Search for, interpret, check and question information; use logical inference to identify implausible and irrelevant information; present in a suitable format for a chosen audience Be discerning in evaluating digital content; respect individuals and intellectual property; use technology responsibly, securely and safely Share ideas using a range of online methods. Develop key skills and ideas about personal safety when using any form of electronic communication Multimedia and word processing Graphics Digital video Music and sound Plan a presentation, combine from a range of sources, organise and refine to suit purpose and audience Create digital artwork by copying/ pasting within and between photographs Plan a storyboard for a video or animation. Create, edit and refine. Create radio programme or sonic postcard by combining sounds 1 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Planning Notes for the new computing curriculum and a guide to terminology. An algorithm is a set of specific steps or instructions for solving a problem. “Simple programs” may be sequences of instructions for controlling the movement of a robot (e.g. Bee Bot, ProBot or Big Trak programmable toy) or an on screen turtle (Logo) or sprite (e.g. Scratch). Modelling is the process of developing a representation of a real world issue, system, or situation, that captures the aspects of the situation that are important for a particular purpose, while omitting everything else. Computational thinking is thinking in a logical, sequenced way to develop a solution to a problem. It is something that people do (rather than computers), and includes the ability to think logically and algorithmically. Cross-curricular planning At all Key Stages, information and communication technology should be used to enhance teaching and learning right across the curriculum: this is often called Technology Enhanced Learning (TEL). (NAACE/BCS 2013) When planning an computing outcome, try to choose one which support objectives in at least one other subject. This is the key to finding sufficient time in the day: if your work is both Literacy and ICT, you can teach two skills in one slot, and if it covers Geography objectives as well, so much the better! Doing this, you may need to teach some lessons discretely and some lessons together, such as doing some knowledge and skills work before in the Literacy unit, then finding time for teaching a computing skill, which will support the Literacy work. Revisiting areas of computing covered previously is also an excellent way of embedding into other subjects: if you have taught a short unit on using a paint package, the children will be ready for a Mathematics lesson using 2D shapes to draw a picture. Of course, some uses of technology are very straightforward and will not need skill teaching beforehand: using an online simulation is an example of this. Skills taught in other years allow the technology to fit behind the History or Science work Sometimes it might also be an opportunity to develop a knowledge of how technology works, or understanding of the principles of computation, digital media or information systems. Differentiation and assessment It is important for all children to learn to the best of their ability. While it is beneficial for more able children to support the less able, using this too much can mean that the less able child never gets a turn (so learns little), or the more able child is held back. Working together gives you huge opportunities for collaboration peer learning and peer coaching. Differentiation can then take place: some children could be given a simpler task, or use the same package but be taught fewer skills to use, while others can spend more time in self- and peer-assessment, planning, evaluating and improving their work. We are currently trialling a new set of levels to help measure pupils overall attainment as they complete the skills and essential knowledge. The level descriptors are at the top of each unit and there will be more guidance available shortly. 2 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Modelling: Please choose the plan which is appropriate for the Control equipment or software you have in school. Modelling (Spreadsheets): Design and write programs that accomplish specific goals; solve problems by decomposing them into smaller parts Key Understanding Key Skills To understand that: to change variables in a spreadsheet to solve spreadsheets can carry out a range of calculations problems one element of the spreadsheet can be changed and to make predictions and changes and check have effects on the other calculations results. problems can be solved by changing variables in to enter formulae for the four operations (+-x/) a computer model into a spreadsheet spreadsheets must be laid out logically to use 'SUM' to calculate the total of a set of spreadsheets work by manipulating formulae numbers in a range of cells to change data in a spreadsheet to answer 'what if...?' questions and check predictions Using a simple layout demonstrated by the teacher, create a simple spreadsheet model and use it to solve problems Outcomes Design and use a spreadsheet to solve a problem by changing variables. Further suggested outcomes: Create a spreadsheet to calculate the area and perimeter of a rectangle (Maths) Use a spreadsheet to calculate the cost of ingredients for biscuits, answering questions about price or quantity changes (Maths, DT) Create a spreadsheet to discover the cheapest way to buy crisps (multipacks or singly) or which size of drinks containers is cheaper, or whether a 3 for 2 deal is better or worse than a percentage discount; use graphs to illustrate (Maths) Suggested resources: spreadsheet program, eg Microsoft Excel 3 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans Modelling (Scratch): Design and write programs that accomplish specific goals, including simulating physical systems Key Understanding Key Skills To understand that: To know in real life what the variables Simulations require programming. and responses are. Programs respond to inputs. To think logically that when x happens y is You have to “tell” the program how to respond to the response. each input. To use “when” blocks to create That these inputs and responses can copy real life responses. To use “if” blocks to have Sprites respond to what other sprites are doing. Use “say” blocks to give information. To test and debug regularly. September 2013 Outcomes Use programming to create a simulation. Further suggested outcomes: Create a science simulation for changes in state, growth, etc (Sci) Create an animation to show journey of Titanic with information buttons (His, geo) Suggested resources: Scratch 4 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans Modelling (Makey Makey/ Lego WeDo): Design and write programs that accomplish specific goals, including simulating physical systems Key Understanding Key Skills To understand that: To use “when_ button pressed” Lots of products require programing. commands in Scratch. These programs often respond to the physical To link sensors/ Makey Makey to a world. computer program. That Makey Makey responds to conducting To ensure complete circuits when using electricity. Makey Makey/ sensors. That Lego WeDo sensors respond to light, To test product and de bug programming movement, etc as well as checking equipment and setup. What water, metal and things with lots of water in them conduct electricity. You have to use software to program responses Activating a sensor is the same as pressing a button in a program. September 2013 Outcomes Use programming and sensors/ Makey Makey to re-create real-life objects Further suggested outcomes: Make a burglar alarm using a movement sensory that makes a noise/ takes a picture etc. (DT) Make a wild life camera/ monitor that captures pictures or counts every time a bird drinks from a bird feeder. (DT) Use Makey Makey to make musical instruments. (Music/ DT) Suggested resources: Scratch used with Makey Makey/ Lego WeDo/ Lego Mindstorms. 5 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans Modelling (Minecraft): Design and write programs that accomplish specific goals, including simulating physical systems Key Understanding Key Skills To understand that: To use Minecraft crafting table to make Minecraft can be used to re-create real life objects. objects. To use Minecraft Wiki to know Making an object that responds to something a combinations for crafting objects. character does in Minecraft is like programming. To use reddust to simulated electricity. You can build things for a purpose or to solve a To use pressure pads and levers as inputs. problem in Minecraft like in real life. September 2013 Outcomes Design and build objects for a purpose in Minecraft. Further suggested outcomes: Build a train track to get from one place to another. (DT) Make a bridge that allows you across and no one else. (DT) Build a field that can be watered when you pull a lever. (DT) Suggested resources: Minecraft 6 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Control: Use logical reasoning to explain how a simple algorithm works and to detect and correct errors in algorithms and programs. Use sequence, selection, and repetition in programs; work with variables and various forms of input and output; generate appropriate inputs and predicted outputs to test program: Key Understanding Key Skills Outcomes Control: Investigate devices in the school and local area controlled Create and refine a sequence of instructions to control to understand that: events, using programmed procedures. by computer. control technology is all around them and that Analyse inputs and outputs of known devices. things do not happen without cause and effect Emulate these inputs and outputs. Example outcomes: these devices rely on a set of instructions write and record a procedure to produce a shape design a “line dance” for a set of Probots, calling on which can be repeated sequences of pre-programmed procedures build a procedure (eg hexagon) and name it. procedures can be named and can call upon create a design to draw a complex shape (eg house, car) write a procedure using other smaller procedures (eg other procedures by calling on several procedures (eg triangle, square) produce a flower by repeatedly drawing a hexagon and Using Hopscotch turning 20 degrees) use repeated procedures to create a row of houses or Make simple predictions about effects of changing a flowers with Probotix or Probot or Hopscotch procedure Use Scratch with Lego We Do Use wait and repeat commands effectively http://info.scratch.mit.edu/WeDo Explore variables in a procedure (If and Then) Make a simple drum machine and link to Scratch through Create more complex procedures to improve efficiency Makey Makey Use trial and error combining blocks to achieve a Make Makey Makey wind chimes and program through specific purpose Scratch. Combine reused blocks with blocks of their own Design a racing car game in Scratch and make a controller devising with Makey Makey. Pupils can identify that there is something wrong with Program Robolab or NXT Lego to follow a racing track. their code and can fix it Link Scratch with eternal sensors to program a range of Design a Lego robot that will stop and turn when it reaches an object. inputs and outputs using Lego WeDo or Makey Makey Suggested resources: Probot and Probotix/ Scratch/ WeDo/ Mindstorms/ NXT/Makey Makey/ Hopscotch/ Kodu 7 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Data Logging: Work with variables and various forms of input and output; generate appropriate inputs and predicted outputs to test program: Key Understanding Key Skills Outcomes Data logging Data logging Plan, carry out and evaluate an investigation using data To understand that: logging technology. Plan an investigation using data logging technology some investigations are more suitable for data Make predictions for this investigation and understand logging than others how to make it a fair test Example outcomes: they need to decide whether snapshot or Carry out the investigation, ensuring accuracy Test how pulse rate varies between different exercises or continuous logging is more appropriate, and Interpret results, draw conclusions and analyse the different people whether to conduct the investigation attached effectiveness of the technology Test how a variety of factors (eg air or soil temperature, to a computer or remotely light level, sound level) affect plant growth) Predict and compare volume levels of different sound sources Investigate sound insulation Investigate how mirrors affect light intensity or how to magnify the light from a light bulb (in torch design) Investigate how changing state affects temperature Suggested resources: Data logger (eg Easisense Q, TTS Data Logger, Log-IT Explorer), temperature probes, pulse meters, linked software. Probot with Probotix software, 8 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Handling Data: Understand computer networks including the internet; how they can provide multiple services, such as the world-wide web; and the opportunities they offer for communication and collaboration: Key Understanding Key Skills Outcomes To understand that: searches can be made using more than one criterion. information found is not always helpful in answering questions. information held on databases may contain errors and that this can affect results there are consequences of data not being accurate. Relate to outside world ( E.g. Police / doctor’s database). computing enables you to search and sift through large amounts of different types of information Search a large (pre-prepared?) database to research information, using a range of search techniques design questions using key words, to search a large pre-prepared database search using and/or (complex searches) search using greater and less than Use graphs to provide supporting evidence for their conclusions check for accuracy by checking data and looking at graphs present results of database research Example outcomes: Search a large pre-prepared database of Victorian census data to draw conclusions about differences in lifestyles then and now (Hist) Search a large pre-prepared database of the planets and stars to compare them according to a range of criteria (Sci) Search a large pre-prepared database of food items to plan a healthy and/ or cheap meal (DT, Sci, PSHE) Create and use a database to record responses from parents/grandparents or carers about: what games they played in the playground? What luxury items they had? Where they travelled for holidays and how they travelled to these places? They compare this with today’s experiences. (Hist) Suggested resources: database software (eg. Textease Database). Possibly a large pre-prepared database 9 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Research: Describe how internet search engines find and store data; use search engines effectively; be discerning in evaluating digital content Key Understanding Key Skills Outcomes To understand that: Search for, interpret, check and question information; use Search the internet for specific logical inference to identify implausible and irrelevant information the Internet may contain material that is information; present in a suitable format for a chosen audience irrelevant, biased, implausible and inappropriate Skim read and sift information Information on the Internet may be copyrighted Check information for accuracy and cannot be used legally Identify irrelevant, biased, implausible Example outcomes: searches can be carried out using more than one and inappropriate information Research a contrasting UK locality to ascertain similarities key word Present findings to a specific audience and differences; select key words and phrases to use in a there are different search engines that work in Use a range of search engines and presentation or fact file (Geog) different ways and some are easier than others. select the most appropriate Research topic on which there are few websites suitable for Some search engines can search specific content Talk about how to use the Internet younger children; condense and sift information to present to e.g. video, images, sounds safely younger children (Lit) responsible Internet use is important and certain Use information found online to Investigate blogs, wikis etc, for evidence of bias and rules are wise to use wherever the Internet is inform presentation work, without implausibility. Briefly create inaccurate web page before accessed copying and pasting text correcting it it is possible to increase Internet safety wherever Use web-based audio and video resources in the study of: you are by following certain guidelines formality of talk; analysis of persuasive language; gesture; presentations are rarely suitable for the audience contexts and purposes for talk if they contain large amounts of copied and Use the World Wide Web as a source of journalistic writing. pasted text. Compare how different sites report world events. Compare with non-electronic formats. Suggested Resources: the Internet; cached content eg Espresso, Knowledge Box;); links page set up by teacher (eg using Microsoft Word); child-friendly search engines eg www.gogooligans.com and www.factmonster.com; search engines for sounds, eg www.findsounds.com and http://audio.lgfl.org.uk 10 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Online communication: Be discerning in evaluating digital content; respect individuals and intellectual property; use technology responsibly, securely and safely Key Understanding To understand that: ideas can be shared using a wide variety of online tools (eg email, discussion, quiz, survey, blog, wiki, video conference) and that these tools are suitable for different purposes the range of online communications available is developing constantly the audience will affect the nature of the work it is important to refine the quality of their work to suit the purpose personal safety when using email and other electronic communications is important cyberbullying is bullying and should not be tolerated Key Skills Outcomes Share ideas using a range of online methods. Develop key skills and ideas about personal safety when using any form of electronic communication Example outcomes Children create a survey to obtain information about transport to school, recycling etc from children in their own and other schools (Geog) Use discussion or blog to peer review own and others’ work Create a blog or contribute to a wiki on a relevant topic (eg character’s diary; encyclopaedia) Research a topic and write an online quiz to test others’ knowledge Take any digitally recorded audio outcomes from © pupils’ work and share with a wider audience via the Internet, possibly through a Podcast Online discussion to peer review scientific investigations Use video conferencing to widen the range of opportunities for meaningful interaction Suggested Resources (Makewaves, Uniservity or other Learning Platform), Making the News, Cybercafe and associated lesson plans: www.thinkuknow.co.uk Initiate and take part in collaborative learning using at least two of o email o discussions o quizzes o surveys o blogs o wikis o web quests o video conferencing o shared online folders o other Develop and understand rules for personal internet safety develop and understand code of conduct for online collaboration, and explain what to do in cases of cyberbullying 11 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Multimedia and word processing: Select, use and combine a variety of software (including internet services) on a range of digital devices to present data and information: Key Understanding Key Skills Outcomes To understand that: Plan a presentation, combine from a range of sources, Evaluate a range of electronic multimedia, and understand the implications appropriate to their given task e.g. key features of layout organise and refine to suit purpose and audience the structure and layout of a presentation needs to be planned and design Primary Literacy Framework: every feature in a presentation Plan structure and layout of presentation must be selected, and that every Presentation of Robin Hood story; present legend in evaluate and select suitable information and media from a range of an audio or digital video file feature chosen should contribute electronic resources to the overall effect aimed at the Presentation of a film including images, voice-over, to use a multimedia authoring program to organise, refine and chosen audience soundtrack and written text present information for a specific audience constant evaluation and Collaboratively produced set of computing help files Create a range of hyperlinks to produce a non-linear presentation adaptation of individual features in hyperlinked pages Through peer assessment and self evaluation children should evaluate and of the whole presentation is Use pictures, text or multimedia effectively to their design and make suitable improvements important support oral presentations multimedia has great potential to When word processing children should: Use an online keyboard tutor inform or persuade format text to indicate relative importance. justify text where appropriate. cut and paste between applications. delete/insert and replace text to improve clarity and mood. make corrections using a range of tools (eg spell check, find and replace) develop confidence using both hands when typing Suggested Resources: Multimedia Authoring packages: Powerpoint, 2Create, Textease Presenter, Photostory, Word processing packages: Textease, Word, Publisher. Keyboard tutor: BBC Dance Mat Typing (www.bbc.co.uk/schools/typing) or Tux Type (free to download from http://tuxtype.sourceforge.net). A range of peripherals (eg digital camera, camcorder, microscope, scanner, sound recorder, microphone) Apps: Explain everything, Splice, , Thinglink, iMovie, , Creative Book Builder, book creator, keynote, Pages 12 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Graphics: Select, use and combine a variety of software (including internet services) on a range of digital devices to present data and information. Key Understanding Key Skills Outcomes To understand that: Create digital artwork by copying/ pasting within and between photographs select, copy and paste within and between Example outcomes: elements from several photographs can be combined photographs Read accounts of celebrity airbrushing in magazines. Do the same with photographs of selves or sections of photographs can be explore “airbrush” historical characters, to make them more or less attractive edited separately techniques to improve Explore symmetry by reflecting one side of a face to another (Maths) photographs, such as used photograph editing and photo Illustrate a story by choosing and editing a photo for the setting, then taking photographs of in magazines with montage are used regularly in the yourself to insert into the background (Lit) celebrities printed media Illustrate the reflection, rotation and translation by copying/ pasting (Maths) Use this to create art in the style of William Morris or Islamic Art (Art, RE, Hist) Suggested Resources: paint program: Revelation Natural Art, Dazzle, Picasa, Digital camera ,Apps: Comic Book , PicCollage 13 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Digital video: Select, use and combine a variety of software (including internet services) on a range of digital devices to present data and information. Key Understanding Key Skills Outcomes To understand that: Plan a storyboard for a video or animation. Create, edit and To use different filming techniques and camera angles e.g. refine. zoom, panning, wide shot etc to create different photographs and video can be Example outcomes: taken from different camera mood/perspective angles and distances for different Plan a video or animation by drawing a storyboard create a news report based on a current event (Lit, effects PSHE) Use a range of sound effects, music and voice-overs to create editing and manipulating software mood/ atmosphere Create an advert for healthy food, using either live can used to enhance images and action or animation (Sci, DT) Select and edit sounds, text, movie clips and other effects to video for a given audience suit purpose and audience Create a copy of a TV program to fit with other work (eg. Weakest Link Henry VIII's wives; historical Through Evaluate and improve work with a view to purpose and the Keyhole or cookery programme) audience Use animation to illustrate water cycle (Sci) Suggested Resources: digital camera, digital camcorder, digital microscope, webcam. Simple video editing software: Windows Movie Maker, Digi Blue software, Revelation Sight and Sound. Photo sequencing software: Photostory. Animation software: stop motion animator, Digi Blue, 2Animate, Revelation Natural Art Apps: imovie, video star, splice. 14 Hi-impact Year 5 Computing Plans September 2013 Music and Sound: Select, use and combine a variety of software (including internet services) on a range of digital devices to present data and information. Key Understanding To understand that: sound can be created and edited using a range of methods sound can be saved and imported into other software sound can be layered and combined to produce a finished piece Key Skills record sounds using sound editing software collect sounds from a variety of sources (online, digital sound recorder) import sounds into sound editing software layer and edit sounds plan, create and refine either a radio programme or play with sound effects or a sonic postcard Save as a web compatible format for uploading and podcasting; share online Outcomes Create radio programme or sonic postcard by combining sounds Example outcomes radio play with sound effects radio programme with jingle sonic postcard of school or local area Produce drama according to the conventions of radio plays. Digitally record dialogue, edit and add music and sound effects. Share outcomes with a wider audience via the Internet Suggested Resources: microphones and sound recorders. Sound editing software: Audacity, Podium. Sonic postcards ideas: www.sonicpostcards.org. Online sources of sounds: www.findsounds.com; Audio Network http://audio.lgfl.org.uk; Apps: Croakit, Makewaves App 15