Experiment 3 Analysis of commercial caustic soda
advertisement

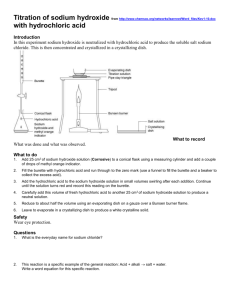
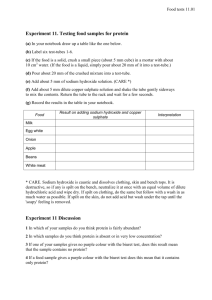
Experiment 3 Analysis of commercial caustic soda (24/9, 25/9) Introduction : Commercial caustic soda(市售的苛性鈉) is an impure sodium hydroxide. It contains few amounts of sodium carbonate. The quantities of sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate in a sample of commercial caustic soda can be determined by titrations with a standardized hydrochloric acid using the method of double indicator (使用雙指示劑的滴定法). In part (A) of this experiment, a standard solution of borax (硼砂) is prepared, and it is used to standardize the hydrochloric acid provided. B4O72﹣ + 2 H﹢ + 5 H2O 4 H3BO3 In part (B), 25.00 cm3 of the solution of caustic soda sample is titrated against the hydrochloric acid with phenolphthalein as indicator first. NaOH(aq) + H﹢(aq) Na﹢(aq) + H2O(l) Na2CO3 (aq) + H﹢(aq) 2 Na+ (aq) + HCO3﹣(aq) Another 25.00 cm3 of the solution of caustic soda sample is titrated against the hydrochloric acid with methyl red indicator. NaOH(aq) + H﹢(aq) Na﹢(aq) + H2O(l) Na2CO3 (aq) + 2H﹢(aq) 2 Na+ (aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(aq) Chemicals : Solid disodium tetraborate-10-water (borax), Na2B4O7 ·10H2O hydrochloric acid solution (to be standardized) unknown solution [ mixture of NaOH and Na2CO3 ] Procedure : (A) Standardization of hydrochloric acid with borax Prepare 250.00 cm3 of 0.04 M standard borax solution. Titrate 25.00 cm3 of the borax solution against the hydrochloric acid with methyl red indicator. (B) Analysis of commercial caustic soda solution Titrate 25.00 cm3 of the unknown caustic soda solution against the hydrochloric acid with phenolphthalein indicator. Then titrate another 25.00 cm3 of the unknown caustic soda solution against the hydrochloric acid with methyl red indicator. Results : (1) Calculate the molarity of your standard borax solution. (2) Calculate the molarity of the hydrochloric acid solution provided. (3) For 25.00 cm3 caustic soda solution, calculate (a) the number of moles of sodium carbonate, (b) the number of moles of sodium hydroxide. (4) Calculate the percentage of sodium hydroxide in caustic soda. 1 Discussion : 1. Explain, with equation(s), why impure sodium hydroxide pellets contain sodium carbonate. 2. Barium chloride (氯化鋇) is usually used for the preparation of carbonate-free sodium hydroxide solution. Suggest the chemical reaction(s) involved (列舉所發生的化學反應). 3. Sodium hydroxide is extremely hygroscopic(極易吸濕) (a) Why sodium hydroxide is seldom used as a hygroscopic substance in our daily life ? (b) Suggest two common drying agents in our daily life. 4. Outline a method to show how 250.00 cm3 of 0.04 M standard borax solution can be prepared. 5. Suggest the advantages that using disodium tetraborate-10-water as a primary standard for the standardization of hydrochloric acid. 6. Discuss whether the method of double indicator can be used to analyze a mixture of sodium hydrogencarbonate and sodium carbonate. References : 1. Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, Skoog and West, Holler 2. Vogel‘s Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, ELBS 3. Pre-University Chemistry, volume 2, Stephen Lee, Pomann 4. A Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, Vogel, ELBS 2 Suggested Answers 3. (a) (b) 5. (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) NaOH is corrosive. CaO, anhydrous CaCl2, silica gel It has a large molar mass. It is easily and economically purified by recrystallization (in water). Heating to constant mass is not necessary. It is practically non-hygroscopic A sharp end point can be obtained with methyl red at room temperature. 6. Yes. In a mixture containing x mol of NaHCO3 and y mol of Na2CO3, at the end point (with phenolphthalein), x mol of HCl is required ; at the end point (with methyl red), (2x + y) mol of HCl is required. Chemicals : About 4.0g of disodium tetraborate-10-water in 250.00 cm3 Standardized 0.1 M HCl(aq) [ 0.04 M ] [ 380 cm3 each ] In 1 dm3 unknown solution contains 3.5 g of NaOH and 2.5 g of Na 2CO3 3