Course Outline – SOC 200: Social Dimensions of Environmental
advertisement

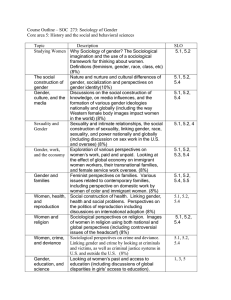
Course Outline – SOC 273: Sociology of Gender Core area 8: Develop a comparative perspective and understanding of one’s place in a global context. Topic Description Studying Women Why Sociology of gender? The Sociological imagination and the use of a sociological framework for thinking about women. Definitions (feminism, gender, race, class, etc) (8%) The social Nature and nurture and cultural differences of construction of gender, socialization and perspectives on gender gender identity(10%) Gender, culture, Discussions on the social construction of and the media knowledge, on media influences, and the formation of various gender ideologies nationally and globally (including the way Western female body images impact women in the world) (8%) Sexuality and Sexuality and intimate relationships, the social Gender construction of sexuality, linking gender, race, sexuality, and power nationally and globally (including discussion on sex work in the U.S. and oversee) (8%) Gender, work, Exploration of various perspectives on women’s and the economy work, paid and unpaid. Looking at the effect of global economy on immigrant women workers, their transnational families, and female service work oversee. (8%) Gender and Feminist perspectives on families. Various issues families related to contemporary families, including perspective on domestic work by women of color and immigrant women. (8%) Women, health, Social construction of health. Linking gender, and reproduction health and social problems. Perspectives on the politics of reproduction including discussions on international adoption (8%) Women and Sociological perspectives on religion. Images of religion women in religion using both national and global perspectives (including controversial issues of the headscarf) (8%) Women, crime, Sociological perspectives on crime and deviance. and deviance Linking gender and crime by looking at criminals and victims, as well as criminal justice systems in U.S. and outside the U.S. (8%) Gender, Looking at women’s past and access to education education, and (including discussions of global disparities in girls’ science access to education). Gender gaps in relationship SLO 8.5 8.2 8.2 8.2, 8.4 8.4, 8.5 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 8.4 8.2, 8.3, 8.5 8.3, 8.4 8.1, 8.3, 8.5 Women, power, and politics Frameworks of feminism to the status of women in science. (8%) Defining power. Women and the state, the law, the military, the government. Discussions of various women’s movements (including discussion of women's activism across the world) (8%) Exploration of various theoretical framework within feminism such as liberal feminism, radical feminism, multiracial feminism, postmodern feminism, queer theory or transnational feminism (10%) 8.1, 8.4, 8.5 8.5