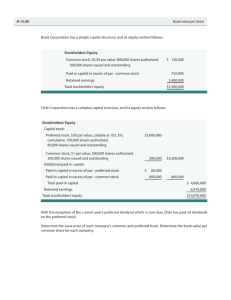
Solution to Problem 3: Cash Dividends
advertisement

ACC301, Spring 2001 Dr. Dow Exam 2 Review Problems PROBLEM 1: LEASES On January 1, 19X1, Lessor Company leased a machine to Lessee Company. Lease payments of $10,000 are due on January 1 of each year beginning on January 1, 19X1. The lease qualifies as a capital lease for both the lessee and lessor (direct financing). Other details are as follows: Lease term Useful life of the asset Cost of the machine to the lessor Fair market value of machine Lessor's implicit interest rate Lessee's incremental borrowing rate Residual value Depreciation Method Present value of minimum lease payments 10 years 10 years $67,590 $67,590 10% 10% Zero Straight-line $67,590 REQUIRED: A. Prepare all journal entries relating to the lease and the leased asset on Lessee Company's books for 19X1 and 19X2. B. Prepare all journal entries relating to the lease on Lessor Company's books for 19X1 and 19X2. PROBLEM 2: LEASES On January 1, 19X1, Lessor Company leased a machine to Lessee Company. Lease payments of $15,000 (including executory costs of $1,379) are due on December 31 of each year. The lease qualifies as a capital lease for both the lessee and the lessor. Other details are as follows: Lease term Useful life of the asset Cost of the machine to the lessor Fair market value of machine Lessor's implicit interest rate (known to lessee) Lessee's incremental borrowing rate Residual value (Guaranteed by lessee) Depreciation Method 8 years 10 years $50,000 $75,000 10% 12% $5,000 Straight-line Required: A. List each of the criteria the lessee should consider in determining whether this is a capital lease and indicate all of the criteria that are satisfied. B. Calculate the depreciation expense the lessee should record each year. C. Is this a direct financing or a sales-type lease for the lessor. Briefly explain. D. Calculate the Lease Payments Receivable the lessor should record at the inception of the lease (January 1, 19X1). Problem 3: Cash Dividends XYB Corporation has 50,000 shares of $2 par value common stock and 1,000 shares of 9%, $10 par value preferred stock issued and outstanding. The preferred stock is cumulative and participates to 12%; dividends in arrears total $1,800. Assuming that XYB declares a total dividend of $14,000 for the year, determine how much of the dividend will be allocated to the common stockholders and to the preferred stockholders. Problem 4: Cash Dividends XYB Corporation has 40,000 shares of $3 par value common stock and 1,000 shares of 7%, $10 par value preferred stock issued and outstanding. The preferred stock is cumulative and participates to 12%; dividends in arrears total $1,400. Assuming that XYB declares a total dividend of $25,000 for the year, determine how much of the dividend will be allocated to the common stockholders and to the preferred stockholders. Problem 5: Cash Dividends Lovejoy, Inc., has 20,000 shares of 10%, $10 par preferred stock and 30,000 shares of $10 par common stock. No dividends have been paid or declared during 1994 and 1995. During 1996, the company distributes $140,000 in dividends. Directions: Calculate the amount that will be distributed to the preferred stockholders and the common stockholders under each of the following assumptions: 1. 2. 3. 4. The preferred is noncumulative and nonparticipating. The preferred is cumulative and nonparticipating. The preferred is cumulative and fully participating. The preferred is cumulative and participating to 15% total. ACC301, Spring 2001 Dr. Dow Exam 2 Review Problems, Page 2 Problem 6: Stockholders’ Equity Transactions Dennis Company's December 31, 19X1 balance sheet contained the following information: Preferred Stock, 5%, $10 par, 50,000 shares authorized, none issued Common Stock, $2 par, 1 million shares authorized, 100,000 shares issued & outstanding Required: Prepare journal entries (if necessary) to record the following 19X2 transactions: 1. Declared a 30% stock dividend on the common stock. The market price of the common stock was $8. 2. Issued 10,000 shares of the preferred stock and 5,000 shares of the common stock for a lump sum price of $175,000. The market price of the common stock was $9. 3. Issued the certificates for the stock dividend (#1). 4. 3,000 shares of common treasury stock were purchased at $15 per share. The shares were originally issued at $5 per share. Dennis uses the cost method. 5. Issued 25,000 shares of common stock for land. The seller of the land was asking $300,000 for the land; the land was appraised for tax purposes at $240,000; the market price of the common stock was $12. 6. 1,000 shares of the treasury stock were reissued at $13 per share. 7. The board of directors appropriated $500,000 of retained earnings for plant expansion. 8. The remaining shares of the treasury stock were retired. 9. Declared and issued a 4 for 1 stock split. Problem 7: Stockholders’ Equity Transactions Dennis Company's December 31, 19X1 balance sheet contained the following information: Preferred Stock, 5%, $10 par, 50,000 shares authorized, none issued Common Stock, $1 par, 1 million shares authorized, 100,000 shares issued & outstanding Required: Prepare journal entries (if necessary) to record the following 19X2 transactions: 1. Declared a property dividend on the common stock. The company will transfer some of its investments in marketable securities to the common stockholders. The marketable securities cost Dennis $500,000; at the date of declaration the market value of the securities was $734,000. 2. Issued 5,000 shares of the preferred stock for $25 per share. 3. Distributed the property dividend declared in #1. 4. 2,000 shares of common treasury stock were purchased at $10 per share. The shares were originally issued at $7 per share. Dennis uses the cost method. 5. Issued 25,000 shares of common stock and 10,000 shares of preferred stock for $350,000. The market price of the common stock was $15 per share and $30 per share for the preferred stock. 6. 500 shares of the treasury stock were reissued at $14 per share. 7. The board of directors appropriated $50,000 of retained earnings for plant expansion. 8. The remaining shares of the treasury stock were retired. 9. Declared and issued a 2 for 1 stock split. ACC301, Spring 2001 Dr. Dow Exam 2 Review Problems, Page 3 Solution to Problem 1: Leases, Part A – Lessee Accounting Lessee’s Lease Amortization Schedule: Date Lease Payment 10% Interest 1/1/X1 1/1/X1 10,000 1/1/X2 10,000 5,759 1/1/X3 10,000 5,335 1/1/X4 10,000 4,868 1/1/X5 10,000 4,355 1/1/X6 10,000 3,791 1/1/X7 10,000 3,170 1/1/X8 10,000 2,487 1/1/X9 10,000 1,735 1/1/X10 10,000 909 Reduction of Lease Obligation Lease Obligation 67,590 10,000 57,590 4,241 53,349 4,665 48,684 5,132 43,552 5,645 37,908 6,209 31,698 6,830 24,868 7,513 17,355 8,265 9,090 9,091 -1 Lessee’s Journal Entries: 1/1/X1 Leased Equipment Under Capital Leases Obligations Under Capital Leases 67,590 1/1/X1 10,000 12/31/X1 1/1/X2 12/31/X2 1/1/X3 Obligations Under Capital Leases Cash 67,590 10,000 Interest Expense Interest Payable 5,759 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation [$67,590/10] 6,759 Interest Payable Obligations Under Capital Leases Cash 5,759 4,241 Interest Expense Interest Payable 5,335 Depreciation Expense Accumulated Depreciation [$67,590/10] 6,759 Interest Payable Obligations Under Capital Leases Cash 5,335 4,665 ACC301, Spring 2001 Dr. Dow 5,759 6,759 10,000 5,335 6,759 10,000 Exam 2 Review Problems, Page 4 Solution to Problem 1: Leases, Part B – Lessor Accounting Lessor’s Lease Amortization Schedule Annual Interest Net Lease on Net Investment Payment Investment Recovery 1/1/X1 1/1/X1 10,000 10,000 1/1/X2 10,000 5,759 4,241 1/1/X3 10,000 5,335 4,665 1/1/X4 10,000 4,868 5,132 1/1/X5 10,000 4,355 5,645 1/1/X6 10,000 3,791 6,209 1/1/X7 10,000 3,170 6,830 1/1/X8 10,000 2,487 7,513 1/1/X9 10,000 1,735 8,265 1/1/X10 10,000 909 9,091 Net Investment 67,590 57,590 53,349 48,684 43,552 37,908 31,698 24,868 17,355 9,090 (1) Lessor’s Journal Entries: 1/1/X1 Lease Payments Receivable ($10,000 X 10) Machine Unearned Interest Income ($100,000 - $67,590) 1/1/X1 12/31/X1 1/1/X2 12/31/X2 Cash Lease Payments Receivable Unearned Interest Income Interest Income Cash Lease Payments Receivable Unearned Interest Income Interest Income ACC301, Spring 2001 Dr. Dow 100,000 67,590 32,410 10,000 10,000 5,759 5,759 10,000 10,000 5,335 5,335 Exam 2 Review Problems, Page 5 Solution to Problem 2: Leases A. Criteria 1: Transfer of ownership test; this criteria is not met. Criteria 2: Bargain purchase option test; this criteria is not met. Criteria 3: Economic life test (75% test); this criteria is met because the lease term (8 years) equals or exceeds 75% of the asset’s economic life (10 years). It is actually 80% of the asset’s economic life. Criteria 4: Recovery of investment test (90% test); this criteria is met because the present value of the minimum lease payments equals or exceeds 90% of the fair market value of the asset. It is actually 100% of the fair market value of the asset (see below for calculation of present value). PV of annual payment (excluding executory costs): (15,000 – 1,379) = 13,621 X 5.3349 = PV of guaranteed residual value: 5,000 X .4665 = Present value of minimum lease payments 72,667 2,333 75,000 B. ($75,000 - $5,000)/8 = 8,750 C. This is a sales type lease since the cost of the machine to the lessor is less than the fair value of the machine. D. Lease Payments Receivable = (8 X ($15,000 - $1,379)) + $5,000 = $113,968 Solution to Problem 3: Cash Dividends Arrears - P.S. Current - P.S. 9% C.S. [($2 X9%) X 50,000] Remainder Total Amount To Preferred Common Be Distributed 14,000 1,800 12,200 900 11,300 9,000 2,300 209 2,091 0 2,909 11,091 Preferred Dividend: $10 par X 9% = $.90 per share X 1,000 shares = $900 per year Allocation of Remainder: Par value of preferred stock (1,000 shares X $10 par) Par value of common stock (50,000 shares X $2 par) Total Par Value $ 10,000 100,000 $110,000 Common: (100,000/110,000) X 2,300 = $2,091 Preferred: (10,000/110,000) X 2,300 = $209 Although the preferred can participate up to 12%, the amount available after distributing the dividends in arrears to the preferred only allows a total current year dividend of 11.09% ($12,200/$110,000) to both the preferred and common. ACC301, Spring 2001 Dr. Dow Exam 2 Review Problems, Page 6 Solution to Problem 4: Cash Dividends Arrears - P.S. Current - P.S. [($10 X 7%) X 1,000] C.S. [($3 X 7%) X 40,000] Additional 5% Remainder Total Amount To Preferred Common Be Distributed 25,000 1,400 23,600 700 22,900 8,400 14,500 500 6,000 8,000 8,000 0 2,600 22,400 The amount available after distributing the dividends in arrears to the preferred is 18.15% ($23,600/$130,000). However, the preferred only participates up to 12%. Therefore, the preferred receives a 12% dividend for the current year. Par value of preferred stock (1,000 shares X $10 par) Par value of common stock (40,000 shares X $3 par) Total Par Value ACC301, Spring 2001 Dr. Dow $ 10,000 120,000 $130,000 Exam 2 Review Problems, Page 7 Solution to Problem 5: Cash Dividends Part 1: Preferred Stock = $10 par X 10% = $1 per share X 20,000 shares - $20,000 per year Common Stock = $140,000 - $20,000 = $120,000 Part 2: Preferred Arrears - P.S. Current - P.S. 10% Remainder Total Part 3: 40,000 20,000 60,000 Preferred Arrears - P.S. Current - P.S. 10% Common [($10 X 10%) X 30,000] Remainder Total Amount To Be Distributed 140,000 100,000 80,000 -0- Common 80,000 80,000 Amount To Be Distributed 140,000 100,000 80,000 50,000 -0- Common 40,000 20,000 20,000 80,000 30,000 30,000 60,000 Allocation of Remainder: Par value of preferred stock (20,000 shares X $10 par) Par value of common stock (30,000 shares X $10 par) Total Par Value $ 200,000 300,000 $500,000 Common: (300,000/500,000) X 50,000 = $30,000 Preferred: (200,000/500,000) X 50,000 = $20,000 Part 4: Arrears - P.S. Current - P.S. 10% Common – 10% Additional 5% Remainder Total ACC301, Spring 2001 Dr. Dow Preferred Common 40,000 20,000 10,000 70,000 30,000 15,000 25,000 70,000 Amount To Be Distributed 140,000 100,000 80,000 50,000 25,000 -0- Exam 2 Review Problems, Page 8 Solution to Problem 6: Stockholders’ Equity Transactions 1. Stock Dividends Declared (or Retained Earnings) Stock Dividend To Be Distributed (100,000 X 30% X $2) 60,000 60,000 2. Cash Common Stock (5,000 X $2 par) Additional Paid-in Capital - Common (5,000 X ($9 - $2)) Preferred Stock (10,000 X $10 par) Additional Paid-in Capital – Preferred ($130,000 - $100,000) 175,000 10,000 35,000 100,000 30,000 3. Stock Dividend To Be Distributed Common Stock 60,000 4. Treasury Stock (3,000 X $15) Cash 45,000 60,000 45,000 5. Land (25,000 X $12) Common Stock (25,000 X $2 par) Additional Paid-in Capital - Common ((25,000 x ($12 - $2)) 6. Cash (1,000 X $13) Retained Earnings Treasury Stock (1,000 X $15) 7. Retained Earnings - Unappropriated Retained Earnings - Appropriated for Plant Expansion 8. Common Stock (2,000 X $2 par) Additional Paid-in Capital ((2,000 X ($5 - $2)) Retained Earnings Treasury Stock (2,000 X $15) 300,000 50,000 250,000 13,000 2,000 15,000 500,000 500,000 4,000 6,000 20,000 30,000 9. Memo entry: Declared a 4 for 1 stock split; shares issued and outstanding increased to 632,000; par value reduced to $.50 per share. Although no journal entry is required, the following journal entry could be made: Common Stock, $2 par (158,000 shares X $2 par) Common Stock, $.50 par (632,000 shares X $.50 par) ACC301, Spring 2001 Dr. Dow 316,000 316,000 Exam 2 Review Problems, Page 9 Additional Comments on Problem 6: Transaction 1: Since this is a large stock dividend, it is recorded at the par value of the additional shares to be issued. Transaction 2: Two classes of stock are sold for a lump sum amount. Only one of the classes has a known market value. Therefore, allocate the market price (5,000 shares X $9 = $45,000) to the common stock and allocate the remaining amount ($175,000 - $45,000 = $130,000) to the preferred stock. Note that the amount allocated to each class of stock is divided between the stock account (par value) and the A.P.I.C. account (excess of par). Transaction 5: The land should be recorded at the fair market value of the stock issued or the asset received, whichever is more reliable. In this case, the market value of the stock is more reliable than the seller’s asking price and the tax appraisal. Transaction 6: The retained earnings is debited since there is no credit balance in the Additional Paid-in Capital from Treasury Stock Transactions account. Transaction 9: There are 158,000 shares of common stock outstanding prior to the split (100,000 + 30,000 + 5,000 - 3,000 + 25,000 + 1,000). Solution to Problem 7: Stockholders’ Equity Transactions 1. Marketable Securities Gain on Appreciation of Marketable Securities 234,000 234,000 Property Dividends Declared (or Retained Earnings) Property Dividends Payable 734,000 734,000 2. Cash Preferred Stock (5,000 X $10 par) Additional Paid-in Capital - Preferred 125,000 3. Property Dividends Payable Marketable Securities 734,000 50,000 75,000 734,000 4. Treasury Stock (2,000 X $10) Cash 20,000 20,000 5. Cash Common Stock (25,000 X $1 par) Additional Paid-in Capital - Common ((194,444 - 25,000) Preferred Stock (10,000 X $10 par) Additional Paid-in Capital - Preferred (155,556 - 100,000) 6. Cash (500 X $14) Treasury Stock (500 X $10) Additional Paid-in Capital – Treasury Stock ACC301, Spring 2001 Dr. Dow 350,000 25,000 169,444 100,000 55,556 7,000 5,000 2,000 Exam 2 Review Problems, Page 10 7. Retained Earnings - Unappropriated Retained Earnings - Appropriated for Plant Expansion 8. Common Stock (1,500 X $1 par) Additional Paid-in Capital – Common Stock (1,500 X ($7 - $1)) Additional Paid-in Capital – Treasury Stock Retained Earnings Treasury Stock (1,500 X $10) 50,000 50,000 1,500 9,000 2,000 2,500 15,000 9. Memo entry: Declared a 2 for 1 stock split; shares issued and outstanding increased to 247,000; par value reduced to $.50 per share. Although no journal entry is required, the following journal entry could be made: Common Stock, $1 par (123,500 shares X $1 par) Common Stock, $.50 par (247,000 shares X $.50 par) 123,500 123,500 Additional Comments on Problem 7: Transaction 5: Two classes of stock are sold for a lump sum amount. Since the market value of each class of stock is known, the amount received should be allocated to each class of stock based on relative market values. Market value of common stock (25,000 shares X $15) Market value of preferred stock (10,000 shares X $30) Total Market Value $375,000 300,000 $675,000 Allocate to common: ($375,000/$675,000) X $350,000 = $194,444. Allocate to preferred: ($300,000/$675,000) X $350,000 = $155,556. Note that the amount allocated to each class of stock is divided between the stock account (par value) and the A.P.I.C. account (excess of par). Transaction 9: There are 123,500 shares of common stock outstanding prior to the split (100,000 - 2,000 + 25,000 + 500). ACC301, Spring 2001 Dr. Dow Exam 2 Review Problems, Page 11