CJi Table of Contents - Criminal Justice Interactive (CJi)
advertisement
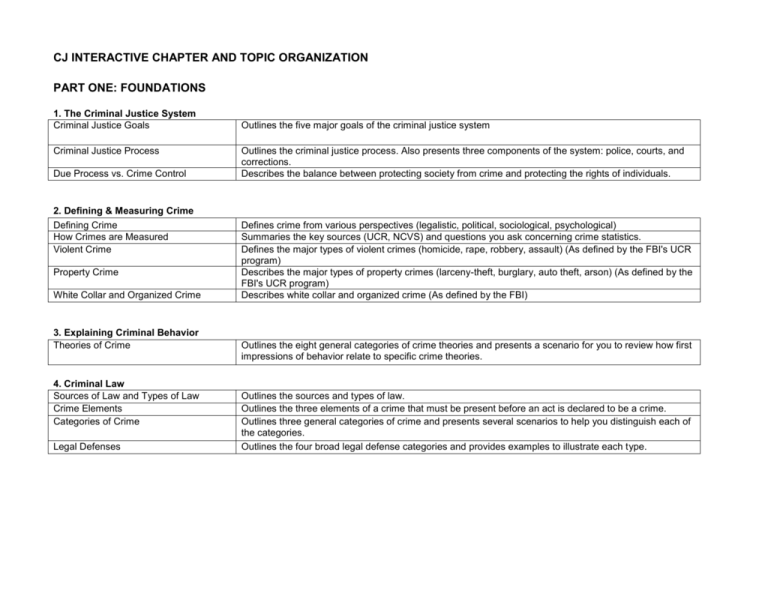
CJ INTERACTIVE CHAPTER AND TOPIC ORGANIZATION PART ONE: FOUNDATIONS 1. The Criminal Justice System Criminal Justice Goals Criminal Justice Process Due Process vs. Crime Control 2. Defining & Measuring Crime Defining Crime How Crimes are Measured Violent Crime Property Crime White Collar and Organized Crime 3. Explaining Criminal Behavior Theories of Crime 4. Criminal Law Sources of Law and Types of Law Crime Elements Categories of Crime Legal Defenses Outlines the five major goals of the criminal justice system Outlines the criminal justice process. Also presents three components of the system: police, courts, and corrections. Describes the balance between protecting society from crime and protecting the rights of individuals. Defines crime from various perspectives (legalistic, political, sociological, psychological) Summaries the key sources (UCR, NCVS) and questions you ask concerning crime statistics. Defines the major types of violent crimes (homicide, rape, robbery, assault) (As defined by the FBI's UCR program) Describes the major types of property crimes (larceny-theft, burglary, auto theft, arson) (As defined by the FBI's UCR program) Describes white collar and organized crime (As defined by the FBI) Outlines the eight general categories of crime theories and presents a scenario for you to review how first impressions of behavior relate to specific crime theories. Outlines the sources and types of law. Outlines the three elements of a crime that must be present before an act is declared to be a crime. Outlines three general categories of crime and presents several scenarios to help you distinguish each of the categories. Outlines the four broad legal defense categories and provides examples to illustrate each type. PART TWO: THE POLICE 5. The Police: History, Structure & Functions History and Professionalism of the Police Outlines the history of the police and its move toward professionalism. Modern American Policing Eras Outlines the four major eras of American Policing. You will learn about each era’s characteristics, the catalyst for the era, examples and the current policing style influenced by that era. Levels of Law Enforcement Outlines the levels of law enforcement: Federal, State, Local, Private, and how each of these levels over lap. Overview of the general roles of police in society (enforcing the law, apprehending offenders, preventing crime, keeping the peace) and operational strategies (patrol, emergency resonse, investigation, problem Police Roles and Functions solving, support services) Overview of typical organizational structure of police agencies to include descriptions of typical line Police Organization operations, staff operations, and "chain of command" overview. Policing Styles Highlights three policing styles: Watchman, Legalistic, and Service. 6. The Police and the Constitution The Fourth amendment Search and Arrest Warrants Warrantless Searches Interrogations and Confessions Remedies for Violations of Rights 7. The Police: Issues and Challenges Ethics and Corruption Types of Force Police Liability Community Policing Explains the terms person, houses, papers, and effects as it relates to the Fourth Amendment terminology. Explains the three warrant components. Describes warrantless searches. Describes how the fifth Amendment is relevant to interrogations and confessions. Examines the civil, criminal, and non-judicial remedies available to individuals when their constitutional rights are violated Describes the law enforcement code of ethics and factors that contribute to police corruption. Highlights the types of force that can be used by police. Explores the areas of liability related to policing. Outlines the four basic principles of community policing and provides interviews with community policing officers. PART THREE: THE COURTS 8. The Courts: History, Structure, and Key Players History and Organization of the Courts Describes the history and organization of the courts. Courtroom Roles Summarizes the key roles in a courtroom The Prosecution and Defense Presents the roles and responsibilities of the prosecution and defense before, during, and after trial The Trial Judge Summarizes the responsibilites of the trial judge The Grand Jury Summarizes the role of the grand jury as compared to trial juries Types of Witnesses Explains and compares/contrasts lay witnesses and expert witnesses 9. Pre-Trial Activities and the Criminal Trial Post-Arrest Activities Overview of the pre-trial process (booking through arraignment) The Bail System Overview of the bail system and process The Pros and Cons of Plea Bargaining Plea bargaining process and pros and cons Steps in the Trial Process Outlines the eight major steps in a trial. Rights at Trial Explains criminal rights, from first contact with a defendant during a trial through the legal appeal process. Jury Deliberation Processes and considerations of jury decision-making 10. Sentencing Sentencing Pre-Sentence Reports Determinate and indeterminate sentencing Capital Punishment The Appeals Process Victim Rights History Outlines basic sentencing categories a defendant can receive. Summarizes pre-sentence reports and process Explains determinate and indeterminate sentencing Describes capital punishment in the United States. Outlines the appeals process. Summarizes key victim rights organizations and legislation. PART FOUR: CORRECTIONS 11. Corrections: History and Institutions History of Prisons History of Women’s Prisons Prisons and Jails Prison Employees Correctional Systems 12. Corrections in the Community The Value of Probation and Parole Objectives and Conditions of Probation Special supervision programs History of Parole Parole Board 13. Life Behind Bars The legal rights of inmates Prison Life: Two Perspectives Special offenders Prison programs Prisoner Reentry Outlines the nine prison eras. Describes the historical evolution of women's prisons Compares and contrasts the roles and characteristics of prisons and jails Explores the roles and responsibilites of various prison employees Explores issues surrounding the privatization of prisons Examines the role of probation and parole in the US Presents common conditions and objectives of probation Presents work-release, halfway houses, electronic monitoring, and community service programs Presents a history of the parole system in the US The role of parole boards Describes the laws that concern inmates' rights Relates the various elements of prison life and subcultures that exist within a prison through two inmate interviews. Explores the challenges to dealing with special offenders (juvenile, mentally ill, elderly, and drug offenders) Presents an overview of different types of common prison programs (educational/vocational, mental health and substance abuse, employment, and recreation programs) Describes challenges to successful prisoner re-entry PART FIVE: JUVENILE JUSTICE 14. The Juvenile Justice System How Juveniles are Processed Difference between Adult and Juvenile Justice system History of the Juvenile Justice Court Juvenile’s Legal Rights Types of Juvenile Offenders Outlines the four major phases and tasks used to process juveniles in the justice system. Describes difference between the Adult Criminal Justice System and the Juvenile Justice System. Outlines the history of the juvenile justice court. Outlines the legal rights of juveniles Describes the types of juvenile offenders.