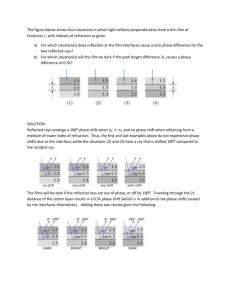
Using models
advertisement
How Science Works focus To construct ray diagrams Breadth of study context Refraction at an interface. Outcome(s) To use a model to explain the refraction of light To describe the limitations of the model Teaching Model focus Using models Planned sequence of activities, including starter and plenary. Describe for each activity, its purpose in the teaching sequence Starter: demo the ripple tank and show plane and circular wave patterns. Explain that rays can be drawn perpendicular to these waves to show the direction of travel. Students should add rays to drawings of the ripples with plane and curved wavefronts. M1 The action of waves passing from air into glass can be modelled by students walking across the classroom (or playground). Line up 6 students and explain that they are each part of the wave and this wave is going to move across the room. Get them to practice walking in step so that they maintain a straight line formation (I find this works best if you count out the steps for them 1, 2,1,2 etc.) Now explain that they are going to cross a line and the ground on the other side of the line is going to make them walk really slowly. Draw a line and get them to march across it (all crossing at the same time) – as they cross the line they should take very small steps (but still in time with your counting 1,2,1,2 etc.) Now ask all students to draw the positions of the students before and after crossing the line. M2 Now repeat the exercise but this time get the students to cross the line at an angle. Encourage them to visualise a water wave or a light wave crossing into a slower medium at an angle Line up your 6 students again and this time draw the line at 45 degrees to their direction of travel. As they approach the line they take normal strides in time with your counting. As each student crosses the line they must switch from taking large steps to small steps, but otherwise keep going in the same direction. As the last student crosses the line ask them to freeze. Now ask all students to draw the positions of students before and after crossing the line. M3 Class practical to observe light refracting at a boundary. Use a semicircular prism as there is only one point of refraction and less chance of confusion. Students make a careful ray diagram of the path of the light Students add wavefronts to the diagram – this is complimentary to the starter where rays were added to wavefront diagrams. Students should now compare this diagram to the diagrams of students crossing the 45 degree line. Does the model explain the behaviour of the light? M4 Students draw up a table with two columns 1. Ways in which the model is like light refraction 2. Ways in which the model is not like light refraction Finally students should suggest improvements to the model or alternative models to explain the phenomenon. One that you might suggest is that the students link arms – this helps get over the issue of individuals not going in the same direction as the wavefront. Significant or uncommon resources Any particular advice or instructions for the teacher.