Microsoft Word Document
advertisement

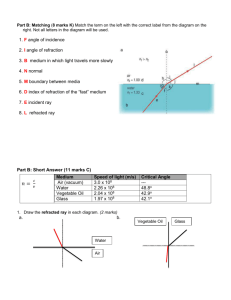
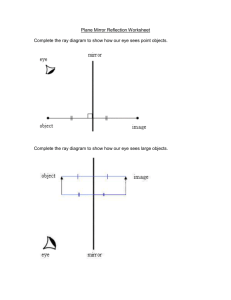
SNC2D Final Exam Outline January 2015 Exam Breakdown – Total 125 marks (30% of final mark) Knowledge 25 marks (40 Multiple Choice) Communication 25 marks (Short Answer, diagrams) Thinking 40 marks (Short Answer, calculations) Application 20 marks (Short Answer) Materials Permitted – Important Information Pencil, pen, highlighter, eraser, ruler, protractor and non-programmable calculator. Students are provided with a Periodic Table of Elements, a polyatomic ions chart, and formulas (index of refraction and thin lens equations) Borrowing of equipment is not permitted. You must be in proper uniform to write the exam!! Topics to Study Chemistry - Chemical vs. physical properties and changes - Elements and the periodic table - protons, electrons, neutrons, atomic number, atomic mass, charge, metals, non-metals, families, patterns of reactivity - Formation of ions and ionic bonds - Naming and writing chemical formulas – ionic compounds, multivalent metals, polyatomic ions, molecular compounds, acids - Lewis or Bohr diagrams for elements and compounds - Counting atoms in compounds - Writing chemical equations and word equations - Reactants and products - Law of conservation of mass - Balancing reactions - Types of reactions – synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, combustion - Predicting products of chemical reactions - Acids and bases – naming, writing formulas, properties - pH scale - Neutralization reactions Optics - What is light and the electromagnetic spectrum - Sources of light – incandescence, fluorescence, bioluminescence, chemiluminescence, phosphorescence, electric discharge - Efficiency of incandescent vs. fluorescent light bulbs - Law of reflection and terminology of reflection (incident ray, reflected ray, angle of incidence, angle of reflection, normal) - Drawing ray diagrams – plane mirrors, concave mirrors, convex mirrors, converging lenses, diverging lenses Describing images in mirrors and lenses using SALT Refraction – definition, rules for refraction, drawing refracted ray Comparing the index of refraction for different media using a diagram Calculating index of refraction (GRASS) Total internal reflection – conditions, critical angle Mirror and lens equations (GRASS) Biology - Organelles in cells – labelling diagrams and functions - DNA – what it is, where it is found, why it is important - Diffusion and osmosis - Cell cycle and mitosis – labelling diagrams and explanation of each stage - Cell structures involved in mitosis – spindle fibres, centrioles, sister chromatids, centromere etc - Cancer - Hierarchy of structure in animals (cell, tissue, organ, organ system) - Types of tissues in animals - Stem cells and differentiation - Digestive system, circulatory system, respiratory system – structure and function of each system (labelling diagrams) - Arteries and veins - Structure of the heart and blood flow - Inhalation and exhalation - How systems work together - Animal cells vs. plant cells - Animal systems vs. plant systems - Photosynthesis