1.3 Human Skeleton
advertisement

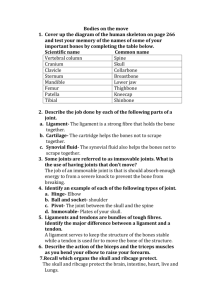
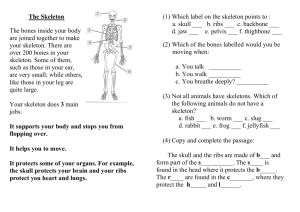
Life Processes 1 Humans as Organisms 1.3 Human Skeleton Sc 2: Life Processes 1 Humans as Organisms 1.3 Human Skeleton P.O.S. Key Stage 2 Sc 2: 2e Key Stage 3 Sc 2: 2e Life Processes 1 Humans as Organisms 1.3 Human Skeleton LEARNING OBJECTIVES To know that skeletons are made of lots of bones. To know that the skeleton is used for support, movement and protection. To be able to show that muscles work in pairs and can only pull. To know that ‘meat’ is muscle. To know that bones are joined by joints. To be able to name types of joints (hinge, ball & socket) ICT LINKS VOCABULARY CD ROMs about the human body PE/Art Skeleton, simple bone names – skull, hip, breast bone etc, muscles, relax, contract, joint ACTIVITIES Feel bones in own arms, legs, fingers, feet, collar bone, ribs, shoulder blades, spine. Match pictures of bones drawn on card to skeletons. Dissect owl pellets and decide if bones are from legs, skull, hip, spine, ribs (SAFETY SYMBOL) Look at x-ray pictures. Use bathroom scales flat against the wall to see which arm/leg exerts the largest force. Measure the length of some bones in the body. Use PE to observe which parts of the body move. - how many places can they find where the body bends? - Does each part bend in the same way? Measure and compare muscles when relaxed and contracted. Make a simple arm model. Get a child to run, walk, hop etc in slow motion and look at which bones, muscles and joints are used. Make “flick books” to show movement. Explore “Human Skeleton” CD Rom (Dorling Kindersley) and worksheet. Explore different types of joints. Compare how they move. RESOURCES Bone pictures, skeletons Owl pellets from Bird Sanctuary of field study centres X-ray pictures Bathroom scales Card, paper, fasteners, elastic bands, shearing elastic Tape measure, string, callipers Card, elastic bands Human skeleton Worksheets POINTS TO NOTE Some children do not realise that bones are connected or that muscles are not just in arms and legs. Also some know the obvious bones in arms, legs, ribs and skull but not the rest. Pupils often think bones are dead. Latin names of bones are not needed nor are the names of different types of joints at Key Stage 2 Life Processes 1 Humans as Organisms 1.3 Human Skeleton OWN ACTIVITIES POSSIBLE INVESTIGATIONS Which finger is the strongest (push on scales, lift weights) Do the size of leg muscles affect how high a person can jump? Which muscle is the strongest? Investigate strength of “bones” (use rolled paper, cardboard tubes) Life Processes 1 Humans as Organisms 1.3 Human Skeleton Name: Date Record Began: Outcomes: NC Level 1 NC Level 4 1 1+ 2 2+ 3 3+ 4 Is able to demonstrate floppy/strong using their own body. Knows that bones protect some body parts e.g. heart, lungs, brain. Asks a wider range of questions and take turns in discussion Knows that bones support the body Names some of the main skeleton parts Can point to obvious joints (knee and elbow) Knows that a skeleton is made up of lots of bones Can give one function of the skeleton. Knows that muscles are for movement Can point to less obvious joints (fingers, jaw, wrist) Can name most of the main bones (skull, shoulder, rib, hip, thigh, lower leg) Can give two functions of the skeleton Can indicate where muscles are on the body. Can give three functions of the skeleton Can name a hinge and ball & socket joint Knows that muscles only pull Can explain the difference between a hinge and ball & socket joint Knows that muscles work in pairs. Can name all the main bones Can explain how muscles work in pairs. Further Comments