r and K Selection
advertisement

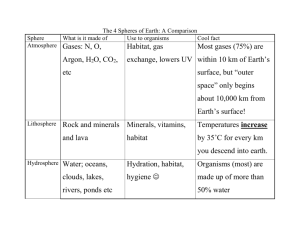
Population Ecology Student Outline – r and K Selection r and K Selection 1. Introduction dN1 / dt = r1N1 dN1 / dt = r1N1 A. r -Selected Individuals • Environmental Characteristics • Rapid Reproduction • Density Independent Mortality • Many Small Young Favored • Energy Allocation B. K-Selected Individuals • Environmental Characteristics • Carrying Capacity • Density Dependent Competition • Energy Allocation C. r and K Selection and the Role of the Environment i. Determining Issues a. Energy b. Reproduction c. Other Issues ii. r-Selection a. Characteristics • Note: Figure 6.9 - Positive Feedback System iii. K-Selection a. Characteristics: • Note: Figure 6.10 - Positive Feedback System Examples of r and K Environments D. Page 1 Population Ecology Student Outline – r and K Selection E. 2. i. r-Environment ii. K- Environment Examples of r and K Selection i. Across Taxa ii. Within Species • Figure 6.11 a. Poa annua (meadow grass) • Population #1 • Population #2 iii. Sarcophagid Fly Limitations of the r/K Scheme A. Litorina sp. study • Figure 6.12 i. The Speices • Littorina saxatalis a. Littorina rudis • Viviparous b. Littorina nigrolineata • Oviparous ii. Habitats Figure 6.12 and Table 6.6 a. Crevice Habitat b. Boulder Habitat iii. Observations a. Crevice Habitat b. Boulder Habitat iv. Conclusion “A life-history strategy, is, therefore, an organism’s unique adaptive response to its whole environment; and simplistic theories must eventually give way to the detailed study of real organisms in the real world” - Begon, Mortimer, Thompson Page 2